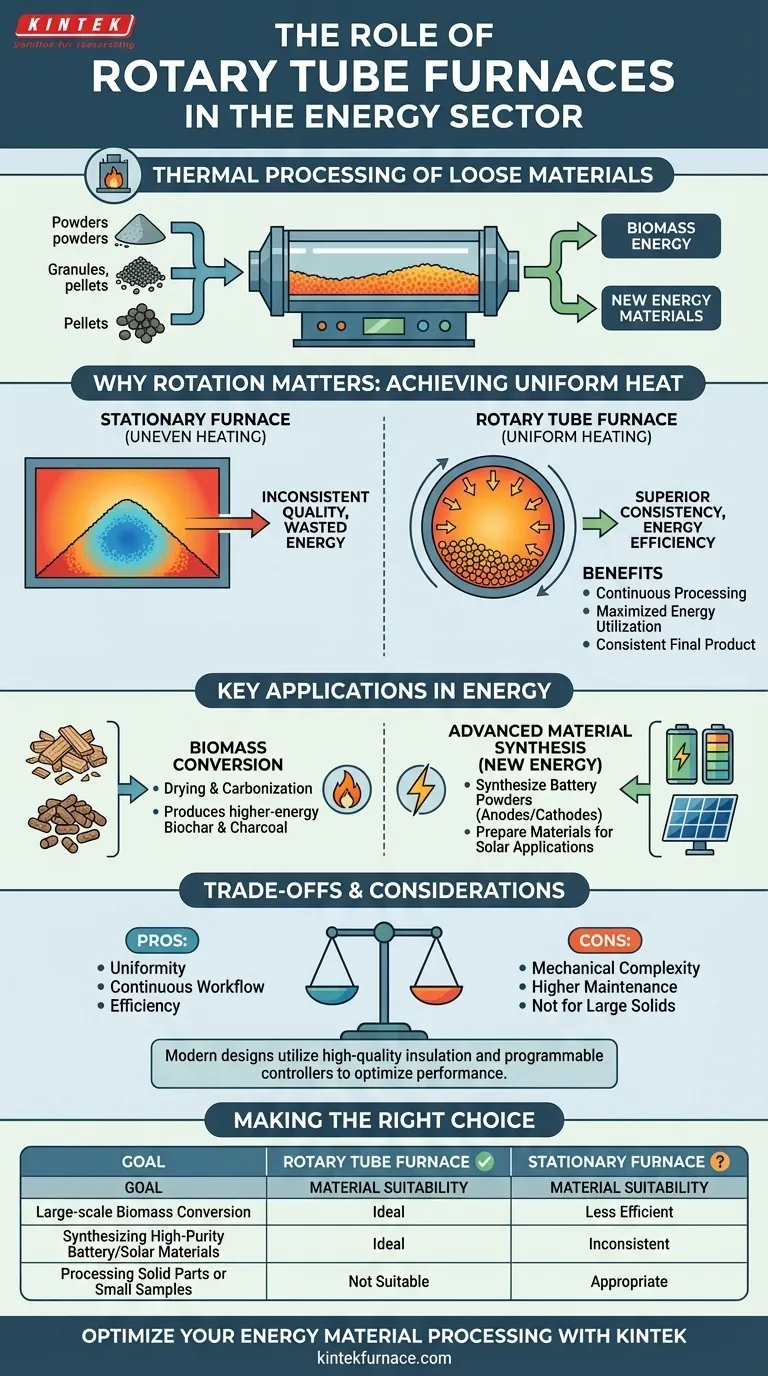
In the energy sector, rotary tube furnaces serve a critical role in the thermal processing of loose materials. They are primarily used for producing biomass energy through the drying and carbonization of materials like wood chips and pellets, as well as for synthesizing the high-performance powders required for modern batteries and solar applications.
The core challenge in processing granular or powdered materials is achieving uniform heat treatment. Rotary tube furnaces solve this by continuously tumbling the material, which ensures every particle is evenly heated, leading to superior energy efficiency and product consistency compared to stationary furnace designs.

The Core Principle: Why Rotation Matters
The defining advantage of a rotary tube furnace is its dynamic heating method. This simple mechanical action provides significant thermal and operational benefits over static alternatives.
Overcoming the Limits of Stationary Furnaces
In a stationary furnace, a pile of loose material heats unevenly. The outer layers can become overheated or charred while the core of the pile remains under-processed or damp.
This inconsistent heating leads to lower product quality and wasted energy, as the furnace must run longer to ensure the core reaches the target temperature.
Achieving Uniform Heat Distribution
The rotation of the furnace tube gently and continuously tumbles the material. This action ensures that every particle is consistently exposed to the heat source.
This uniform heat transfer maximizes energy utilization, reduces overall energy consumption, and results in a highly consistent final product.
Enabling Continuous Processing
The rotating design is perfectly suited for continuous or semi-continuous batch processing. Material can be fed into one end of the tube and processed as it travels to the exit.
This minimizes material handling and is highly beneficial for industrial-scale operations where efficiency and throughput are critical.
Key Applications in the Energy Sector
The unique capabilities of rotary tube furnaces make them indispensable in two key areas of the energy industry: traditional biomass and new energy materials.
Biomass Conversion
Rotary furnaces are used to dry biomass pellets and wood chips to improve their fuel value. They are also used for carbonization (a form of pyrolysis), a process that converts biomass into higher-energy biochar or charcoal.
Uniform heating is crucial in these processes to prevent incomplete drying or inconsistent carbonization, ensuring a reliable and predictable fuel source.
Advanced Material Synthesis (New Energy)
The new energy field relies on precisely engineered materials. Rotary tube furnaces are used to synthesize and treat the high-performance powders that form battery components, such as anodes and cathodes.
The exceptional temperature uniformity guarantees the batch-to-batch consistency required for reliable battery performance. This same principle applies to preparing materials for solar applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Design Factors
While powerful, rotary tube furnaces are not a universal solution. Understanding their specific design context and limitations is key to using them effectively.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotating mechanism, including the motor, drive system, and high-temperature seals, adds mechanical complexity compared to a simple stationary furnace. This introduces additional points of maintenance and potential failure.
Material Suitability
These furnaces are specifically designed for loose materials, such as powders, granules, and pellets. They are not suitable for processing large, solid, or monolithic objects.
The Role of Modern Furnace Design
The efficiency of a modern rotary tube furnace comes from more than just rotation. Features like high-quality ceramic fiber insulation to minimize heat loss and programmable controllers to optimize heating cycles are essential.
These components work together to reduce operational costs and maximize thermal performance. Some advanced models also include air cooling systems to further improve efficiency and temperature control.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right thermal processing technology depends entirely on your material type and production goals.
- If your primary focus is large-scale biomass conversion: A rotary tube furnace is ideal for ensuring consistent drying or carbonization in a continuous workflow.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing high-purity battery or solar materials: The uniform heating of a rotary furnace provides the batch-to-batch consistency required for high-performance applications.
- If your primary focus is processing solid parts or small, static samples: A simpler and more cost-effective stationary box or tube furnace is the appropriate choice.
By understanding the core principle of dynamic heat exposure, you can accurately assess where this technology delivers its greatest value to your project.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Role | Thermal processing of loose materials for energy applications |
| Key Applications | Biomass conversion (drying, carbonization), synthesis of battery and solar materials |
| Core Benefits | Uniform heat distribution, continuous processing, high energy efficiency, superior product consistency |
| Material Suitability | Powders, granules, pellets (not for large solid objects) |
| Common Limitations | Mechanical complexity, higher maintenance compared to stationary furnaces |
Ready to optimize your energy material processing? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for your needs. Our product line includes Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Whether you're scaling up biomass conversion or synthesizing high-performance battery materials, we can help you achieve superior efficiency and consistency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your lab or production process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















