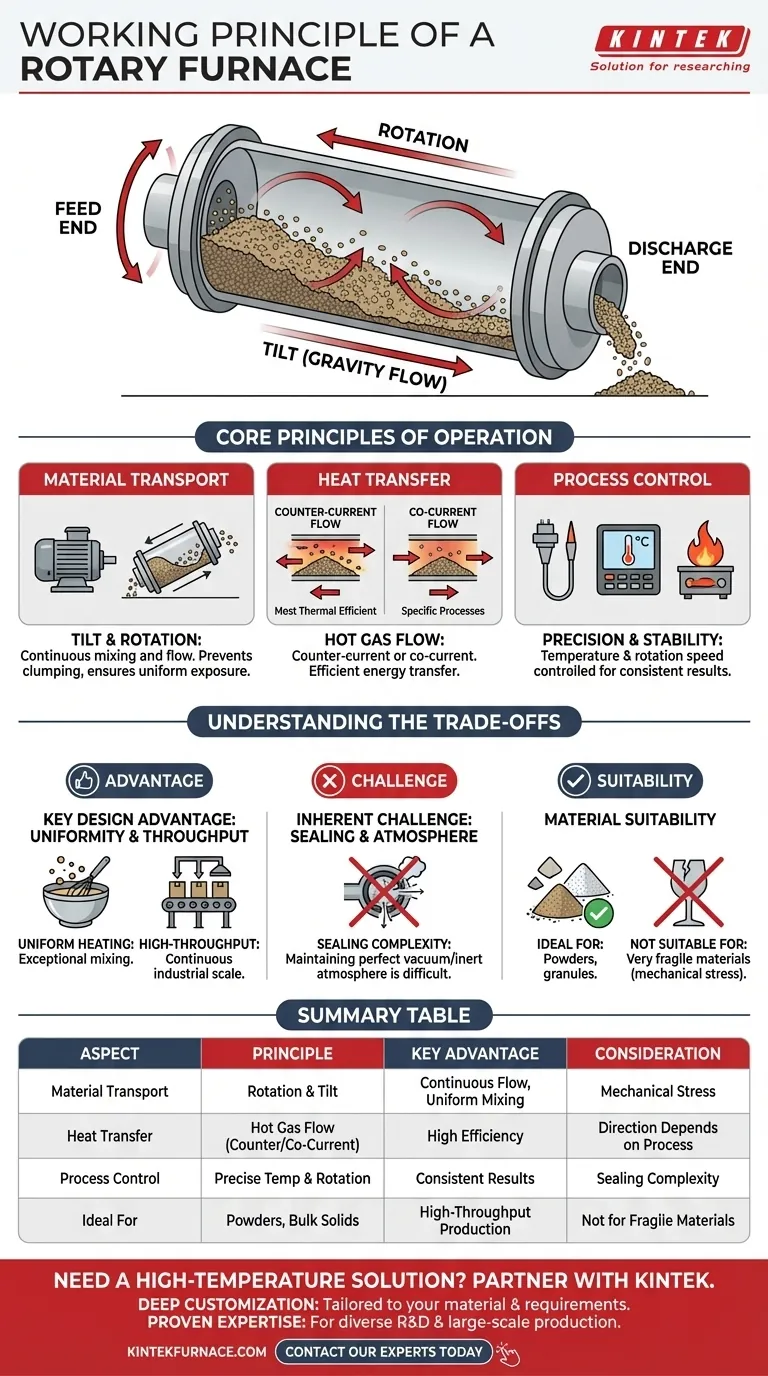
At its core, a rotary furnace operates by tumbling material inside a heated, rotating, and slightly tilted cylinder. This combination of rotation and inclination continuously mixes the material and moves it from the feed end to the discharge end, ensuring every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat source.
The defining principle of a rotary furnace isn't just the application of heat, but the use of mechanical motion—rotation and tilt—to achieve continuous processing and superior heat transfer uniformity. This makes it uniquely suited for transforming granular or powdered materials on a large scale.

The Core Principles of Operation
To fully grasp how a rotary furnace functions, it's best to break its operation down into three interconnected systems: material transport, heat transfer, and process control.
Material Transport: The Role of Tilt and Rotation
The furnace body is a long cylinder mounted at a slight angle to the horizontal. An independent motor rotates this cylinder around its axis.
This design creates a continuous flow. The tilt uses gravity to encourage the material to move from the higher inlet end to the lower outlet end.
Simultaneously, the rotation constantly lifts and tumbles the material. This action is critical for preventing clumping, ensuring all surfaces are exposed to the heat, and stopping material from sticking to the furnace walls.
Heat Transfer: The Flow of Hot Gases
Heat is generated by burning fuel (liquid, gas, or pulverized solid) and channeling the resulting hot gases through the rotating cylinder.
The direction of this gas flow is a key design choice. Most commonly, a counter-current flow is used, where the hot gases enter at the discharge end and travel in the opposite direction of the material. This is the most thermally efficient method.
In some applications, a co-current flow is used, where the gas and material move in the same direction. The choice depends on the specific requirements of the heat treatment process.
Process Control: Ensuring Precision and Stability
Achieving a precise outcome depends on tightly controlling the furnace environment.
A thermocouple inside the furnace measures the temperature and converts it into an electrical signal. This signal is sent to a temperature controller, which adjusts the power to the heating source to maintain the desired temperature profile. The speed of rotation is also controlled to manage how long the material stays in the furnace.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the design of a rotary furnace comes with specific considerations that make it suitable for some applications and less so for others.
Key Design Advantage: Uniformity and Throughput
The primary advantage is the combination of excellent mixing and continuous operation. The tumbling action guarantees exceptionally uniform heating, which is vital for processes like smelting and calcination where consistency is paramount.
Because material is constantly fed in and discharged, rotary furnaces are ideal for high-throughput, industrial-scale production, far surpassing the capacity of static batch furnaces.
Inherent Challenge: Sealing and Atmosphere
The rotating nature of the furnace presents an engineering challenge in maintaining a perfect seal at the inlet and outlet.
For processes that demand a controlled atmosphere, such as a pure vacuum or an inert gas environment, this can be a significant hurdle. While possible, achieving a perfect seal is more complex than in a static furnace.
Material Suitability
The tumbling action that provides such great mixing can also be a disadvantage. The process creates mechanical stress, making it unsuitable for very fragile materials that could be crushed or damaged by the continuous movement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
The working principle of a rotary furnace directly informs its ideal applications. Your decision to use one should be based on your specific process goals.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production of powders or granules (e.g., calcination, drying, reduction): The continuous processing and uniform heat transfer of a rotary furnace make it the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is treating fragile materials that cannot withstand mechanical stress: A static batch furnace or a belt furnace would be a more appropriate solution to avoid product damage.
- If your primary focus is a process requiring a hard vacuum or extremely pure inert atmosphere: Carefully evaluate the sealing technology of the rotary furnace, as a dedicated vacuum batch furnace may provide more reliable atmospheric control.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace is an exceptional tool purpose-built for the uniform, continuous heat treatment of bulk materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Principle | Key Advantage | Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Transport | Cylinder rotation and tilt | Continuous flow and uniform mixing | Mechanical stress on materials |
| Heat Transfer | Counter-current or co-current hot gas flow | High thermal efficiency | Direction choice depends on process |
| Process Control | Precise temperature and rotation speed control | Consistent, repeatable results | Sealing for controlled atmospheres can be complex |
| Ideal For | Powders, granules, bulk solids | High-throughput, industrial-scale production | Not suitable for fragile materials |
Need a High-Temperature Solution for Your Process?
Understanding the working principle is the first step. Implementing the right furnace is what drives success. KINTEK excels at turning thermal processing challenges into reliable, efficient solutions.
Why Partner with KINTEK?
- Deep Customization: We don't just sell standard models. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we tailor our Rotary Furnaces—and our entire line of Muffle, Tube, Vacuum & Atmosphere, and CVD/PECVD Systems—to your unique material, throughput, and atmosphere requirements.
- Proven Expertise for Diverse Labs: Whether you're in R&D or large-scale production, our solutions are engineered for precision and durability, ensuring every particle is processed uniformly.
Ready to achieve superior heat treatment for your bulk materials? Contact our experts today to discuss how a KINTEK rotary furnace can optimize your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing



















