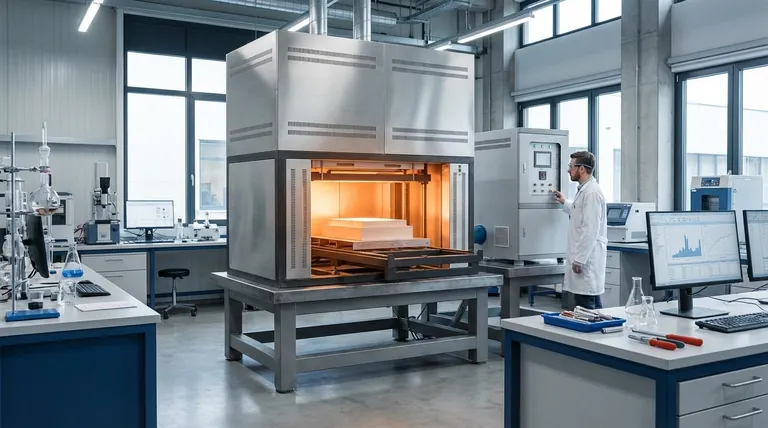
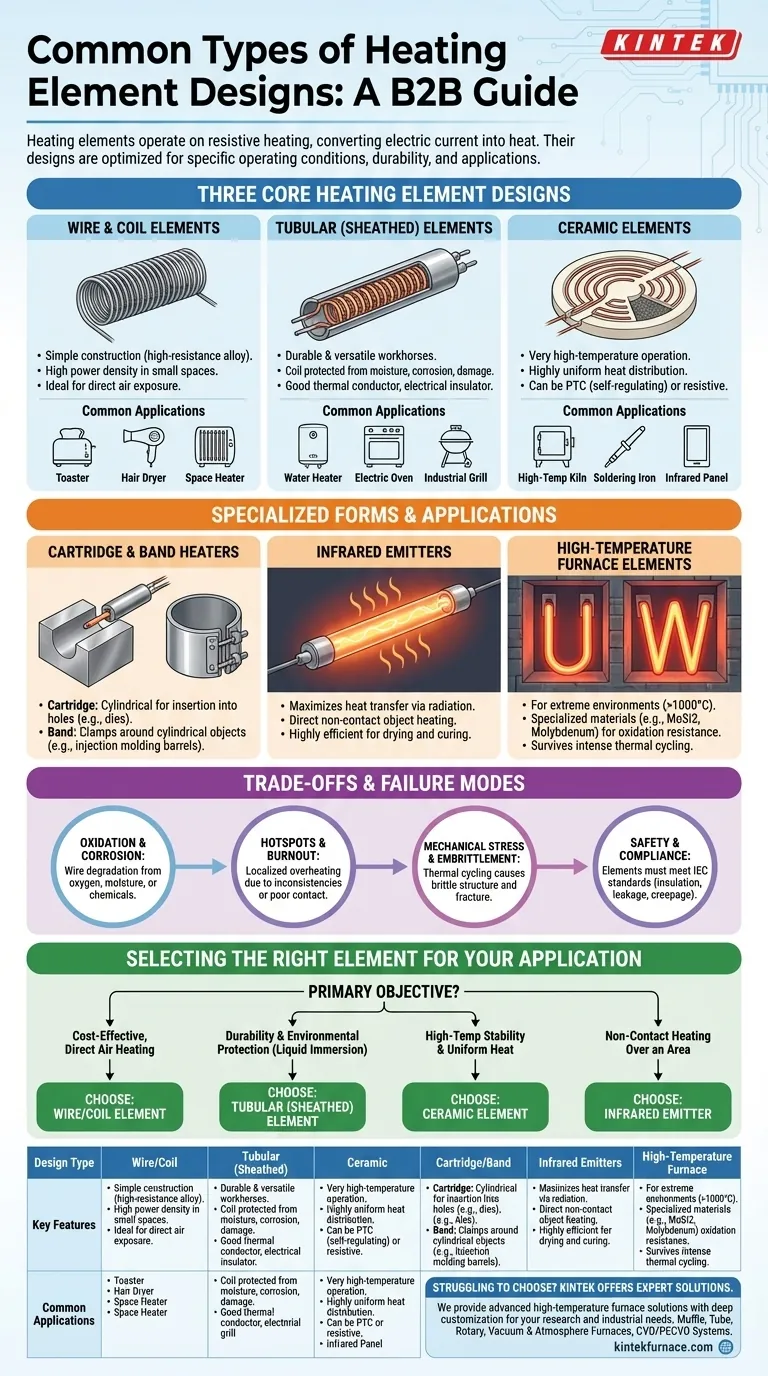
The most common heating elements are broadly classified into three core designs: wire/coil, tubular, and ceramic. Each type uses the principle of resistive heating, where electric current passing through a material generates heat. However, their physical construction and materials are optimized for vastly different operating conditions, temperatures, and applications.
The critical insight is not simply knowing the types of heating elements, but understanding that the element's design—its material, shape, and enclosure—is purposefully engineered to solve a specific problem, whether it's rapid heating, durability in a harsh environment, or precise temperature control.

A Breakdown of Core Heating Element Designs
The fundamental design of an element dictates its performance characteristics. The three primary categories provide a foundation for understanding nearly all electric heating applications.
Wire and Coil Elements
This is the simplest form of heating element, consisting of a length of high-resistance wire, often an alloy like Nichrome (nickel-chromium).
The wire is typically wound into a coil to fit a large amount of heating length into a small space. These are common in applications where the element is directly exposed to air.
Tubular (Sheathed) Elements
Tubular elements represent a significant step up in durability and versatility. They are the workhorses of the heating industry.
Their construction involves a resistive coil (like the wire elements above) housed inside a protective metal tube, or sheath. The space between the coil and the sheath is filled with a compacted ceramic powder, like magnesium oxide, which acts as an excellent electrical insulator but a good thermal conductor.
This design protects the sensitive heating coil from moisture, corrosion, and mechanical damage, making it ideal for immersion in liquids (like in water heaters) or for rugged use in appliances like electric ovens and grills.
Ceramic Elements
Ceramic heaters use advanced ceramic materials, such as positive temperature coefficient (PTC) ceramic, that can act as their own heating element. Others embed a resistive wire within a ceramic body.
Their primary advantages are the ability to operate at very high temperatures and provide highly uniform heat distribution. They are often manufactured as plates, discs, or rods and are used in everything from high-temperature kilns to precision soldering irons and infrared heating panels.
Specialized Forms and Applications
The core designs are frequently adapted into specialized shapes to integrate seamlessly into machinery or to achieve a specific heating effect.
Cartridge and Band Heaters
These are specialized forms of tubular or ceramic elements. A cartridge heater is a cylindrical element designed to be inserted into a hole, perfect for heating metal blocks like industrial dies.
A band heater is designed to clamp around a cylindrical object, such as the barrel of a plastic injection molding machine, providing uniform circumferential heat.
Infrared Emitters
While other elements heat primarily through convection and conduction, infrared emitters are designed to maximize heat transfer through radiation.
These elements, often made from quartz tubes or ceramic panels, heat an object directly without needing to heat the air in between. This makes them highly efficient for applications like industrial drying, curing paints, and space heating.
High-Temperature Furnace Elements
For extreme environments like metallurgical furnaces operating well above 1000°C, specialized materials are required.
Elements made from materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) or pure Molybdenum are formed into "U," "W," or rod shapes. These are designed to survive the intense heat and thermal cycling inside a high-temperature furnace where standard alloys would rapidly oxidize and fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Failure Modes
No heating element lasts forever. Understanding common failure modes is key to selecting the right element and ensuring a long service life.
Oxidation and Corrosion
When a resistive wire is exposed to oxygen at high temperatures, it oxidizes. This process degrades the wire, increases its resistance, and eventually leads to burnout. Sheathed tubular elements are a direct solution to this problem. Similarly, corrosion from moisture or chemicals is a primary concern in applications like water heating.
Hotspots and Burnout
Inconsistencies in a wire's composition or poor contact with terminals can create a hotspot—a small area that gets significantly hotter than the rest of the element. This localized overheating is a leading cause of premature failure.
Mechanical Stress and Embrittlement
Repeated heating and cooling cycles cause the element to expand and contract. This thermal cycling can alter the metal's grain structure over time, making it brittle and susceptible to fracture from vibration or shock.
Safety and Compliance
In any commercial or industrial application, elements must meet safety standards (like those from IEC) that govern insulation strength, leakage current, and creepage distance. These factors prevent electrical shock and ensure the element can be safely integrated into a larger system.
Selecting the Right Element for Your Application
Your choice depends entirely on your primary objective. By aligning the element's strengths with your application's demands, you ensure optimal performance and reliability.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, direct heating in open air: A simple wire or coil element offers the most straightforward solution.
- If your primary focus is durability and environmental protection: A sheathed tubular element is the standard for applications like water heating or industrial ovens.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability and uniform heat: A ceramic element is ideal for industrial furnaces and precision heating systems.
- If your primary focus is non-contact heating over an area: An infrared emitter is the correct choice for tasks like drying, curing, or targeted space heating.
By matching the element's fundamental design to its intended task, you ensure efficient, reliable, and safe thermal performance.
Summary Table:
| Design Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Wire/Coil | Simple, cost-effective, direct air heating | Household appliances, basic heaters |
| Tubular (Sheathed) | Durable, protected from moisture/corrosion | Water heaters, industrial ovens, grills |
| Ceramic | High-temperature stability, uniform heat | Kilns, soldering irons, infrared panels |
| Cartridge/Band | Cylindrical or clamp-on for specific shapes | Industrial dies, plastic injection molding |
| Infrared Emitters | Radiant heating, non-contact | Drying, curing, space heating |
| High-Temperature Furnace | Extreme heat resistance, specialized materials | Metallurgical furnaces above 1000°C |
Struggling to choose the right heating element for your lab or industrial setup? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all supported by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your thermal performance with reliable, efficient heating solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control



















