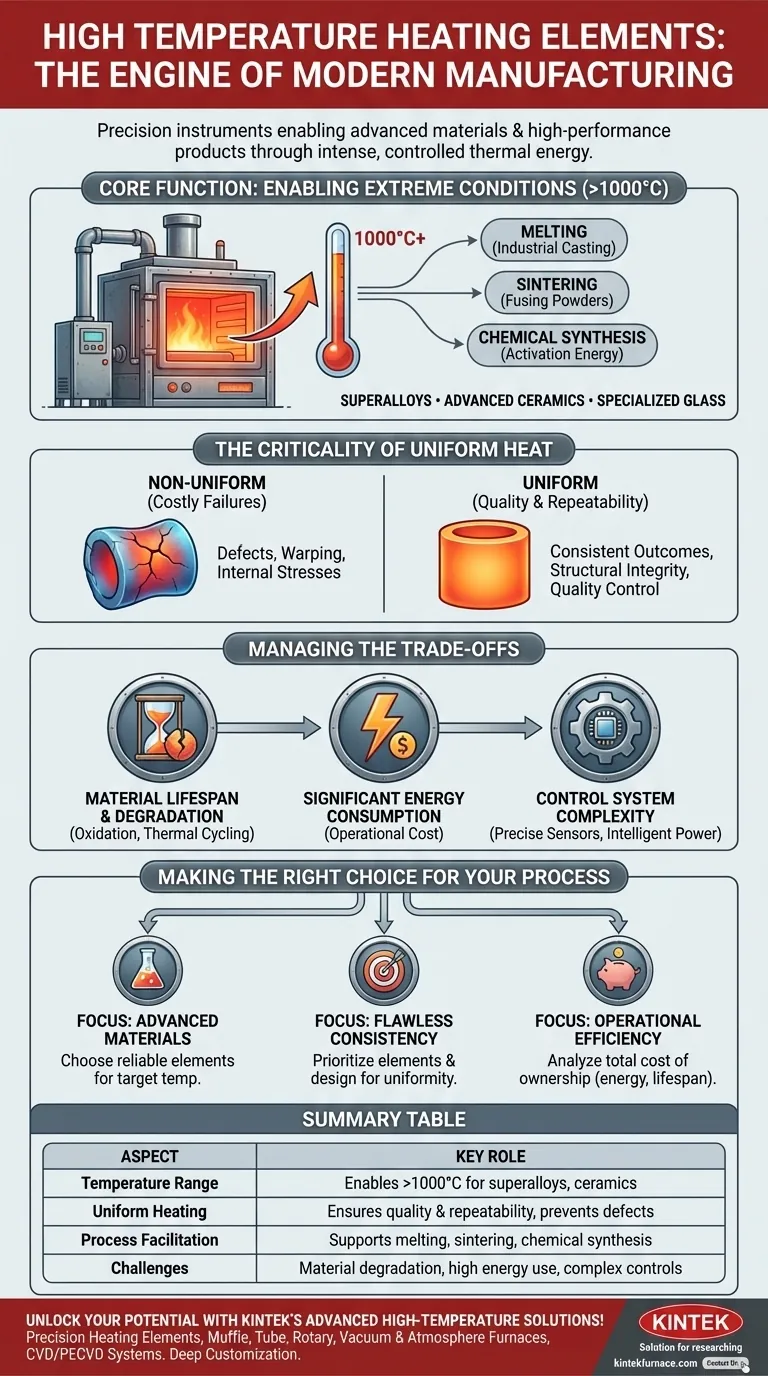
In modern manufacturing, high temperature heating elements are the enabling technology behind the creation of advanced materials and high-performance products. They are not merely sources of heat; they are precision instruments designed to deliver intense, uniform, and reliable thermal energy in environments where standard heating methods would fail. Their primary role is to facilitate transformative processes like melting, sintering, and chemical synthesis that are fundamental to industries from aerospace to electronics.
The true value of a high temperature heating element isn't just its ability to get hot, but its capacity to provide controlled and uniform heat. This precision is the deciding factor between a successful, high-quality product and a costly manufacturing failure.

The Core Function: Enabling High-Temperature Operations
The fundamental role of these elements is to unlock processes that are physically impossible at lower temperatures. They form the heart of industrial furnaces, kilns, and reactors.
Reaching Extreme Temperatures
Many modern materials, including superalloys, advanced ceramics, and specialized glass, require processing temperatures well above 1000°C (1832°F). High temperature elements are specifically engineered from materials like silicon carbide (SiC) or molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) to operate reliably in these extreme conditions.
The Foundation of Material Transformation
This intense heat is the catalyst for physical and chemical change. Processes like industrial casting rely on it to melt metals, sintering uses it to fuse powdered materials into a solid mass, and many chemical reactions depend on it to achieve the necessary activation energy.
Why Uniformity is Non-Negotiable
Simply reaching a high temperature is insufficient. The quality and integrity of the final product depend almost entirely on how evenly that heat is applied.
Ensuring Product Quality
In a process like sintering ceramic parts, temperature uniformity is critical. If one area is hotter than another, it can lead to internal stresses, warping, or incomplete fusion. These defects compromise the structural integrity and performance of the component.
Driving Process Repeatability
Uniform heating ensures that every part in a batch, and every batch run, is exposed to the exact same thermal profile. This repeatability is the cornerstone of quality control in mass production, guaranteeing consistent outcomes from the first unit to the last.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable, high temperature heating elements come with inherent challenges that require careful management. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to successful implementation.
Material Lifespan and Degradation
The very environments these elements create also cause them to degrade over time. Oxidation and thermal cycling gradually reduce their effectiveness and eventually lead to failure. The element's material composition directly impacts its lifespan and resistance to these effects.
Significant Energy Consumption
Generating and maintaining extreme temperatures is an energy-intensive process. The efficiency of the heating element and the quality of the furnace's insulation are critical factors in managing what is often a significant operational cost.
Control System Complexity
Achieving precise temperature uniformity requires more than just a good element. It demands a sophisticated control system with accurate sensors (thermocouples) and intelligent power controllers to constantly adjust energy output and maintain thermal stability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the appropriate heating element strategy depends entirely on your primary manufacturing goal.
- If your primary focus is processing advanced materials: Choose an element material that can comfortably exceed your target temperature without operating at its absolute limit, ensuring reliability.
- If your primary focus is achieving flawless product consistency: Prioritize elements and a furnace design renowned for exceptional temperature uniformity across the entire working volume.
- If your primary focus is maximizing operational efficiency: Analyze the element's energy consumption and expected lifespan to calculate the total cost of ownership, not just the upfront purchase price.
Ultimately, mastering high-temperature heating is about mastering control over a fundamental force, which is the key to unlocking manufacturing innovation and quality.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Role |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Enables operations above 1000°C for materials like superalloys and ceramics |
| Uniform Heating | Ensures product quality and repeatability by preventing defects |
| Process Facilitation | Supports melting, sintering, and chemical synthesis |
| Challenges | Includes material degradation, high energy use, and complex controls |
Unlock the full potential of your manufacturing processes with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with precision heating elements and systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we meet your unique experimental requirements for superior temperature control and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your production quality and innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- Why are SIC heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Self-Protecting Mechanism
- What is the maximum temperature silicon carbide heating elements can withstand? Key Factors for Longevity and Performance
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance



















