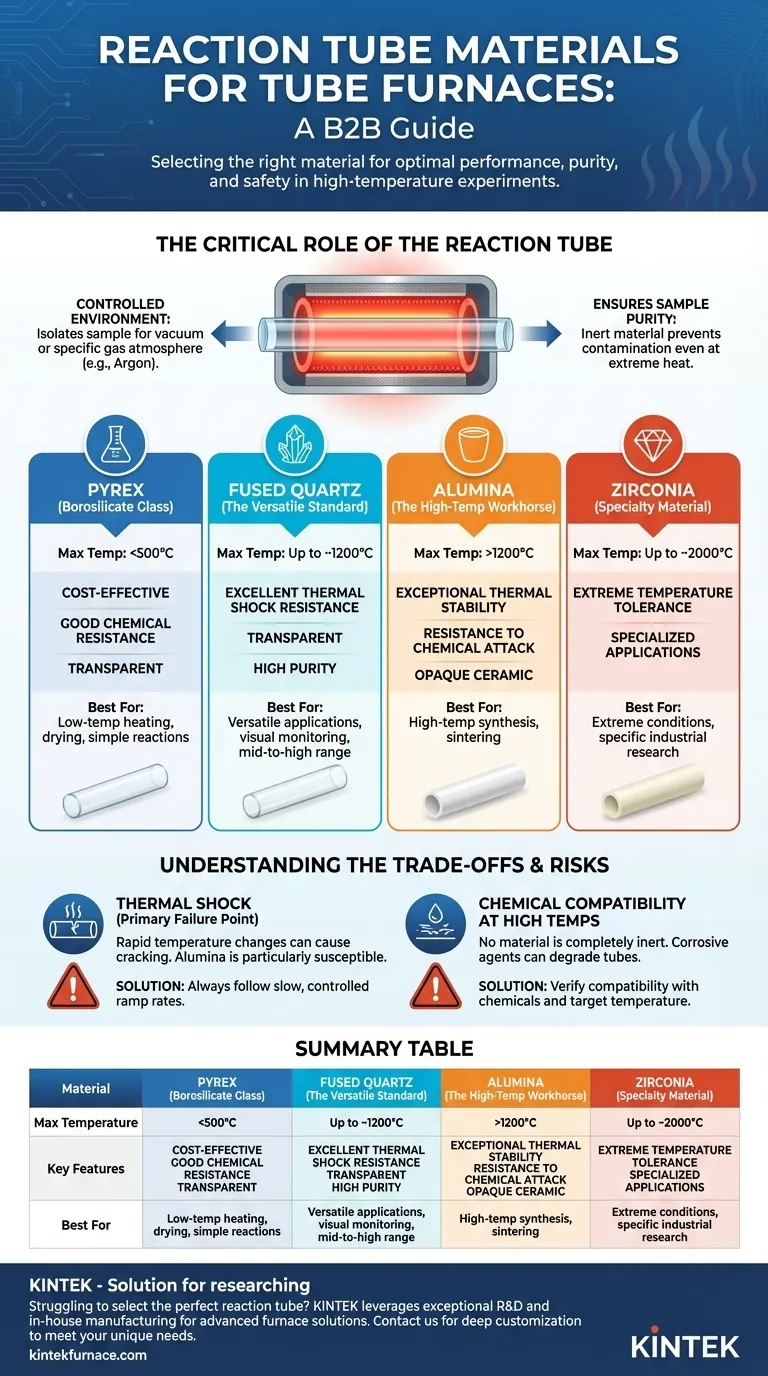
The most common materials for reaction tubes in a tube furnace are alumina, fused quartz, and Pyrex. Each material is selected based on its unique tolerance for temperature, resistance to chemical corrosion, and ability to handle thermal shock, which dictates its suitability for specific laboratory and industrial processes like melting metals, growing crystals, or annealing materials.
Choosing the right reaction tube is a critical decision based on your experiment's maximum temperature. While Pyrex suits lower temperatures and quartz offers a versatile mid-to-high range, alumina is the standard for very high-temperature applications, despite its sensitivity to rapid temperature changes.

The Critical Role of the Reaction Tube
A tube furnace's effectiveness hinges entirely on the performance of its reaction tube. This component is more than just a container; it is the core of the experimental environment.
Creating a Controlled Environment
The primary function of the tube is to isolate the sample from the outside world. It allows you to create a controlled atmosphere—whether a vacuum, an inert gas like argon, or a specific reactive gas—that is essential for the process.
Ensuring Sample Purity
The tube material must be inert and not react with your sample, even at extreme temperatures. A well-chosen tube prevents contamination and ensures the integrity of your results.
A Breakdown of Common Tube Materials
Each material offers a different balance of thermal performance, chemical resistance, and physical properties.
Alumina (Corundum): The High-Temperature Workhorse
Alumina is required for processes demanding very high temperatures, typically above 1200°C. It is a dense, opaque ceramic known for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical attack.
Due to its high purity, alumina is an excellent choice for preventing sample contamination in high-temperature synthesis and sintering applications.
Fused Quartz: The Versatile Standard
Fused quartz is the most common and versatile choice for a wide range of applications up to approximately 1200°C. Its key advantage is its outstanding resistance to thermal shock, meaning it can withstand rapid temperature changes far better than alumina.
Its optical transparency also allows for direct visual monitoring of the process, which can be invaluable. Quartz maintains high purity and excellent chemical stability across its operational range.
Pyrex (Borosilicate Glass): For Low-Temperature Applications
Pyrex is a cost-effective option for lower-temperature work, generally below 500°C. While it has good chemical resistance, it cannot handle the high temperatures that quartz and alumina can. It is best suited for simple heating, drying, or low-temperature reactions where budget is a primary consideration.
Specialty Materials: Zirconia
For extreme conditions, such as temperatures approaching 2000°C (3600°F), specialized materials like zirconia are necessary. These are reserved for highly specific industrial or research applications where conventional materials would fail.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material is not just about maximizing performance; it's about understanding the limitations and potential failure points.
Thermal Shock: The Primary Failure Point
Thermal shock—cracking caused by rapid heating or cooling—is the most common cause of tube failure. Alumina is particularly susceptible to this. Heating or cooling an alumina tube too quickly will likely cause it to break.
To mitigate this risk, always follow a slow and controlled temperature ramp rate. As a rule, smaller-diameter tubes handle thermal gradients better and are less prone to thermal shock than larger ones.
Chemical Compatibility at High Temperatures
While these materials are highly resistant, no material is completely inert under all conditions. Highly corrosive agents at extreme temperatures can still degrade the tube. Always verify the compatibility of your specific chemicals with the tube material at your target operating temperature.
How to Select the Right Tube for Your Process
Make your selection based on a clear understanding of your process requirements.
- If your process is below 500°C and requires simple heating: Pyrex is often a cost-effective and suitable choice.
- If you require high temperatures (up to ~1200°C) and excellent thermal shock resistance: Fused quartz is the most versatile and reliable option, especially if visual observation is needed.
- If you are working at very high temperatures (above 1200°C) and can manage slow ramp rates: Alumina is the necessary material for achieving maximum thermal stability.
- If your application exceeds 1800°C: You must investigate specialty materials like Zirconia to ensure operational safety and success.
Ultimately, matching the material's properties to your specific temperature, chemical, and operational requirements is the key to achieving safe and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature | Key Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Alumina | >1200°C | High thermal stability, chemical resistance | High-temperature synthesis, sintering |
| Fused Quartz | Up to 1200°C | Excellent thermal shock resistance, transparent | Versatile applications, visual monitoring |
| Pyrex | Below 500°C | Cost-effective, good chemical resistance | Low-temperature heating, drying |
| Zirconia | Up to 2000°C | Extreme temperature tolerance | Specialized high-temperature processes |
Struggling to select the perfect reaction tube for your high-temperature experiments? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we tailor our products to meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring optimal performance and purity. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can enhance your lab's efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















