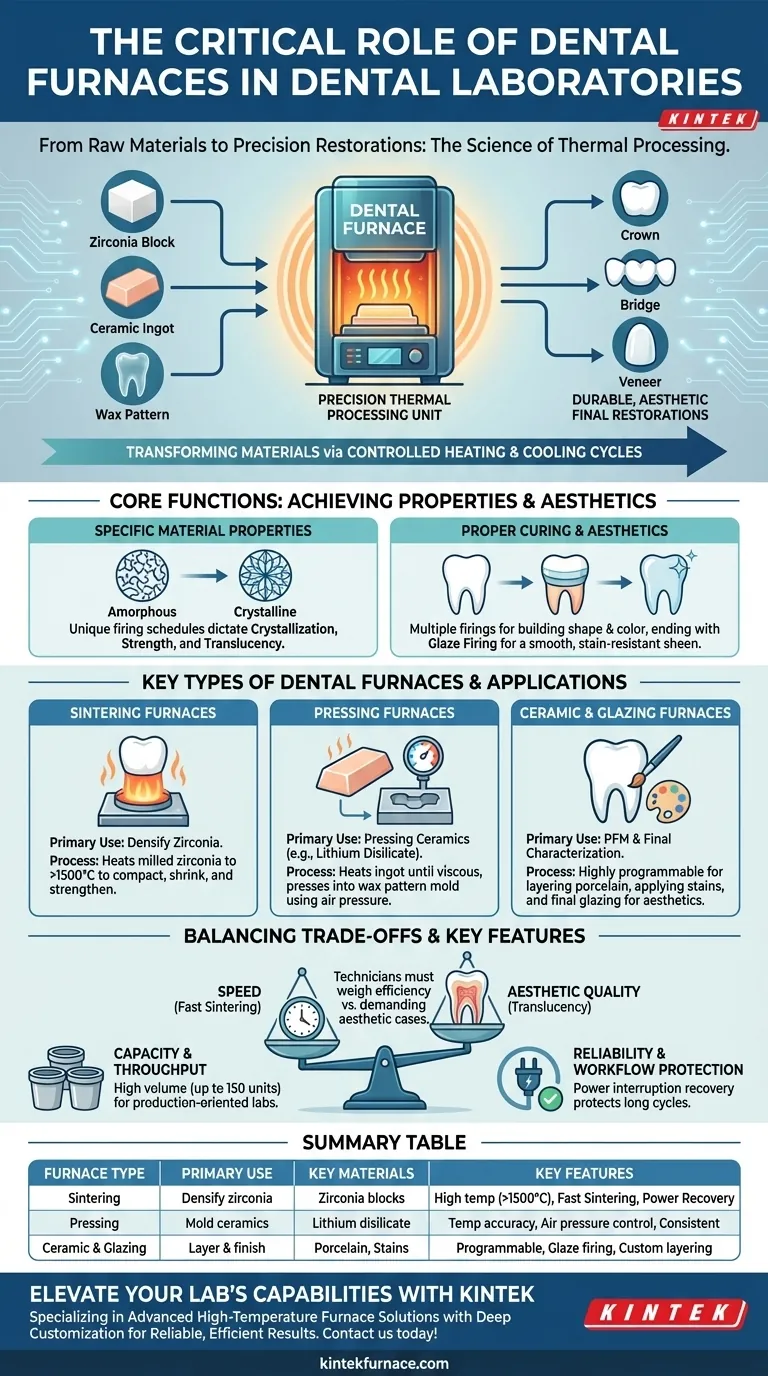
At their core, dental furnaces are the essential thermal processing units in any dental laboratory. They are responsible for transforming raw or partially processed materials like ceramic powders, zirconia blocks, and wax patterns into strong, durable, and aesthetically precise final dental restorations such as crowns, bridges, and veneers.
The role of a dental furnace extends far beyond simple heating. It is a precision instrument designed to execute highly specific temperature cycles that are critical for achieving the final strength, fit, color, and biocompatibility of a dental restoration.

The Core Function: From Raw Material to Final Restoration
A dental furnace is not just an oven; it is the engine that drives the material science behind modern dental prosthetics. Its primary role is to create a perfectly controlled heating environment to trigger specific physical and chemical changes in the material.
Achieving Specific Material Properties
The value of a furnace lies in its precision. Each material, whether it's zirconia or lithium disilicate, requires a unique firing schedule—a precise sequence of heating rates, temperatures, and holding times—to achieve its intended properties. This process ensures the restoration has the correct crystallization structure, which dictates its final strength and translucency.
Ensuring Proper Curing and Aesthetics
For layered porcelain restorations, the furnace is used multiple times to build up shape and color. Each layer of ceramic powder is fired to fuse it to the underlying structure. The final step is often a glaze firing, which creates a smooth, stain-resistant, and natural-looking surface sheen.
Key Types of Furnaces and Their Applications
Different restorations require different materials and processes, which is why laboratories use several types of specialized furnaces.
Sintering Furnaces
These are primarily used for processing zirconia. After a crown is milled from a soft, chalk-like zirconia block, the sintering furnace heats it to extremely high temperatures (often over 1500°C). This process compacts the material, shrinking it to its final, dense, and incredibly strong state.
Pressing Furnaces
Pressing furnaces are used for materials like lithium disilicate (e.g., e.max). In this process, a ceramic ingot is heated until it becomes viscous. The furnace then uses air pressure to "press" the malleable ceramic into a mold created from a burnt-out wax pattern, producing a highly accurate and strong monolithic restoration.
Ceramic and Glazing Furnaces
These are the workhorses for creating porcelain-fused-to-metal (PFM) crowns and for the final characterization of all-ceramic restorations. Their highly programmable cycles allow technicians to fire thin layers of porcelain, apply stains, and complete the final glaze firing to achieve a lifelike aesthetic.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Features
Choosing and using a furnace involves balancing productivity with final quality. Modern features are designed to optimize this balance.
Speed vs. Aesthetic Quality
Many modern furnaces offer fast sintering programs that can significantly reduce processing time. While excellent for efficiency, the fastest cycles may not always yield the highest level of translucency required for demanding anterior aesthetic cases. Technicians must weigh the need for speed against specific case requirements.
Capacity and Throughput
Furnace capacity is a major factor in a lab's productivity. Some models allow for stacking multiple crucibles, enabling the simultaneous processing of up to 150 units. This high throughput is critical for large, production-oriented laboratories.
Reliability and Workflow Protection
A failed firing cycle means lost time, materials, and revenue. Features like power interruption recovery are invaluable, as they allow the furnace to resume its cycle after a brief power outage. This protects long, multi-hour sintering processes from being ruined.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The ideal furnace depends entirely on the type of work your laboratory specializes in. Your decision should be guided by your primary material and production goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume zirconia production: Prioritize a sintering furnace with a large capacity, proven fast-sintering cycles, and robust reliability features like power-outage protection.
- If your primary focus is high-end aesthetic restorations: You need a precision ceramic furnace with highly customizable and accurate firing programs for custom layering, staining, and glazing.
- If your primary focus is pressed ceramics: A dedicated pressing furnace with exceptional temperature accuracy and consistent pressure control is non-negotiable for predictable results.
Ultimately, the dental furnace is the critical link between a digital or analog design and a clinically successful restoration.
Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Primary Use | Key Materials | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sintering Furnaces | Densify zirconia for strength | Zirconia blocks | High temperatures (>1500°C), fast sintering, power interruption recovery |
| Pressing Furnaces | Mold ceramics into precise shapes | Lithium disilicate | Temperature accuracy, air pressure control, consistent results |
| Ceramic and Glazing Furnaces | Layer and finish porcelain for aesthetics | Porcelain, stains | Programmable cycles, glaze firing, custom layering |
Ready to elevate your dental lab's capabilities? At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for dental laboratories. Our diverse product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental and production needs, ensuring reliable, efficient, and high-quality restorations. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can enhance your workflow and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is calibration important for dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Perfect Restorations and Avoid Costly Failures
- Why is precise temperature control important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- Why is proper ventilation important in dental sintering furnaces? Ensure Quality and Safety in Your Lab
- How has the sintering process innovated dental zirconia applications? Boost Strength, Precision, and Efficiency
- What are the effects of overloading a dental sintering furnace? Ensure Predictable, High-Quality Zirconia Restorations



















