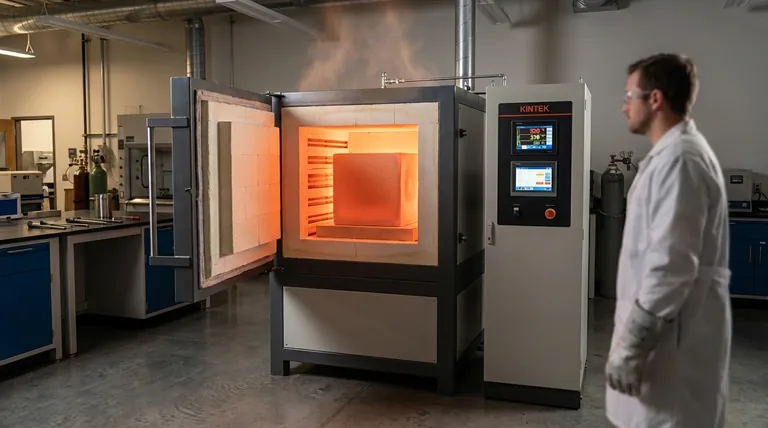
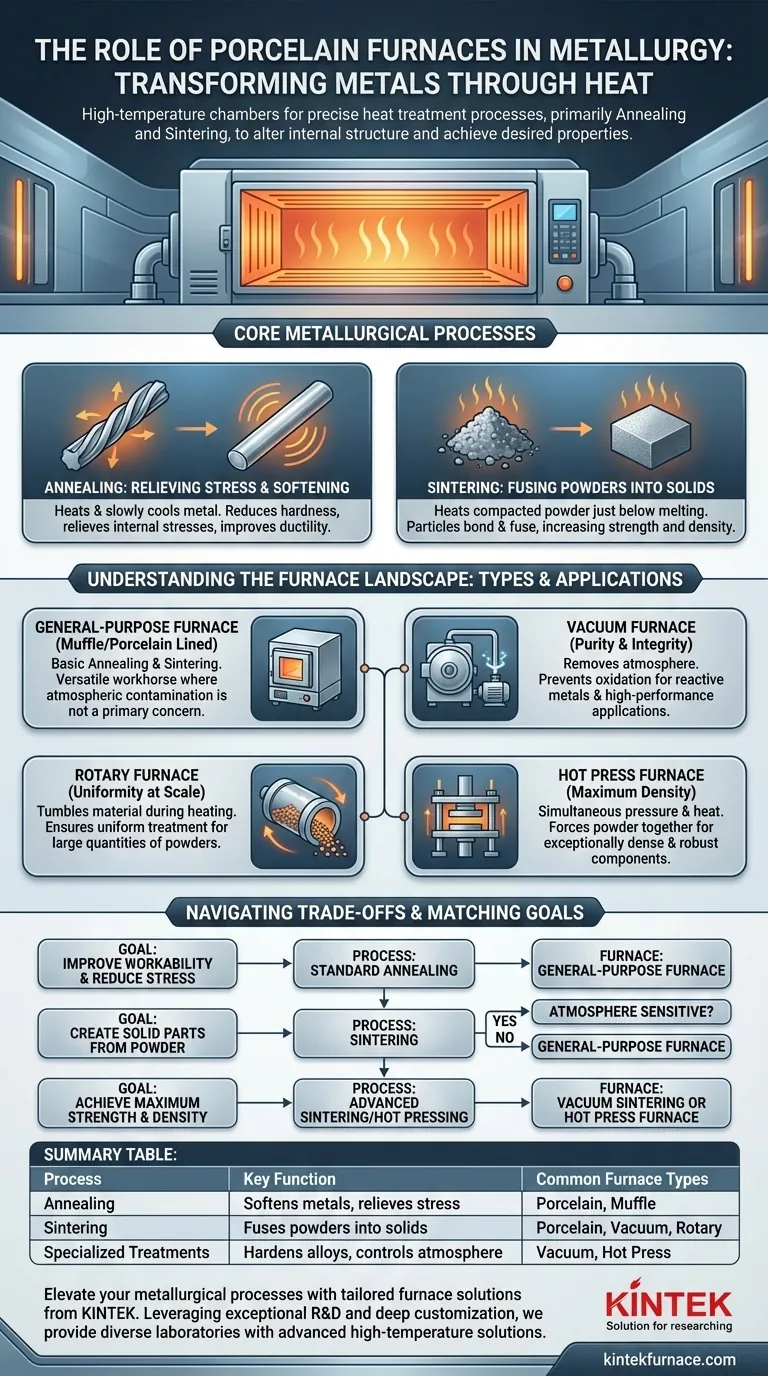
At its core, a porcelain furnace in metallurgy is a high-temperature chamber used for specific heat treatment processes. It primarily serves to execute two critical functions: annealing, which softens metals and relieves internal stresses, and sintering, which fuses metal powders into a solid, dense mass. These processes fundamentally alter a metal's internal structure to achieve desired mechanical properties.
The term "porcelain furnace" often refers to a general-purpose heat treatment oven. The truly critical decision in metallurgy isn't about the furnace material itself, but about choosing the right process—like sintering or annealing—and the right environment—like a vacuum or inert atmosphere—to achieve a specific material outcome.

The Core Metallurgical Processes
To understand the furnace's role, you must first understand the transformative processes it enables. These heat-based treatments are fundamental to modern metallurgy, especially in the field of powder metallurgy.
Sintering: Fusing Powders into Solids
Sintering is the process of taking compacted metal powder and heating it to a temperature just below its melting point.
This intense heat causes the individual particles to bond and fuse, creating a solid or porous component. The primary goal is to increase the material's strength and density.
Annealing: Relieving Internal Stress
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters a metal's microstructure to make it more workable.
By heating a metal to a specific temperature and then slowly cooling it, you can reduce hardness, relieve internal stresses from prior work, and significantly improve its ductility (ability to be stretched or drawn).
Specialized Heat Treatment: For Advanced Alloys
Beyond general annealing, furnaces are used for highly specific treatments of oxidation-prone alloys like titanium or certain stainless steels.
These processes, such as hardening and tempering, require precise temperature control and often a controlled atmosphere to achieve their final, high-performance characteristics without contamination.
Understanding the Furnace Landscape
While "porcelain furnace" is a valid term, it's more useful to think in terms of furnace capabilities. Different metallurgical goals demand different types of furnaces.
General-Purpose Furnaces: The Workhorse
This category, which includes many porcelain-lined muffle furnaces, is used for basic annealing and sintering where atmospheric contamination is not a primary concern. They are the versatile workhorses for many heat treatment tasks.
Vacuum Furnaces: For Purity and Integrity
For reactive metals or high-performance applications, any atmospheric oxygen or nitrogen is a contaminant.
A vacuum furnace removes the atmosphere from the chamber before heating. This prevents oxidation and ensures that powdered metal parts are sintered with minimal distortion and maximum purity.
Rotary Furnaces: For Uniformity at Scale
When producing large quantities of metal powders or ceramic abrasives, consistency is key.
A rotary furnace tumbles the material during heating, ensuring every particle receives uniform heat treatment. This results in highly consistent material properties across an entire batch.
Hot Press Furnaces: For Maximum Density
Some applications require components with nearly 100% theoretical density and superior strength.
A hot press furnace is a specialized tool that applies immense pressure and heat simultaneously. This forces the metal powder particles together during sintering, creating exceptionally dense and robust final components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right furnace is a matter of balancing cost, complexity, and the desired material properties. There is no single "best" option, only the most appropriate one for the task.
Atmosphere Control vs. Cost
A vacuum furnace provides the purest environment but is significantly more complex and expensive to operate than a standard atmospheric furnace. This investment is only justified when working with sensitive materials or for mission-critical parts.
Final Density vs. Process Complexity
Simple sintering in a general-purpose furnace is a straightforward process. Achieving maximum density with a hot press furnace, however, requires more complex equipment and precise control over both temperature and pressure, increasing operational costs.
Throughput vs. Specialization
A rotary furnace is excellent for processing large volumes of powder uniformly. However, it is not suitable for creating a single, large, pre-formed component, where a stationary vacuum or hot press furnace would be required.
Matching the Process to Your Metallurgical Goal
Your final choice depends entirely on what you are trying to achieve with the material.
- If your primary focus is improving workability and reducing stress: A standard annealing process in a general-purpose muffle or porcelain furnace is your most direct solution.
- If your primary focus is creating solid parts from metal powder: Sintering is the required process, and your choice of a standard vs. a vacuum furnace will depend on the metal's sensitivity to atmospheric contamination.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum strength and density for a high-performance part: Advanced methods like vacuum sintering or, for ultimate performance, hot pressing are necessary.
Ultimately, the furnace is the tool, but understanding the underlying metallurgical process is what empowers you to create materials with intention and precision.
Summary Table:
| Process | Key Function | Common Furnace Types |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Softens metals, relieves stress | Porcelain, Muffle |
| Sintering | Fuses powders into solids | Porcelain, Vacuum, Rotary |
| Specialized Treatments | Hardens alloys, controls atmosphere | Vacuum, Hot Press |
Ready to elevate your metallurgical processes with tailored furnace solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior material outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















