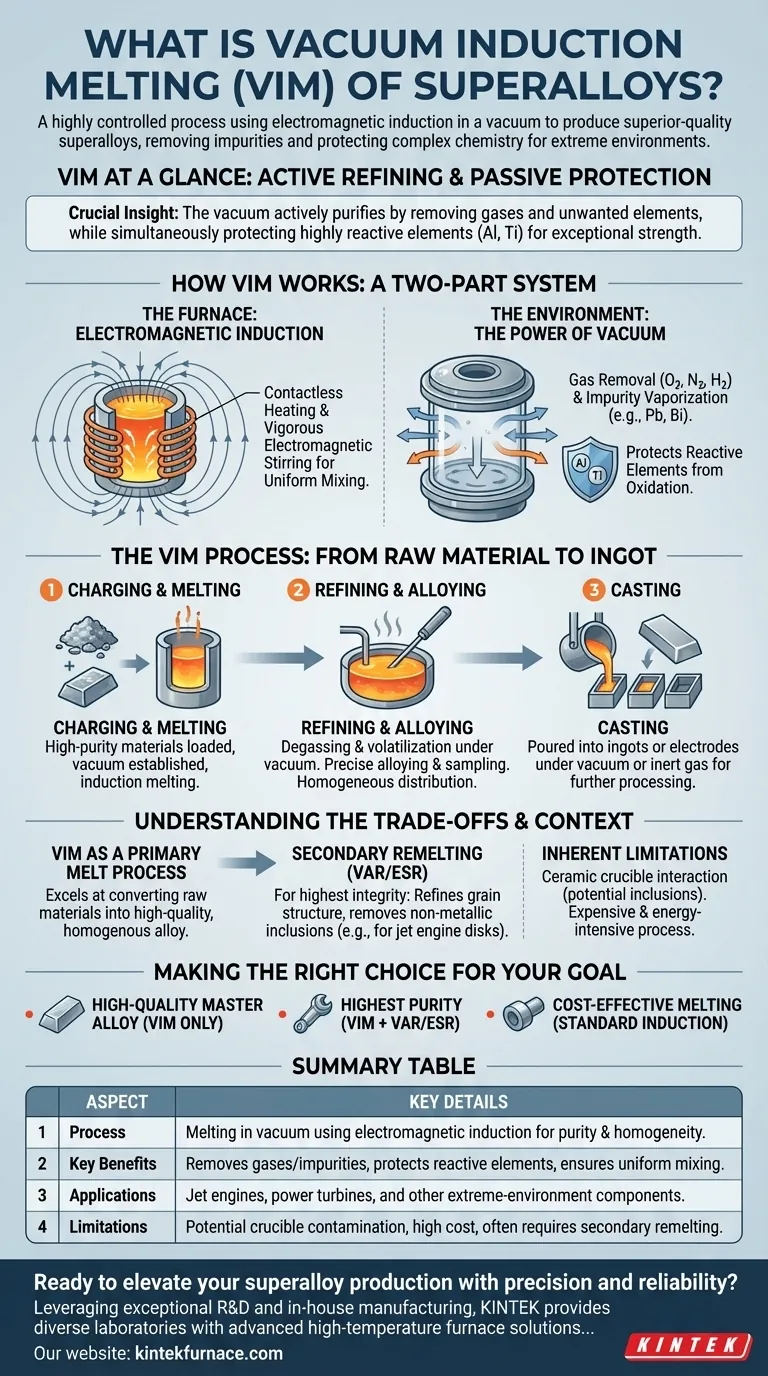
In essence, Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) is a highly controlled process for producing superior-quality superalloys by melting raw materials inside a vacuum chamber using electromagnetic induction. This method removes impurities and protects the precise, complex chemistry required for materials that must perform in extreme environments like jet engines and power generation turbines.
The crucial insight is that the vacuum is not just a passive shield, but an active refining tool. It purifies the metal by removing dissolved gases and unwanted elements while simultaneously protecting the highly reactive elements, like aluminum and titanium, that give superalloys their exceptional strength at high temperatures.
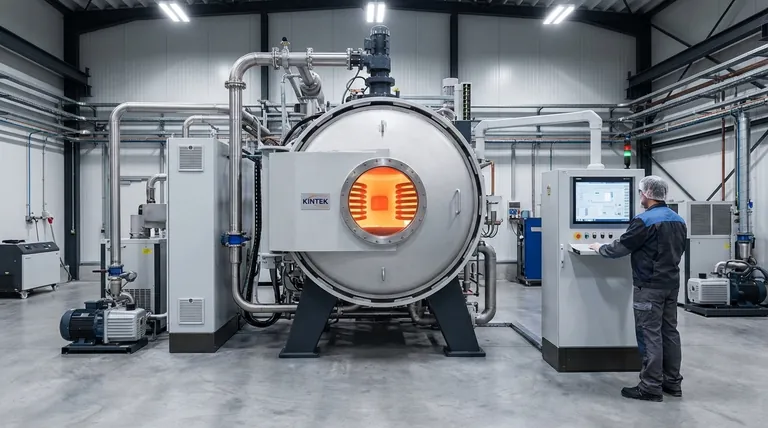

How VIM Works: A Two-Part System
To understand VIM's effectiveness, you must see it as the combination of two core technologies: the heating method and the controlled environment.
The Furnace: Electromagnetic Induction
Induction heating uses powerful, alternating magnetic fields to generate heat directly within the metal charge itself.
This contactless heating method is inherently clean, preventing contamination that could occur with traditional fuel-fired furnaces or electric arcs.
The magnetic fields also create a natural, vigorous stirring action in the molten metal. This electromagnetic stirring is critical for ensuring the alloy is perfectly mixed, resulting in a chemically uniform and consistent final product.
The Environment: The Power of Vacuum
Placing the induction furnace in a vacuum chamber is what elevates VIM to a high-purity process.
First, the vacuum protects the melt by removing atmospheric gases like oxygen and nitrogen. This prevents the formation of oxide impurities (inclusions) that can compromise a material's strength.
Second, the vacuum actively purifies the molten metal. It pulls dissolved gases like hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen out of the liquid, and it also causes harmful, low-boiling-point trace elements (like lead or bismuth) to vaporize and be removed.
Finally, the vacuum enables precise control over the alloy's chemistry. Superalloys depend on reactive elements like aluminum (Al) and titanium (Ti) for their strength. In a normal atmosphere, these elements would rapidly oxidize and be lost. The vacuum protects them, allowing for precise additions to meet exacting specifications.
The VIM Process: From Raw Material to Ingot
The VIM process is a meticulously controlled sequence designed to maximize quality at every stage.
Stage 1: Charging and Melting
High-purity raw metals and alloying elements are loaded into the furnace's crucible, which is sealed inside the vacuum chamber. The air is then pumped out to create the required vacuum level.
Once the vacuum is established, power is applied to the induction coil, melting the charge.
Stage 2: Refining and Alloying
This is the most critical stage. The molten bath is held under vacuum at temperature, allowing for extensive degassing and the volatilization of impurities.
During this refining period, operators can take samples for chemical analysis and make precise additions of alloying elements to hit the target composition perfectly. The electromagnetic stirring ensures these additions are distributed homogeneously.
Stage 3: Casting
After the chemistry is verified, the molten superalloy is poured into molds to create large ingots or electrodes, typically while still under vacuum or a protective inert gas atmosphere (like argon).
These products can either be used directly or, more commonly, serve as the input material for further refinement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Context
While powerful, VIM is part of a larger ecosystem of materials processing. Understanding its role and limitations is key.
VIM as a Primary Melt Process
VIM is a primary melting technique, meaning it excels at converting raw materials into a high-quality, homogenous alloy.
For the most demanding applications, such as rotating jet engine disks, the ingots produced by VIM are often used as electrodes for secondary remelting processes like Vacuum Arc Remelting (VAR) or Electroslag Remelting (ESR). These subsequent steps refine the grain structure and remove any non-metallic inclusions that may have come from the VIM crucible, achieving the ultimate level of material purity.
Inherent Limitations
The primary limitation of VIM is the ceramic crucible that holds the molten metal. Over time, the highly reactive molten superalloy can interact with the crucible, potentially introducing ceramic inclusions into the melt. This is precisely why secondary remelting (which does not use a crucible) is required for the highest-integrity components.
Furthermore, VIM is an expensive, energy-intensive process. Its use is reserved for materials where the demand for extreme performance justifies the significant cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a melt process depends entirely on the performance requirements and cost constraints of the final application.
- If your primary focus is producing a high-quality master alloy from raw materials: VIM is the foundational process for achieving the necessary chemical precision and cleanliness.
- If your primary focus is achieving the absolute highest purity for critical rotating parts: VIM is the necessary first step, which must be followed by a secondary remelting process like VAR or ESR.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective melting of less reactive alloys (e.g., many stainless steels): A standard air or inert atmosphere induction furnace is a more economical and appropriate choice.
Ultimately, mastering the "why" behind VIM is fundamental to specifying and creating materials that can withstand the world's most demanding environments.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Process | Melting in vacuum using electromagnetic induction for purity and homogeneity. |
| Key Benefits | Removes gases and impurities, protects reactive elements, ensures uniform mixing. |
| Applications | Jet engines, power turbines, and other extreme-environment components. |
| Limitations | Potential crucible contamination, high cost, often requires secondary remelting. |
Ready to elevate your superalloy production with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored VIM solutions can enhance your material quality and performance in extreme environments!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- What role does a vacuum induction melting furnace play in Fe-5%Mn-C alloys? Ensure Chemical Integrity and High Purity
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What are some common applications of vacuum induction melting and casting (VIM&C)? Essential for Aerospace, Medical, and Nuclear Industries
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification



















