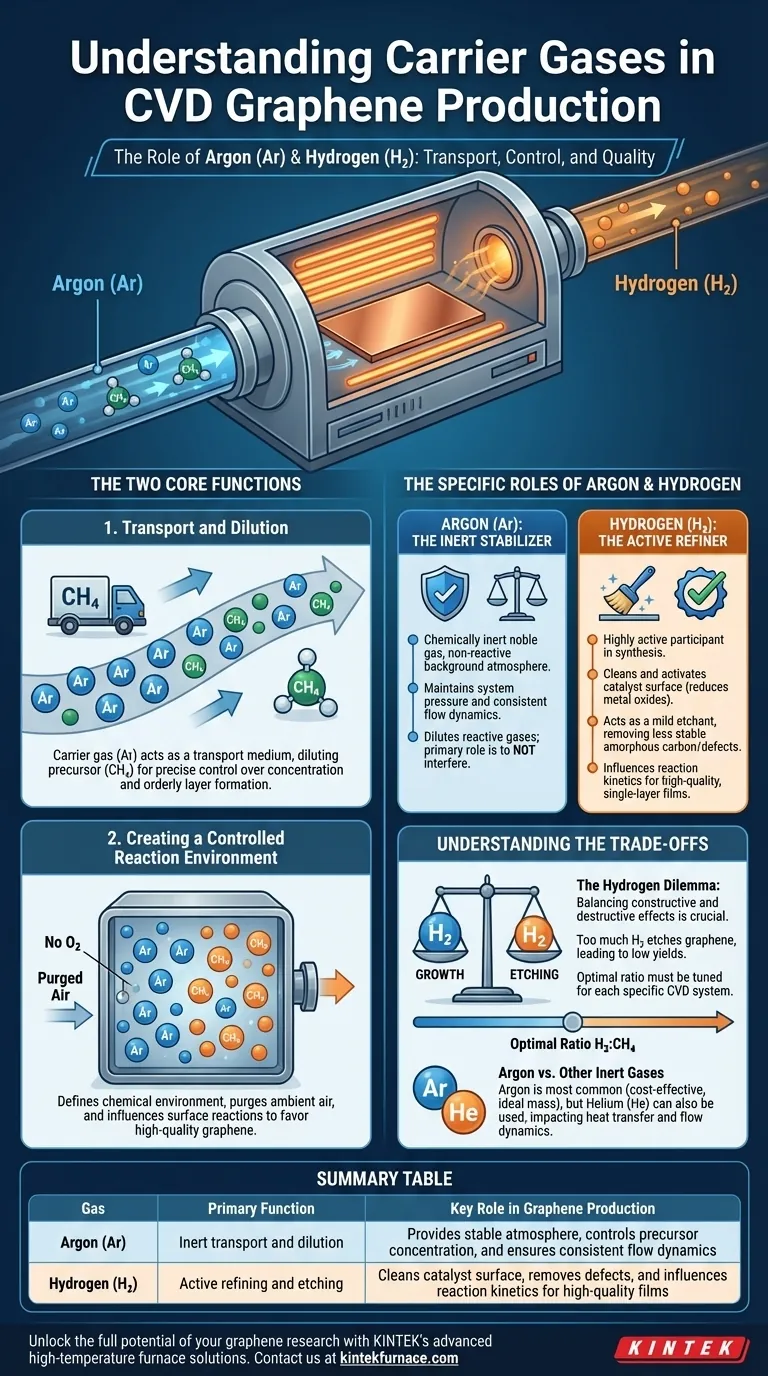
In graphene production via chemical vapor deposition (CVD), the most common carrier gases are Argon (Ar) and Hydrogen (H₂). Their primary function is to transport the carbon precursor gas (like methane) to the hot catalyst surface and to precisely control the chemical environment, which dictates the rate and quality of the graphene growth.
The core challenge in graphene synthesis isn't merely depositing carbon, but controlling its atomic structure. Carrier gases are the primary tool for this control: Argon provides a stable, inert atmosphere for transport, while Hydrogen actively refines the process by cleaning the catalyst and etching away defects to ensure a high-quality, single-layer film.

The Two Core Functions of Carrier Gases
In any CVD process, the gas flowing through the reactor serves two fundamental purposes. Understanding these is key to understanding their role in producing graphene.
Function 1: Transport and Dilution
A "carrier" gas acts as a transport medium. It physically carries the molecules of the reactive precursor gas—typically methane (CH₄)—from the gas inlet to the substrate surface where the reaction occurs.
By using a high flow of an inert gas like Argon, you can heavily dilute the small amount of methane used. This allows for precise control over the precursor concentration, preventing overly rapid, chaotic deposition and promoting the slow, orderly formation of a single atomic layer.
Function 2: Creating a Controlled Reaction Environment
The gas mixture defines the entire chemical environment inside the reactor chamber. Its first job is to purge any ambient air, especially oxygen, which would otherwise oxidize the hot metal catalyst (e.g., copper) and prevent graphene growth.
More importantly, the composition of the gas directly influences the chemical reactions on the catalyst surface, determining whether high-quality graphene forms or if you simply deposit a layer of useless, amorphous carbon.
The Specific Roles of Argon and Hydrogen
While both are often used together, Argon and Hydrogen play distinct and complementary roles. One is a passive stabilizer, and the other is an active refiner.
Argon (Ar): The Inert Stabilizer
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically inert and will not participate in the reactions. Its job is to provide a stable, non-reactive background atmosphere.
Think of Argon as the foundation of the process. It maintains system pressure, dilutes the reactive gases to manageable levels, and ensures a consistent flow dynamic within the chamber. Its primary role is to not interfere.
Hydrogen (H₂): The Active Refiner
Unlike Argon, Hydrogen is a highly active participant in graphene synthesis. It has several critical functions that directly impact the quality of the final film.
First, Hydrogen cleans and activates the catalyst surface. It reduces any native metal oxides (like copper oxide) that form on the substrate, ensuring a pure, catalytically active surface ready for growth.
Second, Hydrogen acts as a mild etchant. It selectively removes less stable carbon structures, such as amorphous carbon or poorly-formed multi-layer islands. This "quality control" function is crucial for achieving a clean, uniform, single-layer graphene sheet.
Finally, Hydrogen influences the reaction kinetics. It can participate in the decomposition of methane, affecting the supply of carbon atoms to the surface and ultimately the growth rate.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The decision to use these gases, particularly Hydrogen, is not without critical trade-offs that every researcher and engineer must manage.
The Hydrogen Dilemma: Growth vs. Etching
The most significant challenge is balancing Hydrogen's constructive and destructive effects.
A certain amount of Hydrogen is essential for etching away defects and achieving high crystal quality. However, too much Hydrogen will etch the graphene itself, potentially faster than it can grow. This can lead to low yields, incomplete films, or even no growth at all.
Finding the optimal ratio of Hydrogen to methane (H₂:CH₄) is one of the most important process parameters and must be carefully tuned for each specific CVD system.
Argon vs. Other Inert Gases
While Argon is the most common inert gas due to its cost-effectiveness and ideal mass for typical flow conditions, other gases like Helium (He) can also be used.
The choice can impact heat transfer and flow dynamics within the reactor, but Argon generally provides the most stable and predictable baseline for developing a graphene growth process.
Optimizing Carrier Gas Flow for Your Goal
The ideal carrier gas mixture depends entirely on your end goal. Use these principles as a guide for your process development.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible crystal quality: Your goal is to use a carefully controlled, low concentration of hydrogen to act as a gentle etchant, prioritizing defect removal over growth speed.
- If your primary focus is rapid deposition or maximizing yield: You may use a lower hydrogen-to-methane ratio, or even a pure Argon/methane mix, to accelerate growth, but this almost always comes at the cost of film quality and uniformity.
- If you are setting up a new CVD system: Begin by establishing a stable, high flow of Argon to control the environment, then carefully introduce small amounts of Hydrogen to find the optimal process window for quality and growth.
Mastering the flow of these gases is the key to transforming a simple carbon deposition into the controlled synthesis of high-quality graphene.
Summary Table:
| Gas | Primary Function | Key Role in Graphene Production |
|---|---|---|
| Argon (Ar) | Inert transport and dilution | Provides stable atmosphere, controls precursor concentration, and ensures consistent flow dynamics |
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Active refining and etching | Cleans catalyst surface, removes defects, and influences reaction kinetics for high-quality films |
Unlock the full potential of your graphene research with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems tailored to your unique needs. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise control over gas environments and process parameters, helping you achieve superior graphene synthesis with high efficiency and yield. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can elevate your laboratory's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How does the pressure range change under vacuum conditions in an atmosphere box furnace? Explore Key Shifts for Material Processing
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas



















