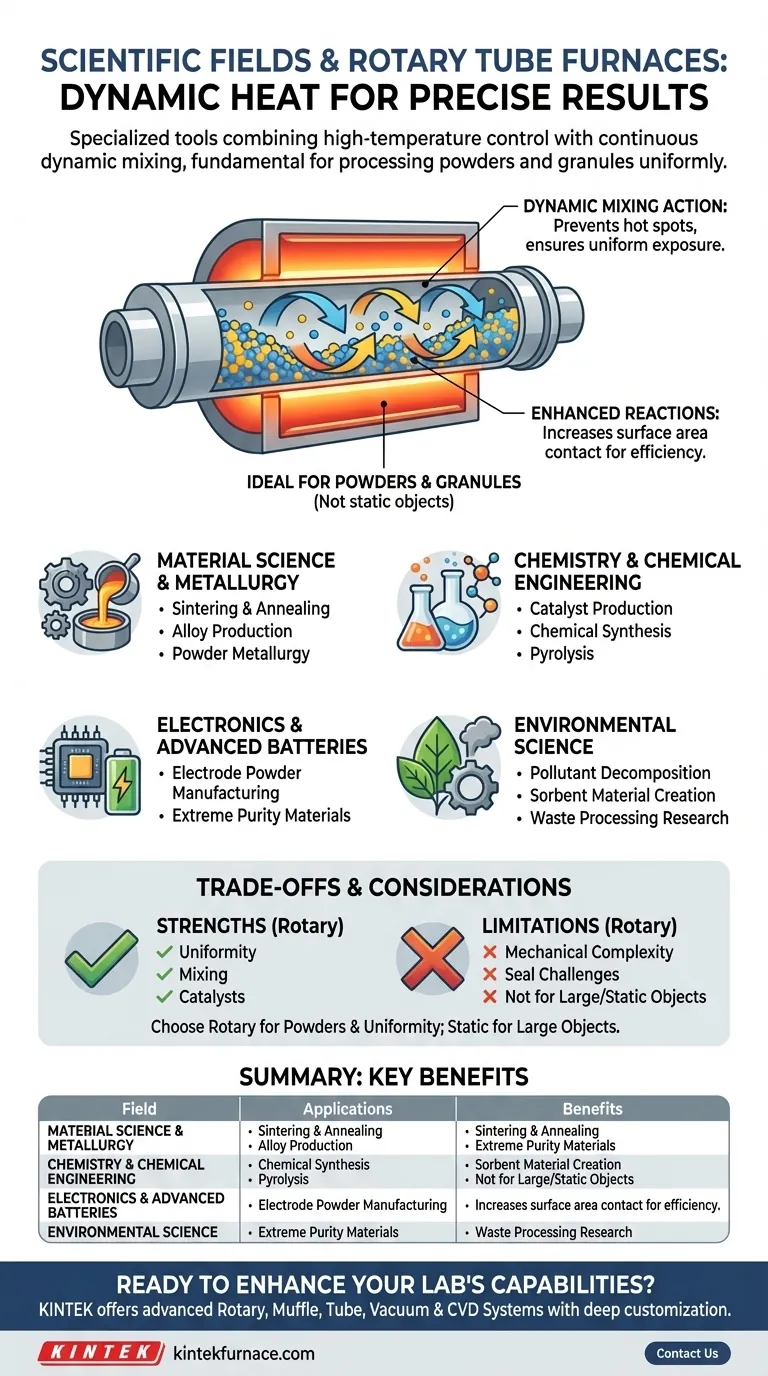
At their core, rotary tube furnaces are specialized tools used across a range of scientific and industrial fields for their unique ability to process materials at high temperatures. They are fundamental in material science, chemistry, metallurgy, and environmental protection, as well as in the manufacturing of electronics, catalysts, and other special materials.
The defining advantage of a rotary tube furnace is its ability to combine precise, high-temperature thermal control with continuous, dynamic mixing. This makes it indispensable for any process requiring uniform heat treatment, synthesis, or reaction of powders, granules, and other solid materials.

The Core Function: Why Rotation Matters
The key to understanding a rotary tube furnace's applications is its rotating process chamber. Unlike a static furnace where a material sits motionless, the rotation provides significant advantages.
Achieving Material Uniformity
Continuous rotation ensures that the material inside tumbles and mixes. This prevents hot spots and guarantees that every particle is exposed to the same temperature profile and atmospheric conditions.
This dynamic movement is critical for processes like drying, roasting, and calcination, where consistency throughout the batch is paramount.
Enhancing Chemical Reactions
For chemical synthesis, especially with solid-phase reactants or catalysts, the constant mixing dramatically improves reaction efficiency.
The tumbling action increases the surface area contact between particles and between the particles and the process gas, leading to faster and more complete reactions.
Ideal for Powders and Granules
These furnaces are specifically designed to handle bulk solids that can flow, such as powders, pellets, and granules.
This is a key differentiator from box furnaces or static tube furnaces, which are better suited for solid, single-piece samples.
Key Applications Across Disciplines
The combination of heat and mixing makes rotary tube furnaces vital in both research laboratories and industrial production settings.
Material Science and Metallurgy
This is a primary application area. Rotary furnaces are used for the high-temperature sintering of metal and ceramic powders to create new alloys, composites, and other advanced materials.
They are also used for heat treatment processes, such as annealing and tempering, to modify the properties of materials in granular form.
Chemistry and Chemical Engineering
The production and activation of catalysts is a major industrial use. The uniform heating and gas exposure are perfect for preparing catalysts used in countless chemical processes.
They are also used for synthesizing specialty chemicals, like zinc oxide or silica gel, and for pyrolyzing materials in a controlled atmosphere.
Electronics and Advanced Batteries
The manufacturing of materials for electronics relies on extreme purity and consistency. This includes producing powders for lithium-ion battery electrodes.
Precise thermal control is fundamental for fabricating these sensitive components, and the rotary action ensures batch-to-batch reliability.
Environmental Science
In environmental research and remediation, these furnaces can be used for the thermal decomposition of pollutants or the creation of sorbent materials designed to capture contaminants.
They are also valuable for studying how materials behave under high-temperature waste-processing conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized instrument. Its strengths in some areas create limitations in others.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor and seals, adds a layer of mechanical complexity compared to a static furnace. This can mean higher initial costs and more demanding maintenance requirements.
Atmosphere Control
While these furnaces can operate with controlled atmospheres (like inert gas or vacuum), maintaining a perfect seal on a rotating tube is more challenging than on a static one. For applications requiring ultra-high vacuum or extremely sensitive atmospheres, a static furnace may be superior.
Not for Static, Large Samples
The design is fundamentally unsuited for processing single, large, or irregularly shaped solid objects. Attempting to do so negates the entire purpose of the rotating mechanism.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Choosing a furnace depends entirely on the physical form of your material and your ultimate processing goal.
- If your primary focus is processing powders or granules uniformly: A rotary tube furnace is the ideal choice due to its dynamic mixing action.
- If your primary focus is creating new catalysts or specialized chemical powders: The enhanced heat and mass transfer in a rotary furnace will significantly improve reaction efficiency.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single, solid object or growing a crystal: A standard, static tube or box furnace would be a more appropriate and simpler solution.
Ultimately, understanding this fundamental principle of dynamic heat treatment is the key to leveraging the rotary tube furnace's full potential.
Summary Table:
| Field | Common Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Material Science & Metallurgy | Sintering, annealing, alloy production | Uniform heating, dynamic mixing for consistency |
| Chemistry & Chemical Engineering | Catalyst production, chemical synthesis | Enhanced reaction efficiency, gas exposure |
| Electronics & Advanced Batteries | Electrode powder manufacturing | Precise thermal control, batch reliability |
| Environmental Science | Pollutant decomposition, sorbent creation | Controlled atmosphere processing |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom high-temperature furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnaces like Rotary, Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs in material science, chemistry, and more. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and drive innovation in your field!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















