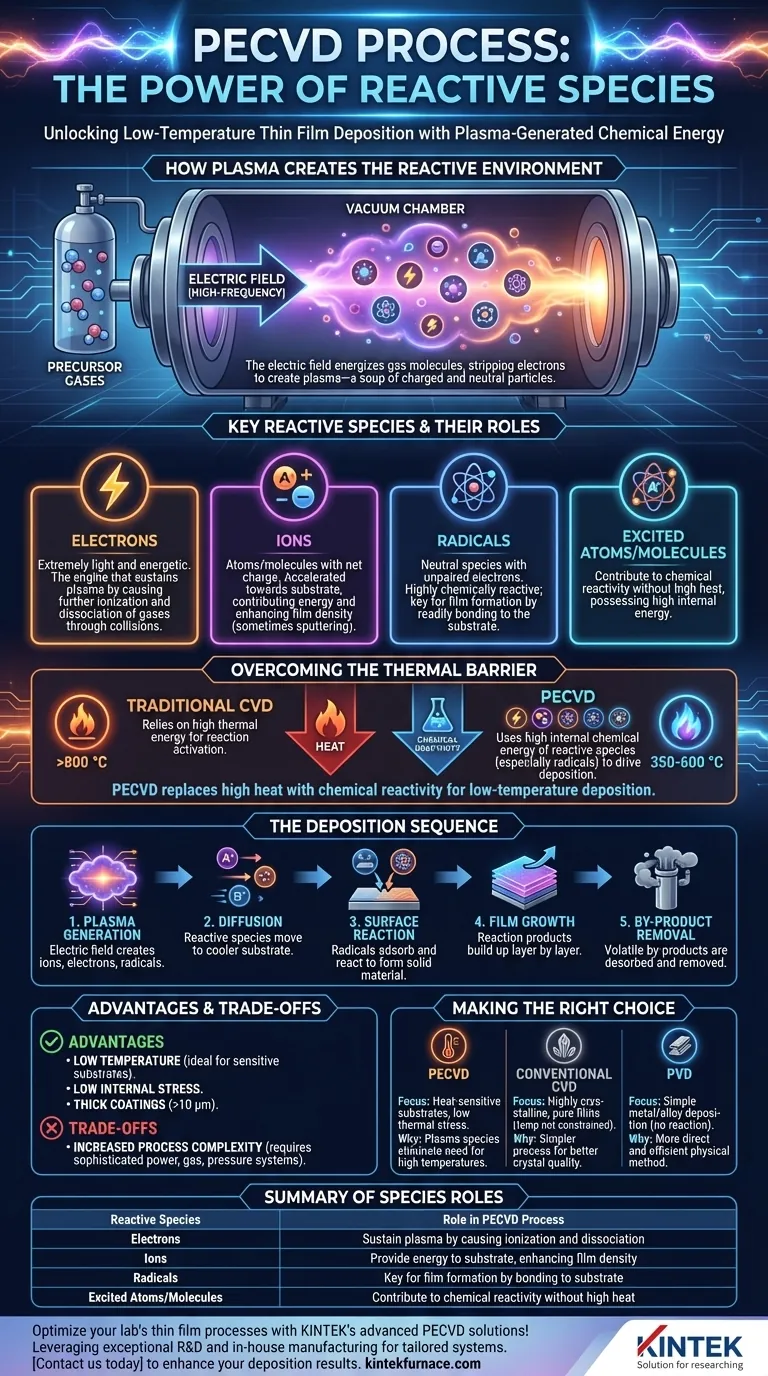
In Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD), the process relies on a specific set of highly reactive chemical species to function. These species are generated when an electric field is applied to the precursor gases, creating a plasma state. The primary reactive species involved are ions, electrons, radicals, excited atoms, and excited molecules.
The fundamental purpose of creating reactive species in PECVD is to replace the high thermal energy required in traditional CVD with the high chemical energy of a plasma. This allows for thin film deposition at significantly lower substrate temperatures, which is the defining advantage of the process.
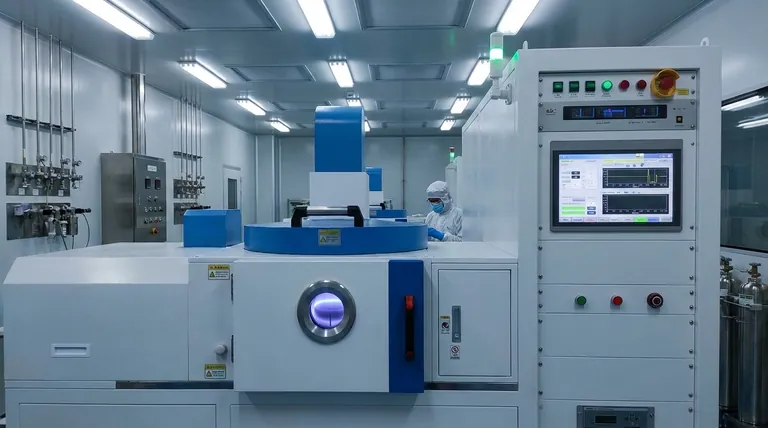

How Plasma Creates the Reactive Environment
The core of PECVD is the controlled generation of plasma. This isn't a chaotic process but a precise method for creating a chemically active environment without extreme heat.
The Initial Step: Gas Ionization
First, precursor gases are introduced into a vacuum chamber. A high-frequency electric field is then applied, which energizes the gas mixture. This energy transfer ionizes the gas molecules, stripping away electrons and creating a soup of charged and neutral particles known as plasma.
The Key Players: A Breakdown of Species
The plasma is not a uniform substance but a mixture of different species, each playing a distinct role.
-
Electrons: These are extremely light and energetic. They are accelerated by the electric field and collide with gas molecules, causing further ionization and dissociation. Electrons are the engine that sustains the plasma.
-
Ions: These are atoms or molecules that have lost or gained an electron, giving them a net positive or negative charge. They can be accelerated by the electric field towards the substrate, contributing energy to the surface and sometimes physically sputtering it, which can enhance film density.
-
Radicals: These are neutral atoms or molecules with unpaired electrons. This makes them highly chemically reactive. Radicals are often the most important species for the actual film formation, as they readily bond to the substrate surface to build the new layer.
How Reactive Species Enable Low-Temperature Deposition
The creation of these species is what allows PECVD to overcome the primary limitation of conventional Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD).
Overcoming the Thermal Energy Barrier
Traditional CVD relies purely on high temperatures (often >800 °C) to provide the activation energy needed for chemical reactions to occur on the substrate. This thermal energy breaks down the precursor gases and drives the deposition.
Replacing Heat with Chemical Reactivity
In PECVD, the high internal energy of the reactive species, particularly radicals, provides the chemical potential for the reaction. These species are inherently unstable and eager to react, so they don't need high substrate temperatures to form a film. This is the key mechanism that allows PECVD to operate at much lower temperatures (typically 350-600 °C).
The Deposition Sequence
The process, driven by these reactive species, follows a clear path:
- Plasma Generation: The electric field creates a plasma containing ions, electrons, and radicals.
- Diffusion: These highly reactive species diffuse from the plasma cloud to the cooler substrate surface.
- Surface Reaction: Radicals and other species adsorb onto the surface and undergo chemical reactions, forming the desired solid material.
- Film Growth: The reaction products build up layer by layer, forming a thin film.
- By-product Removal: Volatile by-products from the reaction are desorbed from the surface and removed by the vacuum system.
Understanding the Advantages and Trade-offs
The use of a plasma-generated reactive environment provides distinct benefits but also introduces process complexity.
The Primary Advantage: Low Temperature
The ability to deposit high-quality films at low temperatures is the most significant advantage. This makes PECVD suitable for depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics, or on devices that cannot withstand high-temperature processing.
Other Key Benefits
PECVD is also known for producing films with low internal stress. Furthermore, it allows for the deposition of thick coatings (greater than 10 μm), a capability not typically found in conventional CVD.
Inherent Process Complexity
The main trade-off is increased system complexity compared to some other methods. A PECVD system requires a sophisticated power source to generate the plasma, along with precise gas distribution and pressure control systems that differ from those used in thermal CVD or Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of reactive species helps you decide when PECVD is the appropriate tool for your fabrication needs.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on heat-sensitive substrates or minimizing thermal stress: PECVD is the superior choice because its plasma-generated reactive species eliminate the need for high process temperatures.
- If your primary focus is depositing highly crystalline, pure films and temperature is not a constraint: Conventional high-temperature CVD may offer a simpler process and yield better crystal quality for certain materials.
- If your primary focus is depositing a simple metal or alloy without a chemical reaction: A Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) method like sputtering or evaporation is often more direct and efficient.
Ultimately, mastering the plasma environment and its reactive species is the key to leveraging the unique capabilities of PECVD for advanced material deposition.
Summary Table:
| Reactive Species | Role in PECVD Process |
|---|---|
| Electrons | Sustain plasma by causing ionization and dissociation of gases |
| Ions | Provide energy to substrate surface, enhancing film density |
| Radicals | Key for film formation by bonding to the substrate |
| Excited Atoms/Molecules | Contribute to chemical reactivity without high heat |
Optimize your lab's thin film processes with KINTEK's advanced PECVD solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like CVD/PECVD, tailored to your unique needs. Our deep customization capability ensures precise performance for temperature-sensitive applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your deposition results and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection



















