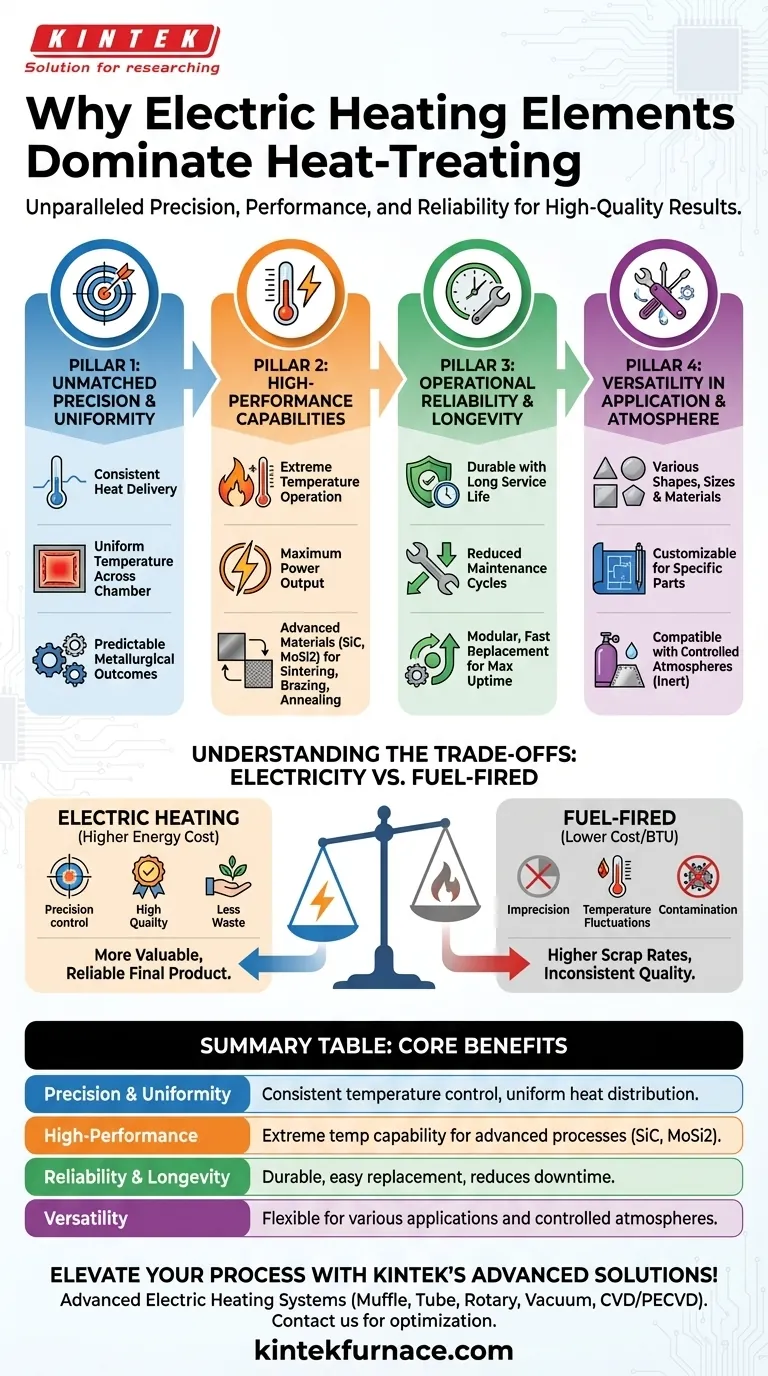
In the heat-treating industry, electric heating elements are popular because they offer an unparalleled combination of precision, high-temperature performance, and operational reliability. Their ability to deliver consistent, uniform heat is critical for achieving specific metallurgical properties, while their durability and ease of replacement minimize costly downtime.
The core reason for the prevalence of electric heating is not just one feature, but its ability to de-risk the entire heat-treating process. It provides the control and consistency necessary to produce high-quality, reliable end products, which is the ultimate goal of any heat-treatment operation.

The Core Pillars of Electric Heating in Heat Treatment
To understand why electric elements dominate, we must look at how their specific characteristics solve the core challenges of modifying metal properties through heat.
Pillar 1: Unmatched Precision and Temperature Uniformity
Electric elements provide exceptionally consistent and efficient heat delivery. This is not a minor convenience; it is fundamental to successful heat treatment.
By converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy at a controlled rate, these systems can maintain a very stable and uniform temperature across the entire furnace chamber.
This precision ensures that every part in a batch receives the exact same thermal cycle, eliminating inconsistencies and guaranteeing predictable metallurgical outcomes.
Pillar 2: High-Performance Capabilities
Modern heat-treating processes often demand extreme conditions. Electric heating elements are specifically engineered to meet these demands.
Materials like Silicon Carbide (SiC) and Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) are chosen for their ability to operate reliably at very high temperatures and deliver maximum power output.
This capability allows for processes like sintering, brazing, and annealing high-strength alloys that are impossible to achieve with less robust heating methods.
Pillar 3: Operational Reliability and Longevity
In an industrial setting, downtime is a significant cost driver. The design of electric heating elements directly addresses this concern.
They are known for their durability and long service life, reducing the frequency of maintenance cycles.
Furthermore, when a replacement is eventually needed, their modular nature makes the process straightforward and fast, maximizing furnace uptime and productivity.
Pillar 4: Versatility in Application and Atmosphere
No two heat-treating jobs are identical. Electric elements offer the flexibility needed to handle a wide range of applications.
Their availability in various shapes, sizes, and materials allows furnaces to be custom-designed for specific parts or processes.
Crucially, elements like MoSi2 are chemically inert and compatible with various controlled atmospheres (e.g., nitrogen, argon). This prevents unwanted reactions with the metal's surface, preserving its integrity and finish.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While electric heating offers clear advantages in control and quality, it's essential to understand its primary trade-off: energy cost.
Electricity vs. Fuel-Fired Systems
Direct-fired gas furnaces can sometimes offer a lower cost-per-BTU for energy. This can make them seem attractive for high-volume, less-sensitive bulk heating operations.
The Hidden Costs of Imprecision
However, the potential for temperature fluctuations and atmospheric contamination in fuel-fired systems can lead to higher scrap rates, rework, and inconsistent product quality.
The higher precision of electric heating often justifies a higher energy cost by yielding a more valuable and reliable final product with less waste.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be based on the specific priorities of your operation.
- If your primary focus is process precision and final product quality: The superior temperature uniformity and atmospheric control of electric heating are non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is operational flexibility for diverse alloys and processes: The material versatility and chemical inertness of electric elements provide a distinct advantage.
- If your primary focus is minimizing direct energy costs for bulk processes with wide tolerances: A fuel-fired system might be a consideration, but you must carefully weigh the risk of reduced product consistency.
Ultimately, electric heating elements are the industry standard because they empower engineers to achieve precise, repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Pillar | Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Precision & Uniformity | Consistent temperature control | Ensures uniform heat distribution for predictable metallurgical results. |
| High-Performance | Extreme temperature capability | Supports processes like sintering and annealing with materials like SiC and MoSi2. |
| Reliability & Longevity | Durable with easy replacement | Reduces downtime and maintenance costs in industrial settings. |
| Versatility | Flexible for various applications | Compatible with controlled atmospheres and customizable shapes and sizes. |
Elevate your heat-treating process with KINTEK's advanced solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-performance electric heating systems, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering unmatched precision, reliability, and efficiency. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your operations and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis



















