Beyond superalloys, many other advanced materials rely on vacuum induction melting (VIM) to achieve their required properties. These include reactive metals like titanium and zirconium, high-purity materials such as specialty steels and magnetic alloys, and a range of other alloys where atmospheric contamination would be catastrophic to performance. VIM is chosen when the chemical composition and purity of the final metal are non-negotiable.
The core principle is not about specific alloy names, but about a specific need: VIM is the solution for any alloy whose performance is critically sensitive to contamination from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, or whose final properties depend on ultra-high purity and precise chemical control.
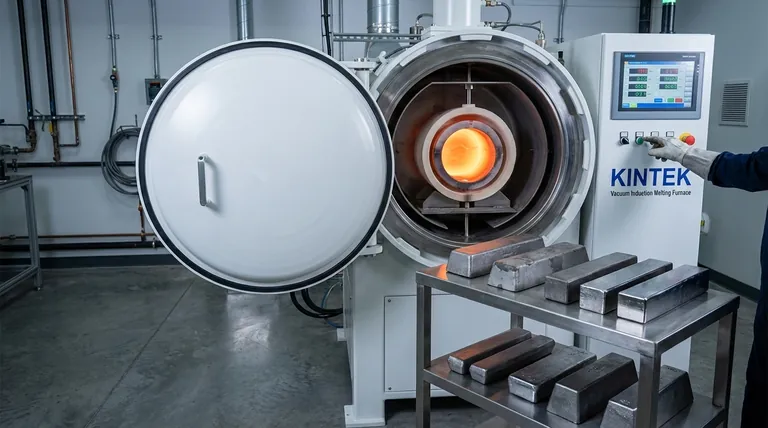

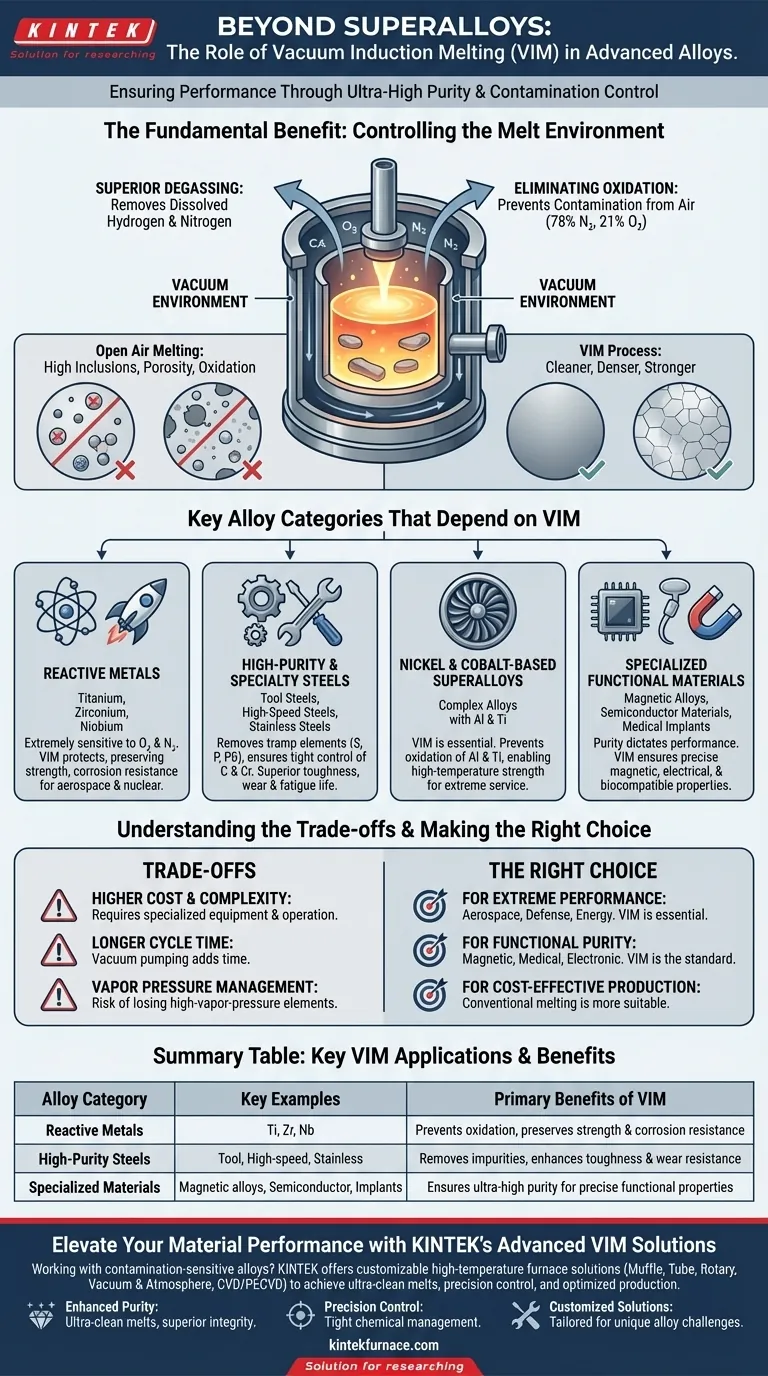
The Fundamental Benefit: Controlling the Melt Environment
The power of VIM comes from performing the entire melting process inside a vacuum. This fundamentally changes the metallurgy compared to melting in open air.
Eliminating Oxidation and Contamination
Melting metal in air exposes it to approximately 78% nitrogen and 21% oxygen. Many valuable alloying elements, such as aluminum, titanium, and chromium, have a high affinity for oxygen and will readily form oxides.
These oxides become inclusions (impurities) within the metal matrix, acting as microscopic stress points that can initiate cracks and lead to premature failure. The vacuum in a VIM furnace removes these gases, preventing oxidation from ever occurring.
Enabling Superior Degassing
Molten metal can hold a significant amount of dissolved gases, particularly hydrogen and nitrogen. As the metal solidifies, its ability to hold these gases drops dramatically, causing them to form pores and voids.
This porosity severely degrades the mechanical properties of the final component. The vacuum environment of VIM actively pulls these dissolved gases out of the molten bath, resulting in a cleaner, denser, and stronger final product.
Key Alloy Categories That Depend on VIM
Based on the need for purity and atmospheric control, several families of alloys are almost exclusively produced or refined using VIM.
Reactive Metals
Metals like titanium, zirconium, and niobium are extremely reactive. When molten, they act like sponges for oxygen and nitrogen, which makes them brittle and unusable if melted in air.
VIM is one of the few methods that can melt these materials while protecting them from atmospheric contamination, preserving their unique strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature properties for aerospace and nuclear applications.
High-Purity and Specialty Steels
This category includes tool steels, high-speed steels, and certain stainless steels. While they can be made via other methods, VIM is used when maximum cleanliness and performance are required.
The process removes undesirable tramp elements like sulfur, phosphorus, and lead, and allows for extremely tight control over key alloying elements like carbon and chromium. This results in superior toughness, wear resistance, and fatigue life.
Nickel and Cobalt-Based Superalloys
While you asked for other alloys, no discussion of VIM is complete without mentioning superalloys. They are the quintessential VIM material for a reason.
Their high-temperature strength depends on reactive elements like aluminum and titanium. VIM is the only way to melt these complex alloys without oxidizing these critical elements, ensuring the formation of the strengthening phases required for jet engine turbine blades and other extreme-service components.
Specialized Functional Materials
This group includes materials where purity directly dictates performance. Magnetic alloys, materials for semiconductor manufacturing, and alloys for medical implants fall into this category.
Even minuscule impurities can drastically alter an alloy's magnetic permeability, electrical conductivity, or biocompatibility. VIM provides the ultra-high-purity environment needed to achieve these precise functional properties reliably.
Understanding the Trade-offs of VIM
While powerful, VIM is not the default choice for all metal production. Its precision comes with clear trade-offs that must be considered.
Cost and Complexity
VIM furnaces are significantly more expensive to build and operate than air-melt furnaces. The need for robust vacuum chambers, powerful pumps, and sophisticated controls adds substantial capital and operational cost.
Cycle Time
Achieving a deep vacuum is not instantaneous. The time required to pump down the chamber before melting can begin makes the overall process slower and less suited for high-volume, low-cost production compared to conventional methods.
Vapor Pressure Limitations
Under a vacuum, elements with a high vapor pressure (like manganese or lead) can "boil off" from the molten bath more easily. While VIM operators can control this by backfilling the chamber with a partial pressure of inert gas, it is a critical process parameter that must be carefully managed to prevent loss of key alloying elements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melting process depends entirely on the alloy's sensitivity and the component's end-use requirements.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme environments: VIM is essential for creating clean, robust superalloys and reactive metals for aerospace, defense, and energy applications.
- If your primary focus is material purity for functional properties: VIM is the standard for producing magnetic, medical, or electronic-grade alloys where impurities would cripple performance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of common alloys: VIM is likely unnecessary and too expensive; conventional air-melting or argon oxygen decarburization (AOD) are more suitable.
Ultimately, choosing VIM is a deliberate engineering decision to invest in material purity to guarantee final component integrity and performance.
Summary Table:
| Alloy Category | Key Examples | Primary Benefits of VIM |
|---|---|---|
| Reactive Metals | Titanium, Zirconium, Niobium | Prevents oxidation, preserves strength and corrosion resistance |
| High-Purity Steels | Tool steels, High-speed steels, Stainless steels | Removes impurities, enhances toughness and wear resistance |
| Specialized Functional Materials | Magnetic alloys, Semiconductor materials, Medical implants | Ensures ultra-high purity for precise functional properties |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK's Advanced Vacuum Induction Melting Solutions
Are you working with reactive metals, high-purity steels, or specialized alloys where contamination control is critical? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
By choosing KINTEK, you benefit from:
- Enhanced Purity: Achieve ultra-clean melts free from atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen, ensuring superior material integrity.
- Precision Control: Gain tight chemical composition management for alloys sensitive to impurities, boosting performance in extreme environments.
- Customized Solutions: Get furnaces designed to handle specific alloy challenges, from vapor pressure limitations to cycle time optimization.
Don't let contamination compromise your results—contact us today to discuss how our VIM expertise can drive your innovations forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















