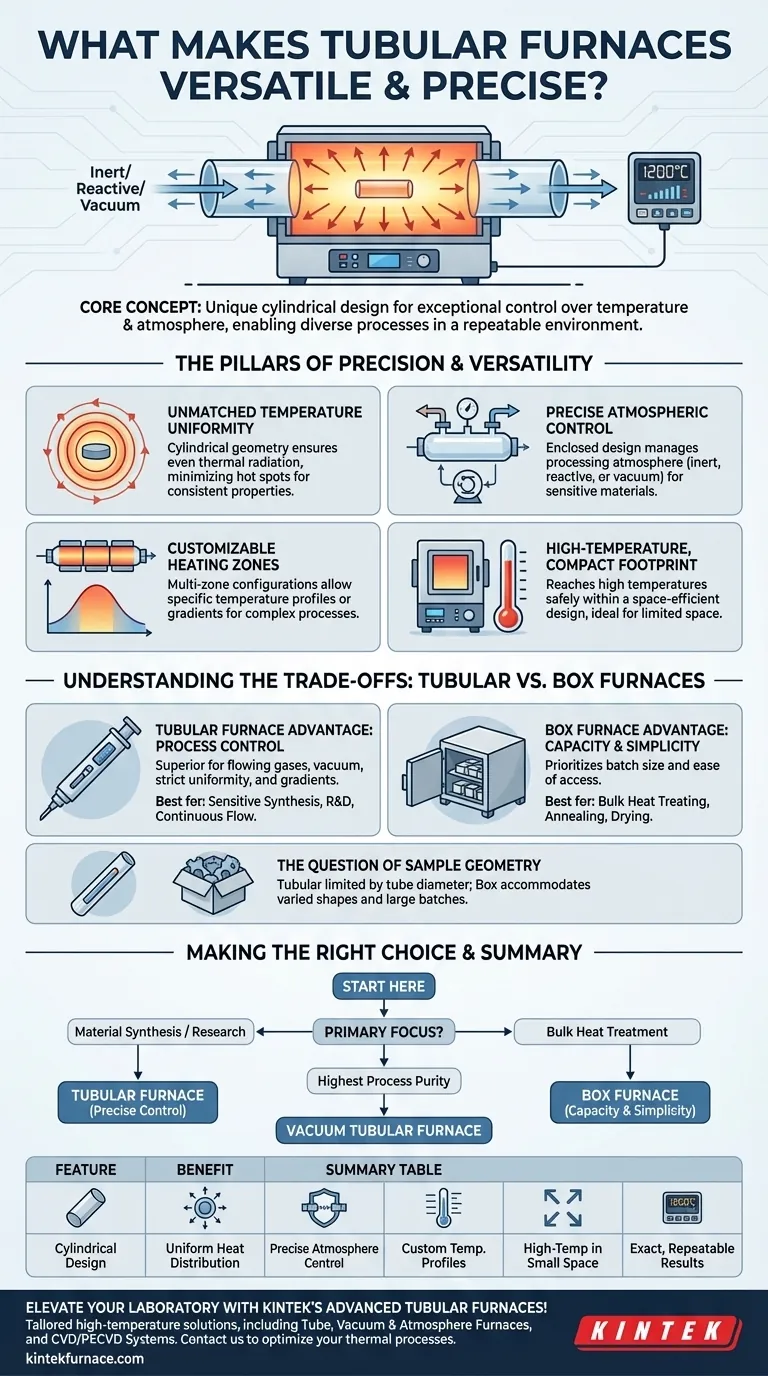
At its core, a tubular furnace's versatility and precision stem from its unique design, which enables exceptional control over both temperature and atmosphere. Its cylindrical heating chamber ensures highly uniform heat distribution, while advanced digital controllers maintain exact temperature setpoints. This combination allows for a wide range of sophisticated thermal processes to be conducted in a compact, repeatable, and controlled environment.
The defining advantage of a tubular furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its power to create a highly specific, isolated, and uniform processing environment. This control over atmosphere and temperature uniformity is what separates it from other furnace types and makes it indispensable for sensitive material processing.

The Pillars of Precision and Versatility
A tubular furnace is more than a simple heater; it is a carefully engineered system where each component contributes to its overall performance. Understanding these pillars reveals why it is a go-to instrument for both research and specialized industrial applications.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
The cylindrical geometry of a tubular furnace is its most fundamental advantage. The heating elements surround the process tube, ensuring that thermal radiation is applied evenly from all directions.
This design minimizes hot spots and temperature gradients across the sample, a critical factor for achieving consistent material properties, crystal growth, or reaction kinetics.
Precise Atmospheric Control
The enclosed tube design is perfectly suited for managing the processing atmosphere, a capability most other furnace types lack.
The tube can be sealed and connected to gas handling systems, allowing users to introduce inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation, reactive gases for chemical processes, or apply a vacuum for purification and degassing.
Customizable Heating Zones
Many advanced tubular furnaces are available in multi-zone configurations. Each zone is independently controlled by its own thermocouple and controller.
This allows an operator to create a specific temperature profile or gradient along the length of the tube. Such control is essential for sophisticated processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD) or zone refining.
High-Temperature Capability in a Compact Footprint
Tubular furnaces are engineered to reach very high temperatures safely and efficiently within a relatively small, space-efficient design.
This makes them ideal for research laboratories or production lines where floor space is at a premium but high-temperature processing is non-negotiable.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Tubular vs. Box Furnaces
To truly appreciate the tubular furnace's role, it's helpful to compare it to the other common laboratory workhorse: the box furnace. Their differences highlight their distinct use cases.
The Tubular Furnace Advantage: Process Control
A tubular furnace excels at process control. If your work involves flowing gases, vacuum, strict temperature uniformity, or temperature gradients, it is the superior choice.
It is best suited for sensitive material synthesis, small-batch R&D, and continuous-flow reactions where the environment is as important as the heat.
The Box Furnace Advantage: Capacity and Simplicity
A box furnace prioritizes batch size and ease of access. Its large, open chamber and swing-out or vertical lift door make it easy to load and unload bulky or numerous samples.
Its simple design makes it versatile for general-purpose heat treating, annealing, and drying, where precise atmospheric control is not the primary requirement.
The Question of Sample Geometry
The most practical distinction is sample shape and size. A tubular furnace is, by definition, limited to samples that can fit within the process tube's diameter.
A box furnace, on the other hand, can accommodate a wide variety of shapes and sizes, making it the practical choice for irregularly shaped parts or large batches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace requires a clear understanding of your primary processing goal. The right tool depends entirely on the task at hand.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis or research: A tubular furnace is superior due to its precise atmospheric and temperature gradient control.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat treatment or processing large items: A box furnace offers better capacity, easier loading, and operational simplicity for less atmosphere-sensitive tasks.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest process purity: Prioritize a vacuum-capable tubular furnace built with corrosion-resistant materials to ensure process integrity.
Ultimately, selecting the correct furnace requires matching the equipment's core strengths to the specific demands of your process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Cylindrical Design | Ensures uniform heat distribution, minimizing hot spots |
| Enclosed Tube | Allows precise control of atmosphere (inert, reactive, vacuum) |
| Multi-Zone Heating | Enables custom temperature profiles for complex processes |
| Compact Footprint | Provides high-temperature capability in space-efficient setups |
| Digital Controllers | Maintains exact temperature setpoints for repeatable results |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced tubular furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line, including Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is enhanced by deep customization to meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our precise and versatile furnaces can optimize your thermal processes and drive innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















