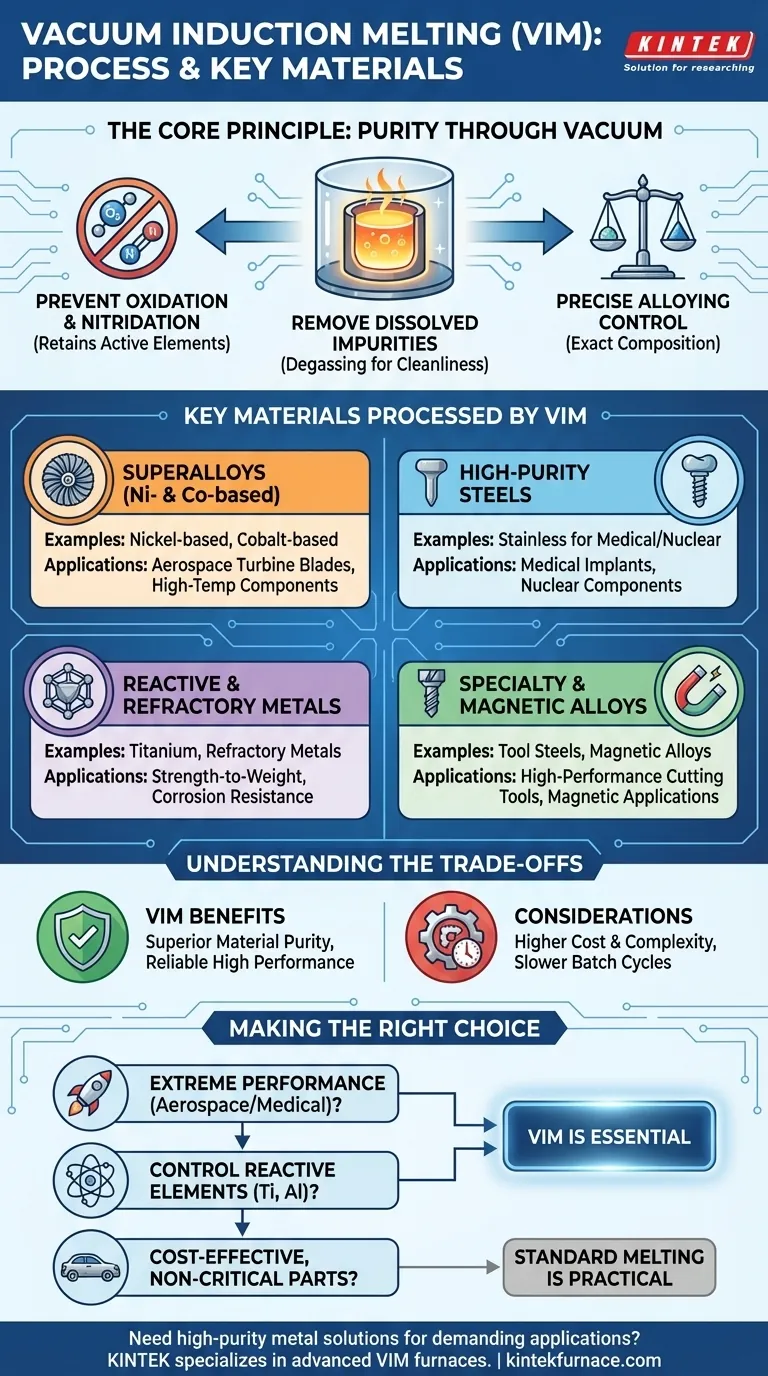
At its core, vacuum induction melting (VIM) is reserved for creating the highest-purity metals and alloys where even trace atmospheric contamination is unacceptable. It is the go-to process for materials destined for extreme environments, including nickel- and cobalt-based superalloys, high-purity stainless steels for medical or nuclear use, reactive metals like titanium, and specialty magnetic alloys. The common thread is a non-negotiable need for superior material properties, cleanliness, and precise chemical control.
The decision to use vacuum induction melting is driven less by the base metal and more by the final application's demand for purity. VIM is chosen when the goal is to eliminate reactions with air and remove dissolved gas impurities, creating a metallurgically clean material that other methods cannot produce.
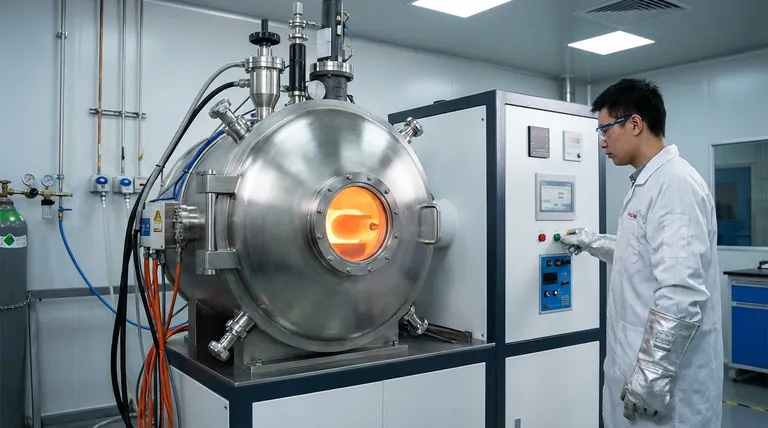

Why Vacuum is the Critical Component
The "vacuum" in VIM is not just an environmental condition; it is an active refining tool. By melting material inside a low-pressure chamber, the process fundamentally changes how the metal behaves, preventing contamination and actively improving its quality.
Preventing Oxidation and Nitridation
Many high-performance alloys contain active elements like titanium, aluminum, and chromium. When melted in air, these elements rapidly react with oxygen and nitrogen, forming brittle oxide and nitride inclusions.
A vacuum removes these reactive gases from the environment. This ensures the valuable alloying elements remain in the metallic solution, contributing to the final properties as intended, rather than being lost as defects.
Removing Dissolved Impurities
Molten metals can hold dissolved gases like oxygen, nitrogen, and hydrogen, which become trapped during solidification, creating porosity and degrading mechanical properties. The low-pressure environment of VIM essentially pulls these dissolved gases out of the melt.
This degassing action is a form of refining that also removes other undesirable elements with high vapor pressures (like lead or bismuth), resulting in an exceptionally clean and dense final product.
Enabling Precise Alloying Control
With no atmosphere to react with, every gram of an alloying element added to the melt is precisely accounted for. This allows for the creation of alloys with extremely tight chemical specifications.
This level of control is impossible in an air-melt furnace, where a portion of the additives would be unpredictably lost to oxidation.
Key Material Categories Processed by VIM
The need for purity and precision dictates which materials benefit most from the VIM process. These are typically materials where performance failure is not an option.
Superalloys (Nickel and Cobalt-based)
These are the primary materials processed by VIM. Used for aerospace jet engine turbine blades and high-temperature industrial components, their strength relies on precise amounts of reactive elements.
VIM is essential to prevent the formation of oxide inclusions that would act as crack initiation sites under extreme stress and heat, leading to catastrophic failure.
High-Purity and Stainless Steels
For applications like medical implants (biocompatibility) and nuclear components (corrosion resistance), material cleanliness is paramount.
VIM removes inclusions that could cause localized corrosion or act as stress risers. This results in steels with superior fatigue life, purity, and corrosion resistance compared to their air-melted counterparts.
Reactive and Refractory Metals
Metals like titanium are highly reactive and will readily absorb oxygen and nitrogen from the air when molten, becoming brittle and useless.
VIM provides the inert environment necessary to melt and alloy these materials without contamination, preserving their desirable properties like strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
Specialty and Magnetic Alloys
The performance of materials like tool steels, high-speed steels, and specific magnetic alloys is acutely sensitive to their chemical composition and internal structure.
VIM delivers the ultra-low gas content and compositional accuracy needed to achieve specific magnetic permeability or the extreme hardness and wear resistance required for high-performance cutting tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While VIM produces superior materials, it is not a universal solution. Its benefits come with practical and economic considerations.
The Cost and Complexity Factor
VIM furnaces are complex systems requiring vacuum pumps, sealed chambers, and sophisticated controls. This makes the equipment significantly more expensive to build, operate, and maintain than standard air-melt furnaces.
Batch Size and Cycle Time
The process is inherently slower than air melting due to the time required to pump down the vacuum chamber before melting and cool the ingot under vacuum after. Furthermore, the size of the vacuum chamber limits the total weight (batch size) of each melt.
When VIM is Overkill
For general manufacturing, automotive components, or structural steels where standard performance is sufficient and cost is a primary driver, VIM is unnecessary. Simpler, more economical methods like standard induction melting or electric arc furnace melting are perfectly suitable for these applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melting process requires aligning the material's end-use requirements with the capabilities and costs of the technology.
- If your primary focus is extreme performance and purity (aerospace, medical, nuclear): VIM is the only process that can reliably deliver the required material integrity and cleanliness.
- If your primary focus is controlling reactive elements (like Ti or Al) in an alloy: VIM is essential to prevent the loss of these elements to oxidation and ensure they contribute to the alloy's properties.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production for less critical parts: Standard air-induction or electric arc melting is the more practical and economical choice.
Ultimately, choosing VIM is a deliberate investment in achieving the highest possible material quality, ensuring performance and reliability where it matters most.
Summary Table:
| Material Category | Key Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Superalloys | Nickel- and cobalt-based alloys | Aerospace turbine blades, high-temperature components |
| High-Purity Steels | Stainless steels for medical/nuclear use | Medical implants, nuclear components |
| Reactive Metals | Titanium, refractory metals | Applications requiring strength-to-weight and corrosion resistance |
| Specialty Alloys | Tool steels, magnetic alloys | High-performance cutting tools, magnetic applications |
Need high-purity metal solutions for demanding applications? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnaces, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, tailored for vacuum induction melting. Our expertise in R&D and in-house manufacturing ensures deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs, delivering superior material purity and performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your projects with reliable, precision-engineered solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries



















