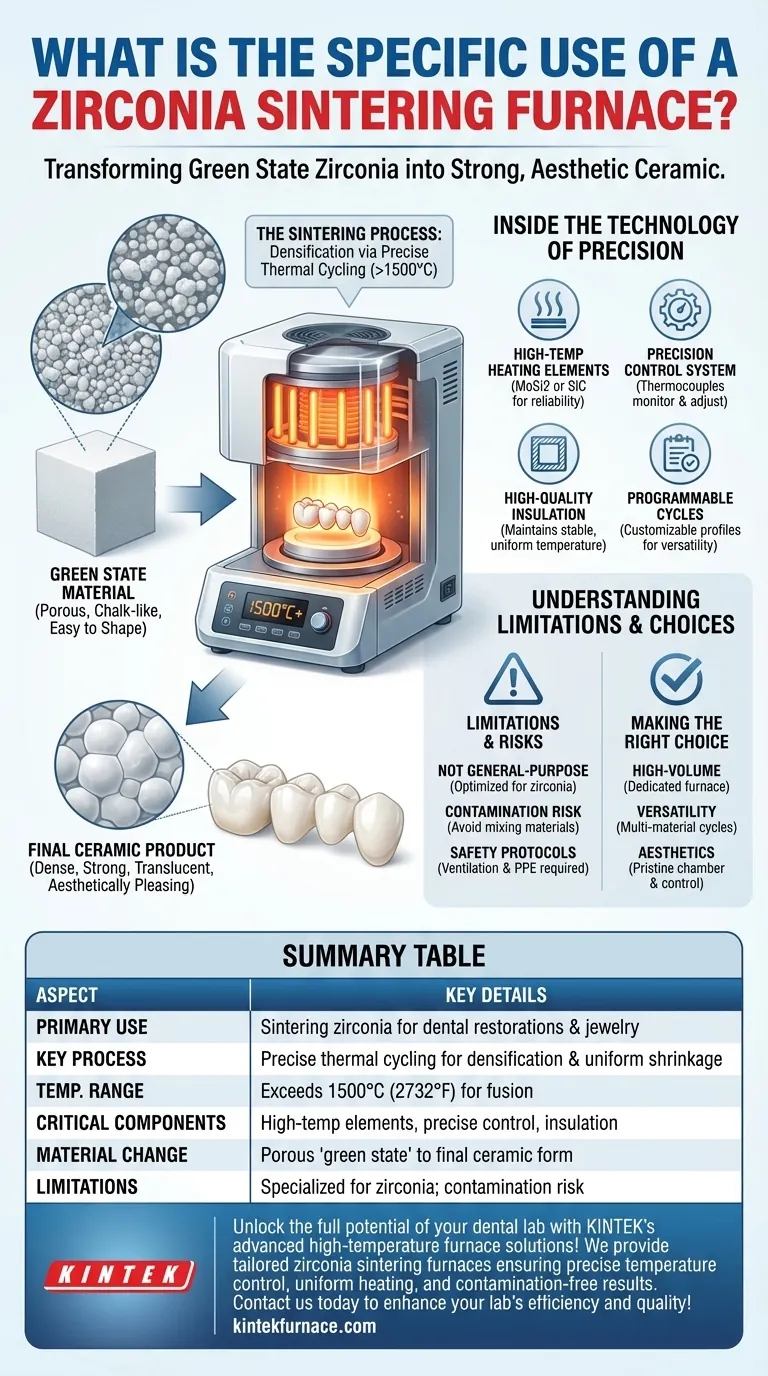
At its core, a zirconia sintering furnace is a highly specialized piece of equipment designed for one critical task: transforming a soft, chalk-like zirconia structure into a dense, exceptionally strong, and aesthetically pleasing final product. This process, known as sintering, is the essential final step in creating modern dental restorations like crowns and bridges, as well as high-end jewelry.
The furnace's specific use is not merely to generate high heat, but to execute a precisely controlled temperature profile. This meticulous control over heating, holding, and cooling cycles is what unlocks the unique strength, durability, and translucency of the zirconia material.

The Transformation: From 'Chalk' to Ceramic
To understand the furnace's purpose, you must first understand the state of zirconia before it enters the furnace.
The "Green State" Material
Zirconia restorations are initially milled from a pre-sintered block. In this "green state" or "white state," the material is porous, oversized, and has the consistency of chalk. It is easy to shape and adjust but has none of the strength required for clinical or functional use.
The Sintering Process
The furnace subjects this green-state material to a specific, pre-programmed thermal cycle. As the temperature rises to peaks often exceeding 1500°C (2732°F), the individual zirconia particles fuse together. This process, called densification, eliminates the porosity and causes the material to shrink uniformly into its final, precise dimensions and immense strength.
Inside the Furnace: The Technology of Precision
A zirconia furnace is not a simple kiln. Its value comes from a combination of specialized components working in unison to guarantee a predictable and repeatable outcome.
High-Temperature Heating Elements
To reach the required temperatures, these furnaces use robust heating elements, typically made of molybdenum disilicide (MoSi2) or silicon carbide (SiC). These materials are chosen for their ability to perform reliably and cleanly at extreme temperatures without degrading.
The Temperature Control System
This is the brain of the operation. A sophisticated controller, guided by precise thermocouples, constantly monitors and adjusts the temperature inside the chamber. This ensures the furnace follows the programmed sintering cycle—including the ramp rate (how fast it heats), the hold time, and the cooling rate—with extreme accuracy.
High-Quality Insulation
To maintain a stable and uniform temperature zone, the furnace chamber is lined with high-purity ceramic fiber insulation. This minimizes heat loss, ensuring energy efficiency and preventing temperature fluctuations that could compromise the final restoration.
Programmable Cycles for Versatility
Different types of zirconia (e.g., high-strength vs. high-translucency) require different sintering profiles. A key feature of these furnaces is the ability to program and save custom cycles, allowing a dental lab to consistently process various materials from different manufacturers. Some units can also perform cycles for glass ceramics or glazing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, a zirconia sintering furnace is a specialized tool with specific operational considerations.
Not a General-Purpose Kiln
While some furnaces can sinter other ceramics, their design is optimized for zirconia. The heating elements and chamber materials are chosen to prevent any chemical reactions or discoloration that could ruin the aesthetics of translucent zirconia. Using it for incompatible materials can lead to poor results or contamination.
The Risk of Contamination
A furnace dedicated to zirconia sintering ensures a clean environment. Using the same furnace for different processes, such as firing metals or different types of ceramics, can introduce trace elements into the chamber that contaminate subsequent zirconia batches, causing discoloration and compromising the biocompatibility.
Adherence to Safety Protocols
Operating at such high temperatures necessitates strict safety measures. Proper ventilation is critical to manage any fumes, and users must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE). Following the manufacturer's specific operational and safety guidelines is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting and using a zirconia furnace properly depends entirely on your operational goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, consistent zirconia restorations: A dedicated, programmable furnace is essential for achieving the efficiency and repeatable quality required for production.
- If your primary focus is material versatility in a smaller lab: Choose a furnace with a wide range of verified, pre-set programs for zirconia, glass ceramics, and glazing to maximize the utility of a single machine.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest aesthetic results: Prioritize a furnace known for its pristine chamber and exceptionally precise temperature control to prevent any discoloration of highly translucent materials.
Ultimately, the zirconia sintering furnace is the critical instrument that unlocks the full clinical and aesthetic potential of modern ceramic dental materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Sintering zirconia to create dense, strong dental restorations and jewelry |
| Key Process | Precise thermal cycling for densification, eliminating porosity and ensuring uniform shrinkage |
| Temperature Range | Exceeds 1500°C (2732°F) for effective particle fusion |
| Critical Components | High-temperature heating elements (e.g., MoSi2, SiC), precise temperature control, quality insulation |
| Material State Change | Transforms porous 'green state' zirconia to final ceramic form |
| Limitations | Specialized for zirconia; risk of contamination if used for other materials |
Unlock the full potential of your dental lab with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide tailored zirconia sintering furnaces that ensure precise temperature control, uniform heating, and contamination-free results for superior dental restorations. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's efficiency and quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is calibration important for dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations and Avoid Costly Failures
- What factors determine the quality of sintered zirconia restorations? Master Material, Equipment, and Technique
- What is the purpose of dental sintering furnaces? Transform Zirconia into Durable, High-Quality Dental Restorations
- What are the effects of overloading a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Predictable, High-Quality Zirconia Restorations
- Why is precise temperature control important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations



















