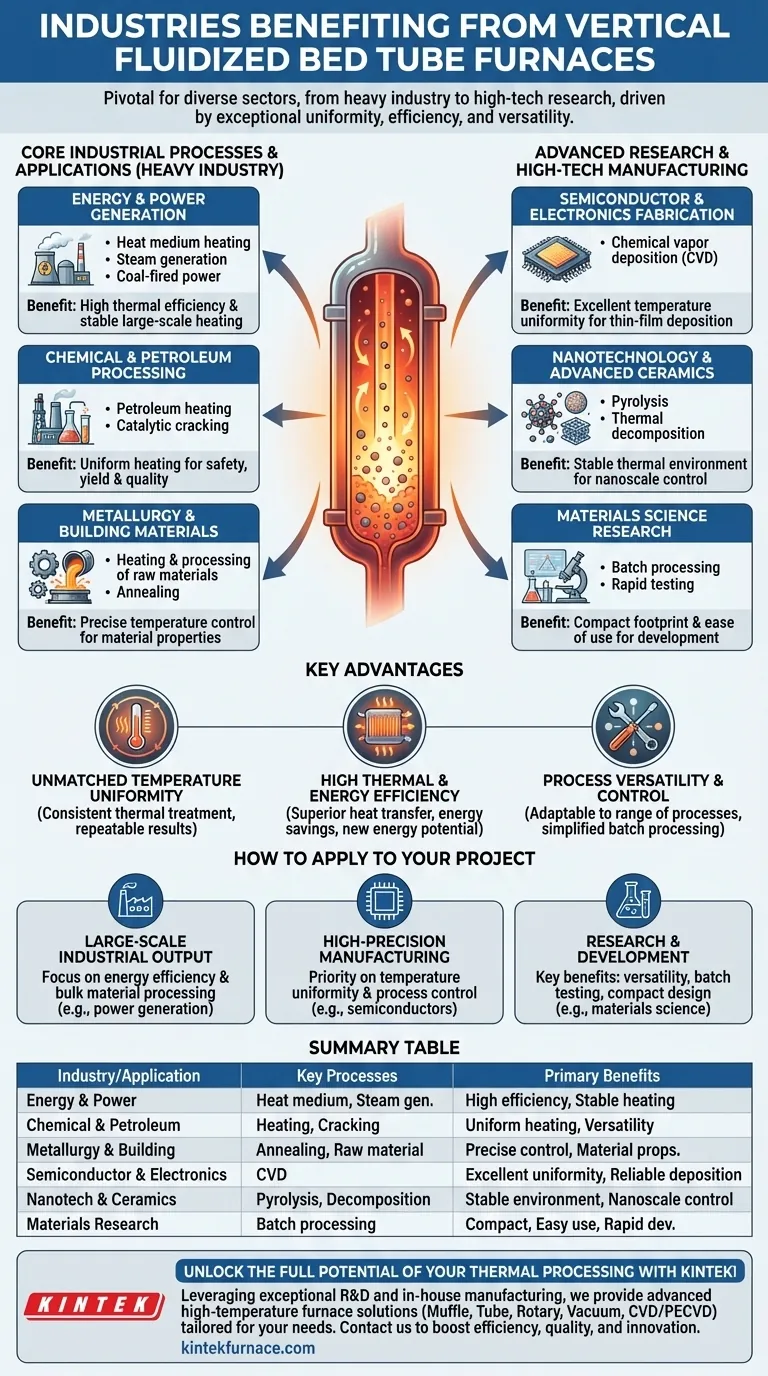
Beyond general material processing, vertical fluidized bed tube furnaces are pivotal in a diverse range of sectors, including heavy industries like metallurgy, chemical processing, and power generation, as well as high-tech fields such as semiconductor manufacturing, nanotechnology, and advanced ceramics. Their use extends from large-scale industrial heating to the precise fabrication of next-generation materials.
The widespread adoption of these furnaces is driven by their unique combination of exceptional temperature uniformity, high thermal efficiency, and process versatility. This allows industries to achieve consistent, high-quality results for sensitive material processing, from large-scale chemical reactions to delicate semiconductor fabrication.

Core Industrial Processes and Applications
The primary value in heavy industry stems from the furnace's ability to deliver efficient and stable heat on a massive scale.
Energy and Power Generation
These furnaces are integral to the energy sector. They are used for heat medium heating in various industrial plants and play a crucial role in steam generation.
In traditional power infrastructure, they are employed in coal-fired power stations to generate electricity, leveraging their efficiency to maximize energy output.
Chemical and Petroleum Processing
In the chemical industry, vertical fluidized bed furnaces are used for critical processes like petroleum heating and catalytic cracking.
The uniform heating ensures that these complex chemical reactions proceed efficiently and safely, leading to higher yields and better product quality.
Metallurgy and Building Materials
The metallurgy and building materials sectors rely on these furnaces for the fundamental heating and processing of raw materials.
Processes like annealing metals to improve their ductility and durability are common applications, where precise temperature control is essential for achieving the desired material properties.
Advanced Research and High-Tech Manufacturing
In high-technology fields, the furnace's precision and control are more important than its scale. It serves as a tool for creating and refining advanced materials.
Semiconductor and Electronics Fabrication
The manufacturing of semiconductors demands an extremely controlled, high-temperature environment. Vertical tube furnaces provide this for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
The excellent temperature uniformity along the tube is critical for depositing thin films onto wafers, ensuring the reliability and performance of electronic components.
Nanotechnology and Advanced Ceramics
Researchers in nanotechnology and advanced ceramics use these furnaces to synthesize new materials through processes like pyrolysis and thermal decomposition.
The furnace's ability to create a stable, uniform thermal environment is essential for controlling the structure and properties of materials at the nanoscale.
Materials Science Research
For materials scientists in laboratory settings, these furnaces are invaluable. Their relatively compact footprint makes them ideal for facilities with limited space.
The simplified loading and unloading of samples facilitate convenient batch processing, allowing for rapid testing and development of new materials and processes.
Understanding the Key Advantages
The broad applicability of this technology is rooted in three core technical benefits that solve common industrial and research challenges.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The most significant advantage is the excellent temperature uniformity maintained along the length of the processing tube.
This consistency eliminates hot spots and ensures that every part of the sample or material receives the same thermal treatment, resulting in highly repeatable and reliable outcomes.
High Thermal and Energy Efficiency
The fluidized bed design facilitates superior heat transfer, leading to highly efficient and uniform heating characteristics.
This not only enhances processing speed but also translates to significant energy savings and improved environmental performance, making it a forward-looking technology. There is strong potential for its expanded use in the new energy sector.
Process Versatility and Control
These furnaces are not single-task devices. They can be adapted for a wide range of thermal processes, from simple heating and annealing to complex chemical depositions.
The vertical orientation simplifies sample handling and makes them particularly well-suited for batch processing, increasing throughput in both research and manufacturing environments.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice should be guided by whether your primary goal is industrial throughput, manufacturing precision, or research flexibility.
- If your primary focus is large-scale industrial output: Your main drivers are energy efficiency and the ability to process bulk materials, as seen in power generation and chemical cracking.
- If your primary focus is high-precision manufacturing: Your priority is the furnace's temperature uniformity and process control for applications like semiconductor fabrication or advanced ceramics.
- If your primary focus is research and development: The key benefits are process versatility, ease of use for batch testing, and a compact design suitable for a laboratory environment.
Ultimately, the adaptability of the vertical fluidized bed tube furnace makes it a foundational tool for both industrial optimization and material innovation.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Key Processes | Primary Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Energy & Power Generation | Heat medium heating, Steam generation, Coal-fired electricity | High thermal efficiency, Stable large-scale heating |
| Chemical & Petroleum Processing | Petroleum heating, Catalytic cracking | Uniform heating for safety and yield, Process versatility |
| Metallurgy & Building Materials | Annealing, Raw material processing | Precise temperature control, Improved material properties |
| Semiconductor & Electronics | Chemical vapor deposition (CVD) | Excellent temperature uniformity, Reliable thin-film deposition |
| Nanotechnology & Advanced Ceramics | Pyrolysis, Thermal decomposition | Stable thermal environment, Nanoscale material control |
| Materials Science Research | Batch processing, Sample testing | Compact footprint, Ease of use, Rapid development |
Unlock the full potential of your thermal processing with KINTEK! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for industries like metallurgy, chemical processing, semiconductors, and nanotechnology. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is enhanced by deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can boost your efficiency, quality, and innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















