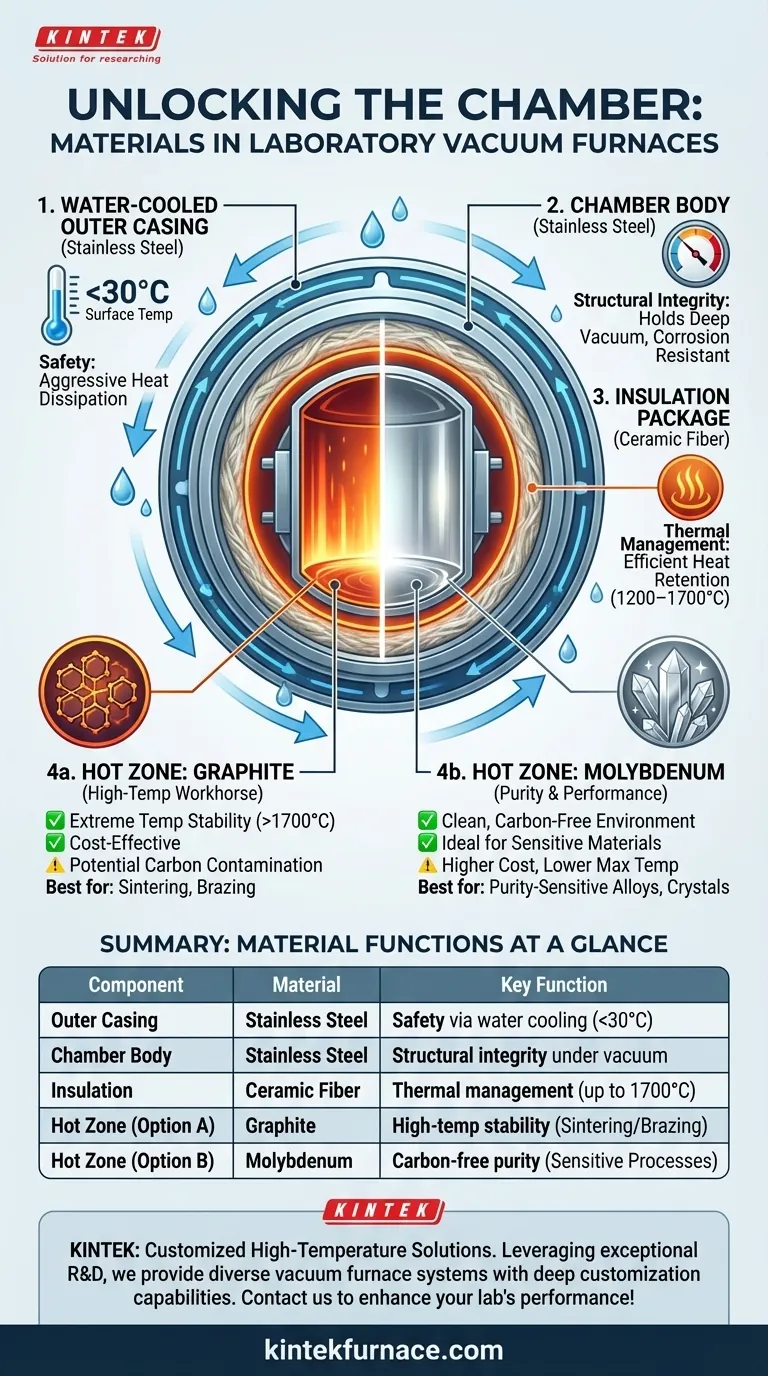
At the core of every laboratory vacuum furnace is a chamber constructed from a precise combination of materials designed to handle extreme conditions. These chambers primarily use a water-cooled stainless steel outer casing for safety, an inner structure often made of molybdenum or graphite for high-temperature work, and ceramic fiber insulation for thermal management. The specific material choice for the internal "hot zone" directly dictates the furnace's capabilities.
The selection of materials for a vacuum furnace chamber is a direct function of its intended operating temperature and the required chemical purity. Each component, from the internal hot zone to the external casing, is chosen to balance heat retention, structural integrity, and operator safety in an oxygen-free environment.

The Anatomy of a Vacuum Furnace Chamber
A laboratory vacuum furnace chamber is not a single piece of metal but a system of nested layers, each with a specific purpose. Understanding these layers is key to understanding the furnace's overall performance.
The Outer Casing: The First Line of Safety
The outermost layer of the chamber is a water-cooled casing, typically made of stainless steel. This component is non-negotiable for safety and system stability.
Its primary function is to circulate water to aggressively dissipate heat, keeping the external surface temperature below 30℃ (86°F). This ensures the furnace is safe for operators to be near even when the interior is at thousands of degrees.
The Chamber Body: Structural Integrity Under Vacuum
The main structural vessel responsible for holding the vacuum is built from stainless steel. This material is chosen for its excellent strength, durability, and corrosion resistance.
It must withstand the immense external atmospheric pressure when a deep vacuum is pulled inside, all while providing a clean, non-reactive boundary for the internal processing environment.
The Insulation Package: Managing Extreme Heat
Between the hot interior and the cooled outer wall lies a critical insulation package. This is most often composed of ceramic fiber.
This material is exceptionally effective at preventing heat from escaping the hot zone, which provides two major benefits: high energy efficiency and precise temperature control. It is rated for continuous use in the 1200–1700℃ range, making it ideal for a wide array of thermal processes.
Inside the Hot Zone: Materials for Extreme Temperatures
The "hot zone" is the heart of the furnace where the actual heating takes place. The material choice here is the most critical factor determining the furnace's performance limits and application suitability. The two most common options are graphite and molybdenum.
Graphite: The High-Temperature Workhorse
For applications requiring very high temperatures, graphite is the standard material for the chamber's interior walls and heating elements.
Graphite possesses incredible thermal stability and actually becomes stronger as it gets hotter, making it perfect for the most demanding processes. It is often the choice for applications pushing beyond 1700℃.
Molybdenum: Purity and Performance
For processes where chemical purity is paramount, the hot zone is constructed from or lined with molybdenum. This refractory metal offers a very "clean" heating environment.
Molybdenum is used when the material being processed is sensitive to carbon. Using a graphite chamber in such cases could lead to carbon contamination, altering the material's properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Graphite vs. Molybdenum
The decision between a graphite and a molybdenum hot zone is a fundamental choice based on your specific scientific or production goals. Neither is universally "better"; they serve different needs.
When to Choose Graphite
Graphite is preferred for its superior high-temperature capability and generally lower cost. It is the go-to material for processes like sintering, brazing, and heat treating where slight carbon interaction is not a concern.
The primary trade-off is the potential for carbon contamination. The high-temperature vacuum environment can cause carbon from the chamber to transfer to the sample, which is unacceptable for certain alloys, ceramics, and crystals.
When to Choose Molybdenum
A molybdenum hot zone is chosen when cleanliness is the top priority. It creates an all-metal, carbon-free environment essential for processing reactive or high-purity materials.
The trade-offs for this purity are a typically lower maximum operating temperature compared to graphite and a significantly higher initial cost. Molybdenum is also more susceptible to oxidation if the vacuum is compromised.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of chamber material must align directly with the requirements of the materials you intend to process.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures for processes like sintering or graphitizing: A graphite-based hot zone is the industry standard for its thermal robustness and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive alloys or materials where carbon contamination is unacceptable: A molybdenum-lined hot zone is the necessary choice to ensure the chemical purity of your final product.
- If your primary focus is safety and structural integrity regardless of the hot zone: A furnace built with a water-cooled stainless steel outer casing is the essential foundation for any reliable system.
Understanding these material choices empowers you to select or specify a furnace that precisely matches the technical demands of your research or production.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Key Function |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Casing | Stainless Steel | Safety via water cooling, keeps surface below 30°C |
| Chamber Body | Stainless Steel | Structural integrity under vacuum, corrosion resistance |
| Insulation | Ceramic Fiber | Thermal management, efficient heat retention up to 1700°C |
| Hot Zone | Graphite | High-temperature stability, ideal for sintering and brazing |
| Hot Zone | Molybdenum | Carbon-free environment, essential for purity-sensitive processes |
Need a Customized High-Temperature Solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced vacuum furnace systems. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements for temperature, purity, and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- Why is a high-vacuum environment necessary for sintering Cu/Ti3SiC2/C/MWCNTs composites? Achieve Material Purity
- What is the role of vacuum pumps in a vacuum heat treatment furnace? Unlock Superior Metallurgy with Controlled Environments
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement



















