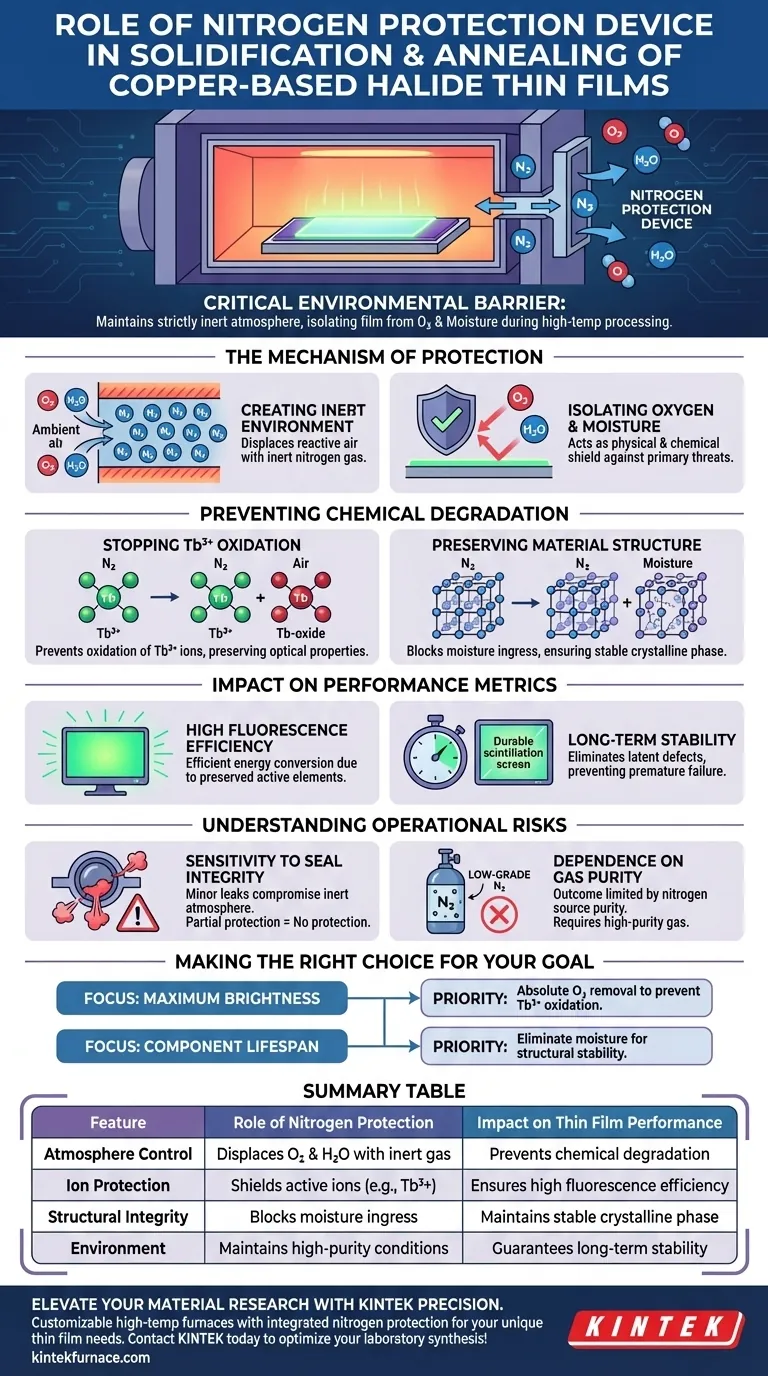
A nitrogen protection device serves as a critical environmental barrier during the solidification and annealing of copper-based halide thin films. Its primary function is to maintain an strictly inert atmosphere, effectively isolating the developing film from ambient oxygen and moisture. This controlled environment is essential for preserving the chemical integrity of the material during high-temperature processing.
By eliminating exposure to reactive elements, the device prevents the oxidation of active ions and structural degradation. This directly secures the high fluorescence efficiency and long-term stability required for effective scintillation screens.

The Mechanism of Protection
Creating an Inert Environment
The solidification and annealing processes often involve elevated temperatures, which make materials significantly more chemically reactive.
A nitrogen protection device displaces the ambient atmosphere within the processing chamber. It replaces reactive air with inert nitrogen gas, ensuring that the film does not come into contact with environmental contaminants.
Isolating Oxygen and Moisture
The two primary threats to copper-based halide films are oxygen and atmospheric moisture.
The device acts as a physical and chemical shield, preventing these elements from interacting with the film surface. This isolation is not merely a precaution; it is a fundamental requirement for successful synthesis.
Preventing Chemical Degradation
Stopping the Oxidation of Tb3+ Ions
A specific vulnerability in these materials is the presence of Tb3+ (Terbium) ions.
Without nitrogen protection, these ions are highly susceptible to oxidation when exposed to heated air. Oxidation of these ions alters the electronic structure of the material, which destroys its intended optical properties.
Preserving Material Structure
Beyond specific ions, the overall lattice structure of the halide film is sensitive to degradation.
Moisture ingress can destabilize the crystalline structure during solidification. By maintaining a dry nitrogen atmosphere, the device ensures the material solidifies into the correct, stable phase without structural defects.
Impact on Performance Metrics
Ensuring High Fluorescence Efficiency
The ultimate goal of these thin films is usually light emission or detection, known as fluorescence.
The protection provided by the nitrogen device is directly responsible for high fluorescence efficiency. By preventing the chemical breakdown of the active elements (like Tb3+), the device ensures the energy conversion within the film remains efficient.
Guaranteeing Long-Term Stability
For applications like scintillation screens, the material must perform consistently over time.
Exposure to oxygen or moisture during processing introduces latent defects that lead to premature failure. The nitrogen atmosphere ensures the long-term stability of the screen by eliminating these initial chemical weaknesses.
Understanding the Operational Risks
Sensitivity to Seal Integrity
While the nitrogen device is effective, it introduces a reliance on perfect mechanical isolation.
If the device has even a minor leak, the "inert" atmosphere becomes compromised. Because the material is so sensitive to oxidation, partial protection is often equivalent to no protection, leading to a wasted batch.
Dependence on Gas Purity
The quality of the outcome is strictly limited by the purity of the nitrogen source.
Using low-grade nitrogen that contains trace amounts of moisture or oxygen will defeat the purpose of the device. The process requires a supply of high-purity gas to be effective.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your nitrogen protection setup, align your process parameters with your specific performance targets:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Brightness: Prioritize the absolute removal of oxygen to prevent the oxidation of Tb3+ ions, which directly dictates fluorescence efficiency.
- If your primary focus is Component Lifespan: Focus on eliminating moisture during solidification to ensure the structural stability required for long-term durability.
Strict control over the atmospheric environment is the single most important factor in transitioning copper-based halides from raw chemicals to high-performance optical devices.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role of Nitrogen Protection | Impact on Thin Film Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere Control | Displaces oxygen and moisture with inert gas | Prevents chemical degradation and oxidation |
| Ion Protection | Shields active ions like Tb3+ from air exposure | Ensures high fluorescence efficiency and brightness |
| Structural Integrity | Blocks moisture ingress during solidification | Maintains stable crystalline phase and prevents defects |
| Environment | Maintains high-purity, strictly inert conditions | Guarantees long-term stability for scintillation screens |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let oxidation or moisture compromise your copper-based halide research. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable with integrated nitrogen protection to meet your unique thin film processing needs.
Whether you require maximum fluorescence efficiency or long-term structural stability, our expert-grade high-temp furnaces provide the strictly inert environment essential for your success. Contact KINTEK today to optimize your laboratory synthesis!
Visual Guide
References
- Haifeng Chen. Study on rare-earth element-doped copper halides. DOI: 10.54254/2977-3903/2025.23781
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a molten salt bath furnace facilitate AISI 304 nitriding? Expert Guide to Superior Surface Hardness
- Why is a vacuum system composed of molecular and mechanical pumps essential? Ensure Purity in Magnetron Sputtering
- How do lab high-temp furnaces and air quenching coordinate in o-LISO synthesis? Master the Thermal Transition
- Why is vacuum freeze-drying necessary for FeNC/MXene catalysts? Preserving 2D Architecture for Peak Performance
- How does a precision temperature-controlled furnace regulate chemical composition in Cu-Cu2O heterostructures?
- What is the role of temperature control equipment in 60Si2CrV steel processing? Ensure Hardness and Longevity
- What type of furnace is used for heat treatment? Choose the Right Solution for Your Materials
- Why is a stainless steel high-pressure autoclave essential for starch hydrogenation? Unlock Peak Reaction Efficiency



















