For applications involving platinum group metals (PGMs), induction furnaces are uniquely suitable due to their ability to provide an exceptionally clean melting environment combined with precise, repeatable temperature control. This combination is critical for preserving the inherent purity and high value of materials like platinum, iridium, and rhodium, which have no tolerance for the contamination or temperature variance common in other smelting methods.
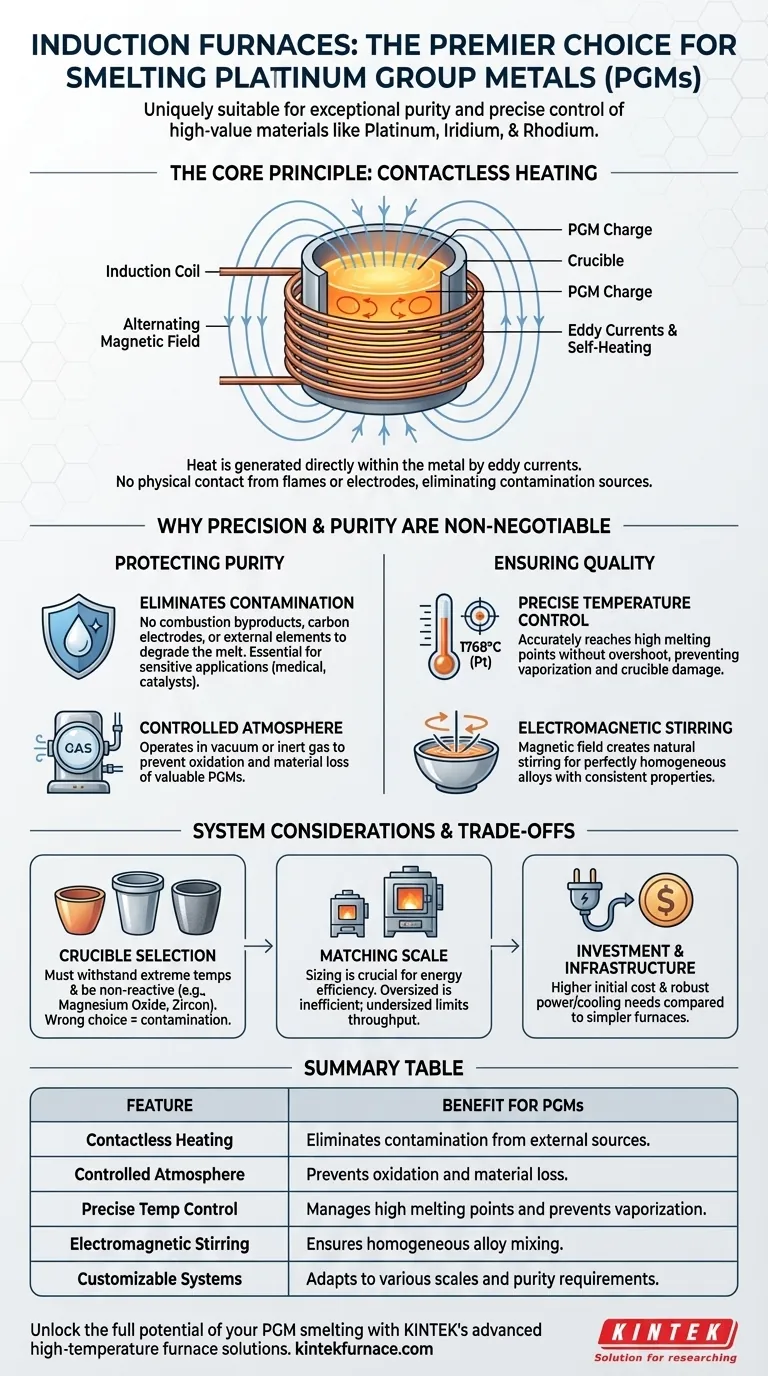
The suitability of induction furnaces for PGMs stems from their core technology: electromagnetic induction. By heating the metal directly without any physical contact from a flame or electrode, this process inherently eliminates major sources of contamination while enabling the surgical precision required to manage the unique properties of these valuable metals.

The Core Principle: How Induction Heating Protects Purity
The primary advantage of an induction furnace lies in its fundamental mechanism. Understanding this principle clarifies why it is the superior choice for materials where purity is paramount.
Direct, Contactless Heating
An induction furnace uses a powerful, alternating magnetic field generated by a copper coil. This field induces strong electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the conductive PGM charge inside the crucible. The metal’s own electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and efficiently, essentially turning the metal into its own heating element.
Eliminating Contamination Sources
Unlike fuel-fired or arc furnaces, the induction process involves no combustion byproducts, carbon electrodes, or external heating elements that can degrade and introduce impurities into the melt. This clean heating is essential for PGMs used in sensitive applications like medical equipment and chemical catalysts, where even trace contamination can lead to failure.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
Because there is no need for oxygen to support combustion, induction furnaces can operate with a tightly controlled atmosphere. This allows for melting in a vacuum or under a blanket of inert gas, which is crucial for preventing the oxidation of the valuable metals and any alloying elements present.
Why Precision Is Non-Negotiable for PGMs
Platinum group metals are not only valuable but also possess challenging metallurgical properties. Their high melting points and sensitivity to temperature deviations demand a level of control that induction technology is uniquely positioned to deliver.
The Critical Role of Temperature Control
PGMs like platinum and iridium have extremely high melting points (1768°C and 2446°C, respectively). Induction systems allow for precise power input, enabling operators to reach and hold these target temperatures without overshooting, which could vaporize valuable material or damage the crucible.
Ensuring Homogeneous Alloys
The magnetic field that heats the metal also creates a natural stirring action within the molten bath. This electromagnetic stirring ensures that all elements are distributed evenly, resulting in a perfectly homogeneous alloy. This is critical for applications where consistent material properties are a requirement.
Preventing Material Loss
Precise control over temperature and a sealed environment dramatically reduce losses from oxidation and vaporization. When dealing with some of the most expensive materials on earth, minimizing these losses has a direct and significant impact on profitability.
Understanding the Trade-offs and System Components
While highly effective, an induction furnace is a system. Its performance is dependent on correctly matching its components to the application and understanding its operational requirements.
The Critical Choice of Crucible
The furnace itself is only one part of the equation. The crucible—the vessel that holds the molten metal—is equally important. It must be able to withstand extreme temperatures and be chemically non-reactive with the specific PGM being melted. For platinum and steel, materials like magnesium oxide, zircon, and corundum are often required. Using the wrong crucible will lead to melt contamination or catastrophic failure.
Matching Furnace to Scale
Induction furnaces are available in a wide range of capacities, from small tabletop units melting a few kilograms to large industrial systems handling hundreds. Sizing the furnace correctly for your typical batch size is essential for achieving optimal energy efficiency and melt times. An oversized furnace is inefficient for small melts, while an undersized one limits throughput.
Initial Cost and Infrastructure
The initial capital investment for an induction furnace system can be higher than for simpler fuel-fired furnaces. They also require robust electrical infrastructure to provide the necessary power and often incorporate water-cooling systems to manage heat in the induction coils, which adds to system complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right smelting technology requires aligning its capabilities with your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum purity and alloy precision: The non-contact heating and controlled atmosphere of an induction furnace are essential for applications in the medical, aerospace, and catalyst industries.
- If your primary focus is jewelry manufacturing: Induction provides the control needed to maintain precise color, prevent the loss of valuable material, and ensure the consistent quality required for high-end products.
- If your primary focus is scaling production efficiently: Ensure you select an induction furnace and crucible system appropriately sized for your batch requirements to maximize energy efficiency and throughput.
By understanding these principles, you can confidently leverage induction technology to master the precise and demanding process of working with platinum group metals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit for PGMs |
|---|---|
| Contactless Heating | Eliminates contamination from external sources |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Prevents oxidation and material loss |
| Precise Temperature Control | Manages high melting points and prevents vaporization |
| Electromagnetic Stirring | Ensures homogeneous alloy mixing |
| Customizable Systems | Adapts to various scales and purity requirements |
Unlock the full potential of your platinum group metal smelting with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with induction furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior purity, efficiency, and cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your metal processing operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability



















