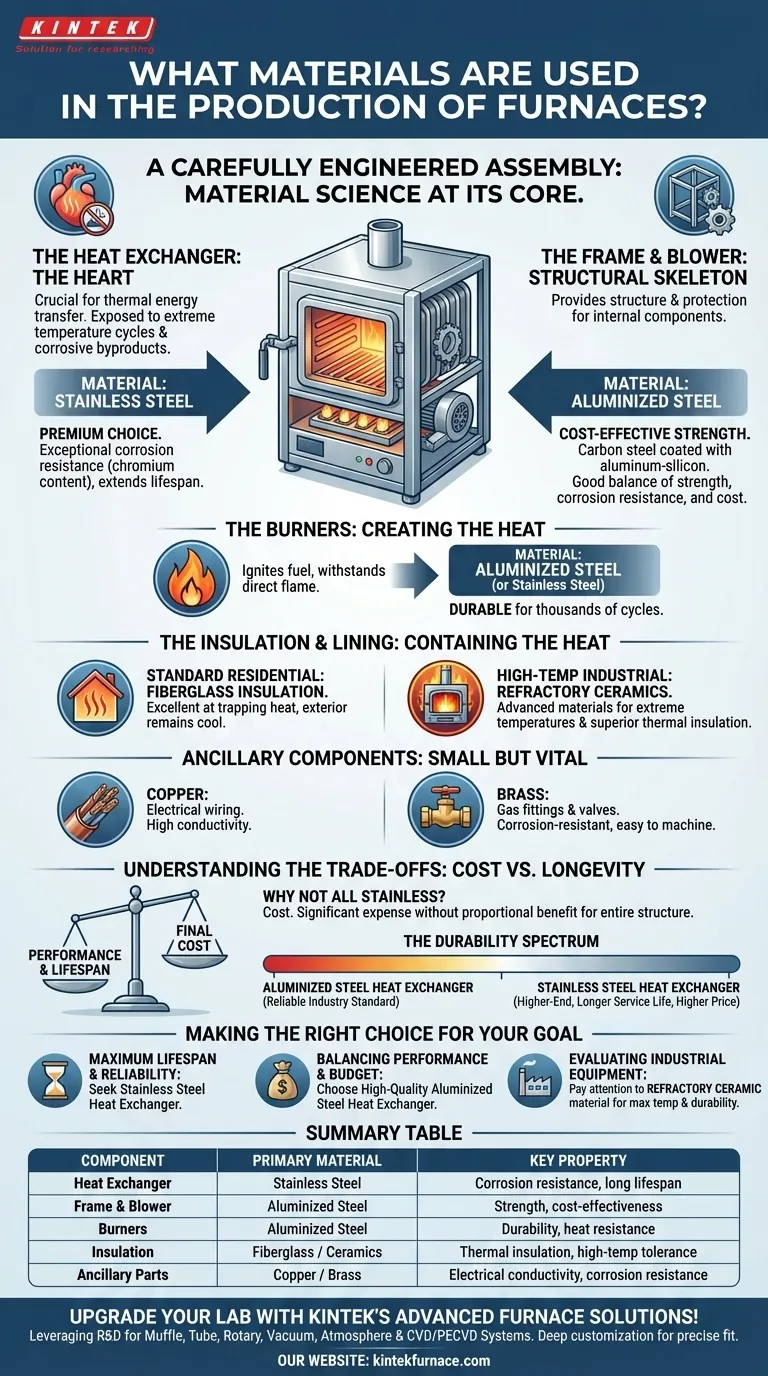
At its core, a furnace is a carefully engineered assembly of specific metals and insulators, each chosen for its unique ability to handle heat, resist corrosion, and provide structural integrity. The primary materials used are stainless steel, aluminized steel, and various forms of ceramic or fiberglass insulation, supplemented by copper and brass for electrical and gas components.
Furnace construction is a deliberate exercise in material science. The choice of each material is dictated by its specific role—balancing extreme heat resistance in the core, corrosion-proof durability in the heat exchanger, and cost-effective strength for the outer structure.

The Anatomy of a Furnace: A Material-by-Material Breakdown
To understand why certain materials are used, you must look at the function of each furnace component. The demands on the heat exchanger are vastly different from those on the outer cabinet.
The Heat Exchanger: The Heart of the System
The heat exchanger is where the crucial transfer of thermal energy occurs. It is constantly exposed to the corrosive byproducts of combustion and extreme temperature cycles.
For this reason, stainless steel is the premium material for heat exchangers. Its superior chromium content provides exceptional resistance to rust and corrosion, significantly extending the furnace's lifespan.
The Frame and Blower: The Structural Skeleton
The furnace's cabinet, or frame, along with the housing for the blower, provides the necessary structure and protection for the internal components.
These parts are typically constructed from aluminized steel. This is carbon steel coated with an aluminum-silicon alloy, offering a good balance of strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness for components not directly exposed to the most intense heat and corrosive gases.
The Burners: Creating the Heat
The burners are responsible for safely igniting the fuel to generate heat. They must be durable enough to withstand direct flame and high temperatures.
Like the frame, burners are often made from aluminized steel or occasionally higher-grade stainless steel, providing the necessary durability to operate reliably over thousands of cycles.
The Insulation and Lining: Containing the Heat
Effectively containing the heat is critical for both efficiency and safety. Different materials are used depending on the furnace's maximum temperature.
For standard residential furnaces, the cabinet is lined with fiberglass insulation. This material is excellent at trapping heat, ensuring it is directed into your home and that the exterior of the furnace remains cool to the touch.
In high-temperature industrial furnaces, the heating chamber itself is constructed from refractory ceramics. These advanced materials are designed to withstand extreme temperatures while providing superior thermal insulation.
Ancillary Components: The Small but Vital Parts
A furnace relies on a network of smaller components to function. Copper is universally used for electrical wiring due to its high conductivity, while brass is often used for gas fittings and valves because it is corrosion-resistant and easy to machine into precise shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Longevity
The selection of furnace materials is a direct reflection of an engineering trade-off between performance, lifespan, and final cost.
Why Not Use Stainless Steel for Everything?
The primary reason is cost. Stainless steel is significantly more expensive than aluminized steel. Using it for the entire furnace structure would make the unit prohibitively expensive for most consumers without adding proportional performance benefits.
The Durability Spectrum
Furnace manufacturers offer a spectrum of quality. A furnace with an aluminized steel heat exchanger is a perfectly reliable and common industry standard. A furnace with a stainless steel heat exchanger represents a higher-end, more durable option designed for a longer service life, which is reflected in its higher price point.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your new understanding of these materials can directly inform your purchasing or evaluation process.
- If your primary focus is maximum lifespan and reliability: Seek out a furnace that explicitly features a primary and/or secondary heat exchanger made from stainless steel.
- If your primary focus is balancing performance and budget: A furnace with a high-quality aluminized steel heat exchanger is a dependable and cost-effective choice for most residential applications.
- If you are evaluating industrial equipment: Pay close attention to the specific refractory ceramic material used, as this dictates the furnace's maximum operating temperature and durability under constant use.
By understanding what a furnace is made of, you can better judge its quality, predict its longevity, and make a truly informed decision.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Material | Key Property |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Exchanger | Stainless Steel | Corrosion resistance, long lifespan |
| Frame and Blower | Aluminized Steel | Strength, cost-effectiveness |
| Burners | Aluminized Steel | Durability, heat resistance |
| Insulation | Fiberglass / Ceramics | Thermal insulation, high-temperature tolerance |
| Ancillary Parts | Copper / Brass | Electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance |
Upgrade your lab with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capability ensures precise fit for your unique experimental needs—enhance efficiency and reliability today. Contact us now to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of ceramic heating elements over metal ones? Superior Durability, Efficiency & Safety
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- How does the operating atmosphere affect MoSi2 heating elements? Maximize Temperature & Lifespan
- Are silicon carbide heating elements customizable? Optimize Your High-Temp Furnace Performance
- Which heating element is most effective? The definitive guide to choosing the right material for your application.
- What is the typical lifespan of 1700 type MoSi2 heating elements at different temperatures? Maximize Element Longevity
- How do in-situ heaters and precision current sources cooperate to stabilize the SkBL in NdMn2Ge2?
- What are the main types of alloys used for manufacturing heating elements? Discover the Best Alloys for Your Heating Needs



















