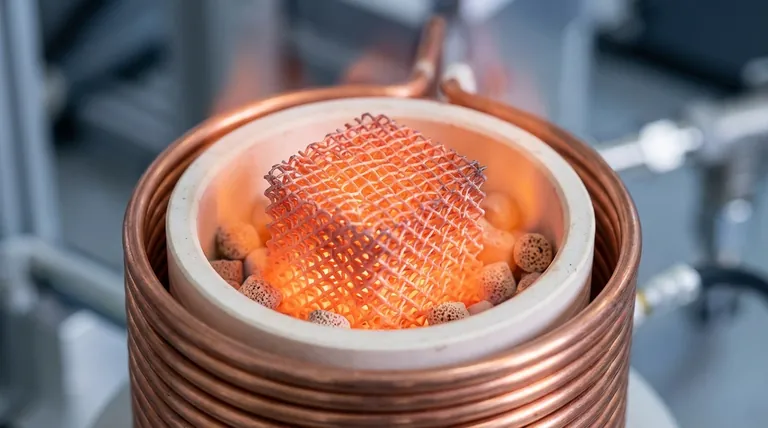
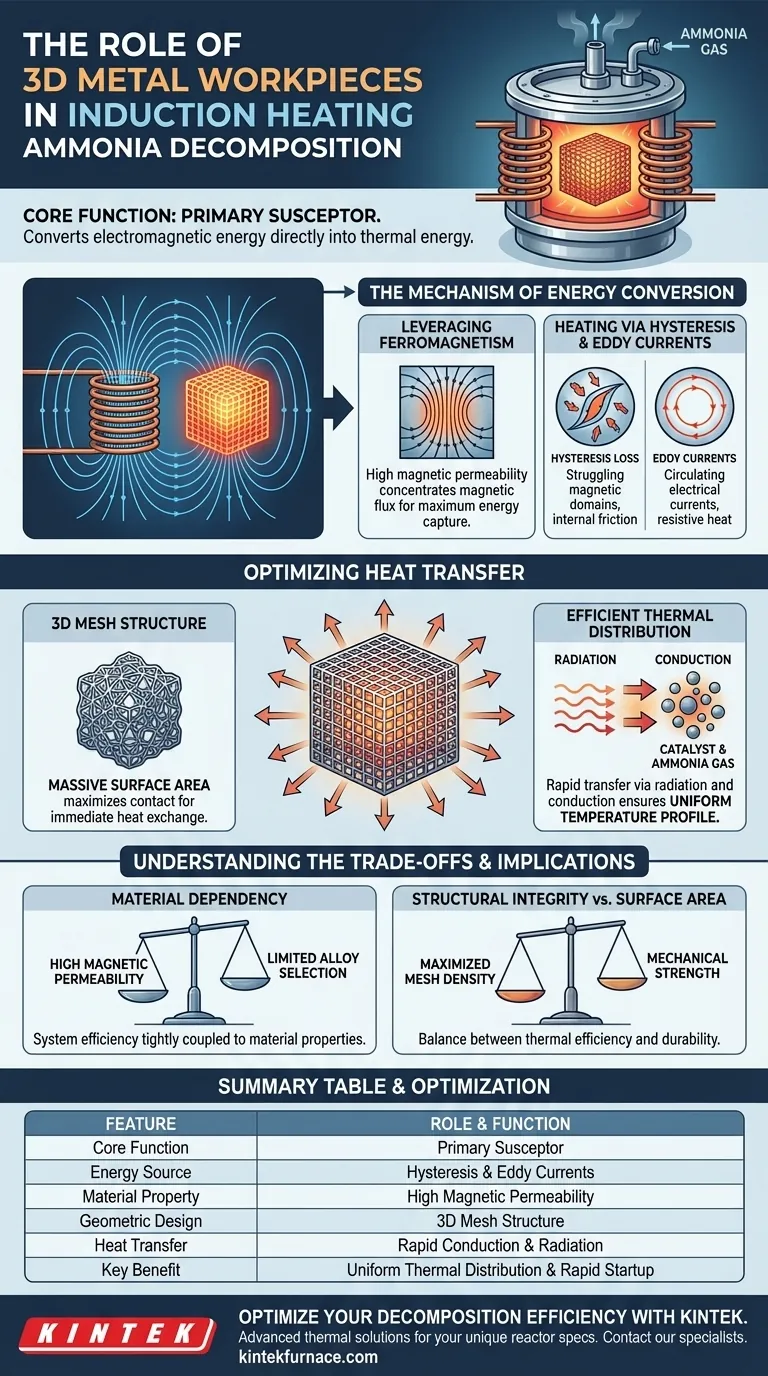
3D metal workpieces serve as the primary susceptors within the reactor system. By leveraging the high magnetic permeability of ferromagnetic materials, these components capture electromagnetic energy and convert it directly into thermal energy through hysteresis loss and eddy current effects, driving the decomposition process.
These workpieces bridge the gap between magnetic energy and chemical reaction. Their mesh structure maximizes surface area, ensuring rapid, uniform heat transfer to the ammonia gas and catalyst particles while optimizing internal thermal distribution.

The Mechanism of Energy Conversion
Acting as Primary Susceptors
The fundamental role of these workpieces is to act as a "susceptor." In induction heating, the electromagnetic field does not heat the gas directly; it heats a conductive material.
The 3D metal workpiece absorbs the electromagnetic field generated by the induction coil. Because it is the primary target of this energy, it becomes the heat source for the entire reactor chamber.
Leveraging Ferromagnetism
The efficiency of these workpieces relies on their material composition. They are made from ferromagnetic materials that possess high magnetic permeability.
This property allows the material to concentrate magnetic flux lines. This concentration is essential for maximizing the energy capture from the induction field.
Heating via Hysteresis and Eddy Currents
The conversion of magnetic energy to heat occurs through two distinct physical phenomena.
First, hysteresis loss occurs as the magnetic domains within the metal struggle to align with the rapidly changing magnetic field, generating internal friction.
Second, eddy currents are induced electrical currents that flow through the metal, generating resistive heat. Together, these effects cause the workpiece to heat up rapidly.
Optimizing Heat Transfer
The Advantage of a 3D Mesh Structure
The physical geometry of the workpiece is just as critical as its material properties. A 3D mesh structure provides a massive surface area compared to solid plates or simple rods.
This increased surface area maximizes contact with the surrounding environment. It ensures that the heat generated within the metal is not trapped but is immediately available for exchange.
Efficient Thermal Distribution
The ultimate goal is to heat the ammonia gas and the catalyst. The 3D structure facilitates this by transferring thermal energy quickly via radiation and conduction.
This geometry prevents hot spots and ensures the temperature is uniform throughout the reactor. A uniform temperature profile is vital for consistent ammonia decomposition rates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Material Dependency
The system's efficiency is tightly coupled to the magnetic properties of the workpiece.
If the material used does not have sufficiently high magnetic permeability, the ability to capture energy through hysteresis drops significantly. This restricts material selection to specific ferromagnetic alloys.
Structural Integrity vs. Surface Area
While a fine mesh increases surface area for heat transfer, it must remain structurally sound under high heat.
There is a balance to be struck between maximizing the mesh density for thermal efficiency and maintaining the mechanical strength required to support the catalyst and withstand thermal cycling.
Implications for Reactor Design
When designing or evaluating an ammonia decomposition reactor using this technology, consider your specific performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is rapid startup: Prioritize materials with the highest possible magnetic permeability to maximize hysteresis loss for immediate heat generation.
- If your primary focus is reaction consistency: Ensure the 3D mesh geometry is uniform to guarantee even heat distribution via radiation and conduction to the catalyst.
The 3D metal workpiece is not just a passive heating element; it is an active energy converter that defines the thermal efficiency of the entire decomposition process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Role & Function in Reactor |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Primary Susceptor (Energy Conversion) |
| Energy Source | Hysteresis loss and Eddy current effects |
| Material Property | High magnetic permeability (Ferromagnetic) |
| Geometric Design | 3D Mesh structure for maximum surface area |
| Heat Transfer | Rapid conduction and radiation to catalyst/gas |
| Key Benefit | Uniform thermal distribution and rapid startup |
Optimize Your Decomposition Efficiency with KINTEK
Are you looking to enhance your laboratory or industrial heating processes? KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions backed by expert R&D and precision manufacturing. Whether you require Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, or CVD systems, our high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique reactor specifications and research needs.
Maximize your energy conversion today. Contact our specialists now to discover how our advanced heating technologies can drive your innovation forward.
Visual Guide
References
- Débora de Figueiredo Luiz, Jurriaan Boon. Use of a 3D Workpiece to Inductively Heat an Ammonia Cracking Reactor. DOI: 10.3390/suschem6040043
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Stainless Steel Quick Release Vacuum Chain Three Section Clamp
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key advantages of using induction furnaces for metal casting? Boost Efficiency and Quality in Your Foundry
- What is an induction-heated vacuum furnace and what is its primary use? Achieve Ultimate Metal Purity for High-Performance Alloys
- Why is repeated melting necessary for AlCoCrFeNi2.1 HEA? Achieving Chemical Uniformity in High-Entropy Alloys
- Why is supplier reputation important when purchasing an induction melting furnace? Ensure Long-Term Reliability and Lower Costs
- How does induction heating contribute to a cleaner work environment? Boost Quality & Sustainability
- Why is the hydraulic vacuum dispersion method suitable for high-melting-point metals like cast iron and steel?
- What is the role of a Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace in chromium-steel prep? Secure Purity & Composition Control
- What role does vacuum induction melting gas atomization play in Ni3Al/Cr7C3? Master Composite Powder Preparation











