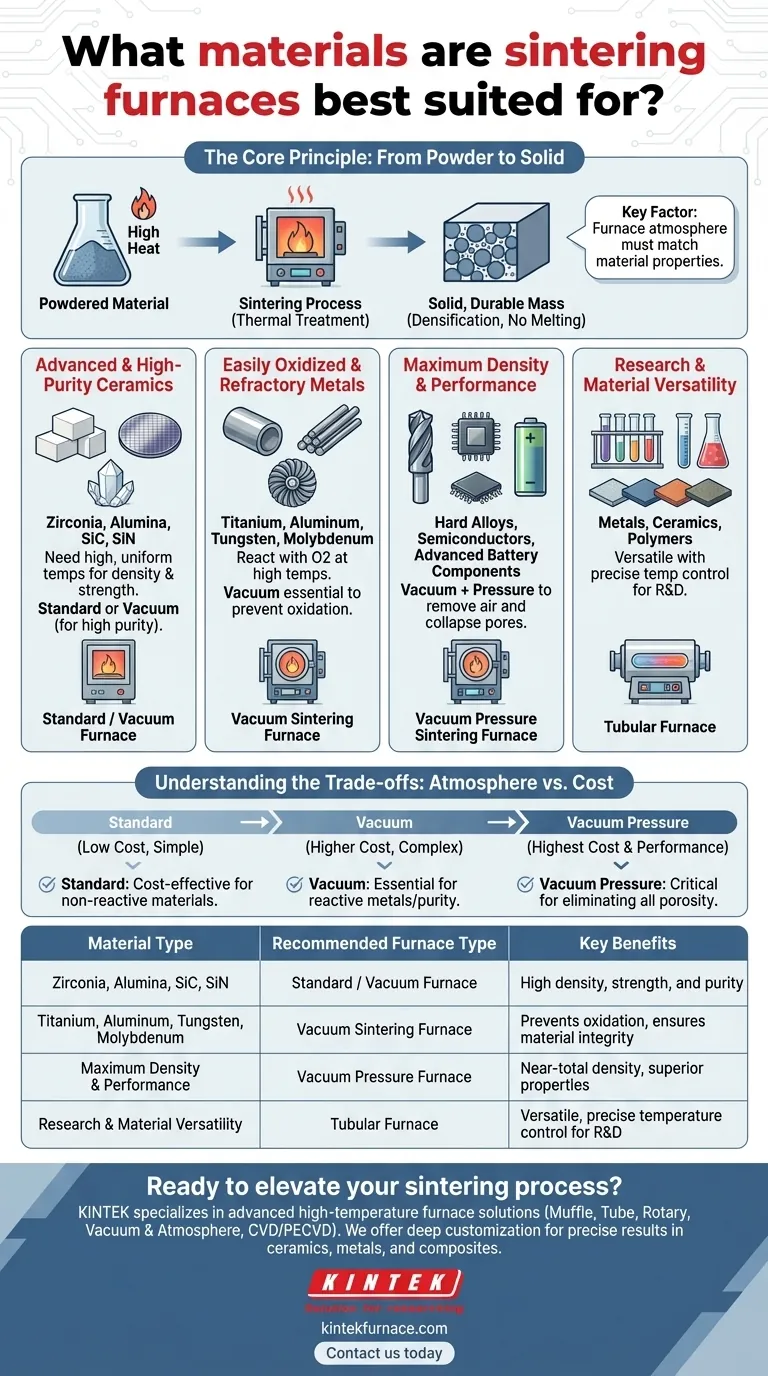
In essence, sintering furnaces are best suited for compacting powdered materials into a solid, durable mass using high heat. This process is fundamental for a wide range of materials, most notably advanced ceramics like zirconia, metals and alloys like titanium and stainless steel, and specialized composites used in semiconductor and battery production. The key is that the material is heated to just below its melting point, allowing the particles to fuse together.
The critical factor is not just the material itself, but the specific type of furnace used. The choice between a standard, vacuum, or pressure-assisted furnace depends entirely on the material's chemical properties, especially its tendency to react with air at high temperatures.
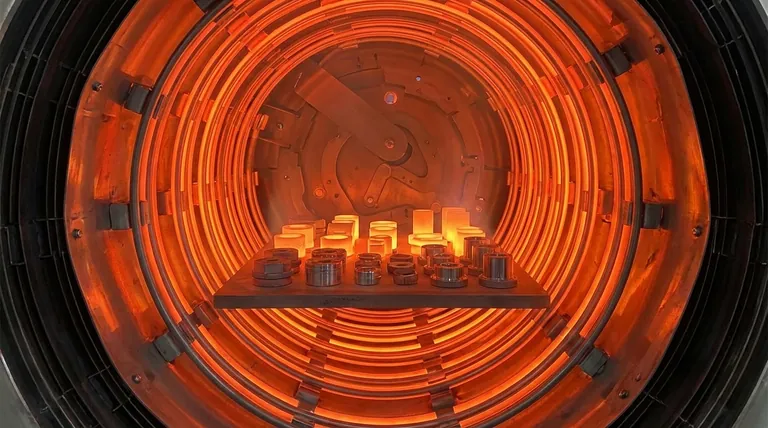

The Core Principle: From Powder to Solid
The Sintering Process
Sintering is a thermal treatment that applies heat to a powdered material to induce densification and create a solid object.
Unlike melting, the material never becomes fully liquid. Instead, the high temperature causes the atoms in the powder particles to diffuse across their boundaries, fusing them together and gradually eliminating the gaps between them.
The result is a strong, dense part with specific, desirable properties that are often impossible to achieve through casting or machining.
Matching the Furnace to the Material
The specific type of sintering furnace dictates which materials can be processed successfully. The primary differentiator is the furnace's internal atmosphere, which prevents unwanted chemical reactions.
For Advanced and High-Purity Ceramics
Materials like zirconia, alumina, silicon carbide, and silicon nitride are prime candidates for sintering. They require very high and uniform temperatures to achieve optimal density and strength.
While some can be processed in standard high-temperature furnaces, a vacuum environment is often preferred to produce high-purity, high-density parts for demanding applications.
For Easily Oxidized and Refractory Metals
This is where vacuum sintering furnaces are essential. Metals like titanium, aluminum, tungsten, and molybdenum, as well as superalloys and certain stainless steels, react readily with oxygen at high temperatures.
Sintering these materials in a normal atmosphere would result in oxidation, making them weak and brittle. A vacuum removes the oxygen, preserving the metal's integrity and allowing for proper fusion.
For Maximum Density and Performance
Applications requiring the absolute highest density and strength, such as hard alloys, semiconductor materials (e.g., silicon wafers), and advanced battery components (e.g., solid-state electrolytes), often use a vacuum pressure sintering furnace.
This technology first uses a vacuum to remove air and impurities. Then, it applies high inert gas pressure during the process, which physically helps collapse any remaining pores to achieve near-total density.
For Research and Material Versatility
Tubular furnaces are highly valued in both research and small-scale industrial settings for their versatility and precise temperature control.
They can accommodate a wide range of materials, including metals, ceramics, and even some polymers, making them ideal for developing new materials and testing different sintering parameters before scaling up production.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Atmosphere vs. Cost
The most important decision when choosing a sintering process revolves around the furnace's atmosphere, which directly impacts cost and complexity.
The Standard Approach
Sintering in a normal air atmosphere or with a simple inert gas purge is the most straightforward and cost-effective method. This is suitable for materials that are not reactive with oxygen, such as many common ceramics.
The Investment in Vacuum
A vacuum furnace is a significant investment. Its complexity is higher, but it is the only way to successfully process reactive metals or achieve the ultra-high purity required for semiconductor and medical applications. The vacuum environment is non-negotiable for these materials.
The Peak Performance of Pressure
Adding pressure capabilities to a vacuum furnace further increases cost and complexity. However, for applications where eliminating all porosity is critical to performance—such as in cutting tools or high-wear components—this investment is necessary to achieve superior material properties.
Selecting the Right Furnace for Your Goal
Your choice of furnace should be guided directly by your material and your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is processing non-reactive ceramics: A standard high-temperature furnace is often a cost-effective and sufficient solution.
- If your primary focus is processing reactive or refractory metals: A vacuum sintering furnace is essential to prevent oxidation and ensure material integrity.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and purity: A vacuum pressure sintering furnace is the ideal choice for demanding applications like hard alloys or advanced composites.
- If your primary focus is research and development with diverse materials: A versatile tubular furnace provides the precise control needed for experimentation and process validation.
Ultimately, selecting the right sintering furnace is about matching its atmospheric control to your material's specific chemical and physical requirements.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Recommended Furnace Type | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Ceramics (e.g., Zirconia, Alumina) | Standard or Vacuum Furnace | High density, strength, and purity |
| Reactive Metals (e.g., Titanium, Tungsten) | Vacuum Furnace | Prevents oxidation, ensures material integrity |
| High-Performance Alloys & Composites | Vacuum Pressure Furnace | Near-total density, superior properties |
| Research Materials (e.g., Metals, Ceramics, Polymers) | Tubular Furnace | Versatile, precise temperature control for R&D |
Ready to elevate your sintering process? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed to deliver precise results for materials like ceramics, metals, and composites. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure your unique experimental requirements are met efficiently. Contact us today to discuss how we can help optimize your sintering applications and boost your productivity!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum heat treatment furnace play in TBC post-processing? Enhance Coating Adhesion
- What is the purpose of a 1400°C heat treatment for porous tungsten? Essential Steps for Structural Reinforcement
- What are the benefits of using a high-temperature vacuum furnace for the annealing of ZnSeO3 nanocrystals?
- What is the purpose of setting a mid-temperature dwell stage? Eliminate Defects in Vacuum Sintering
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness



















