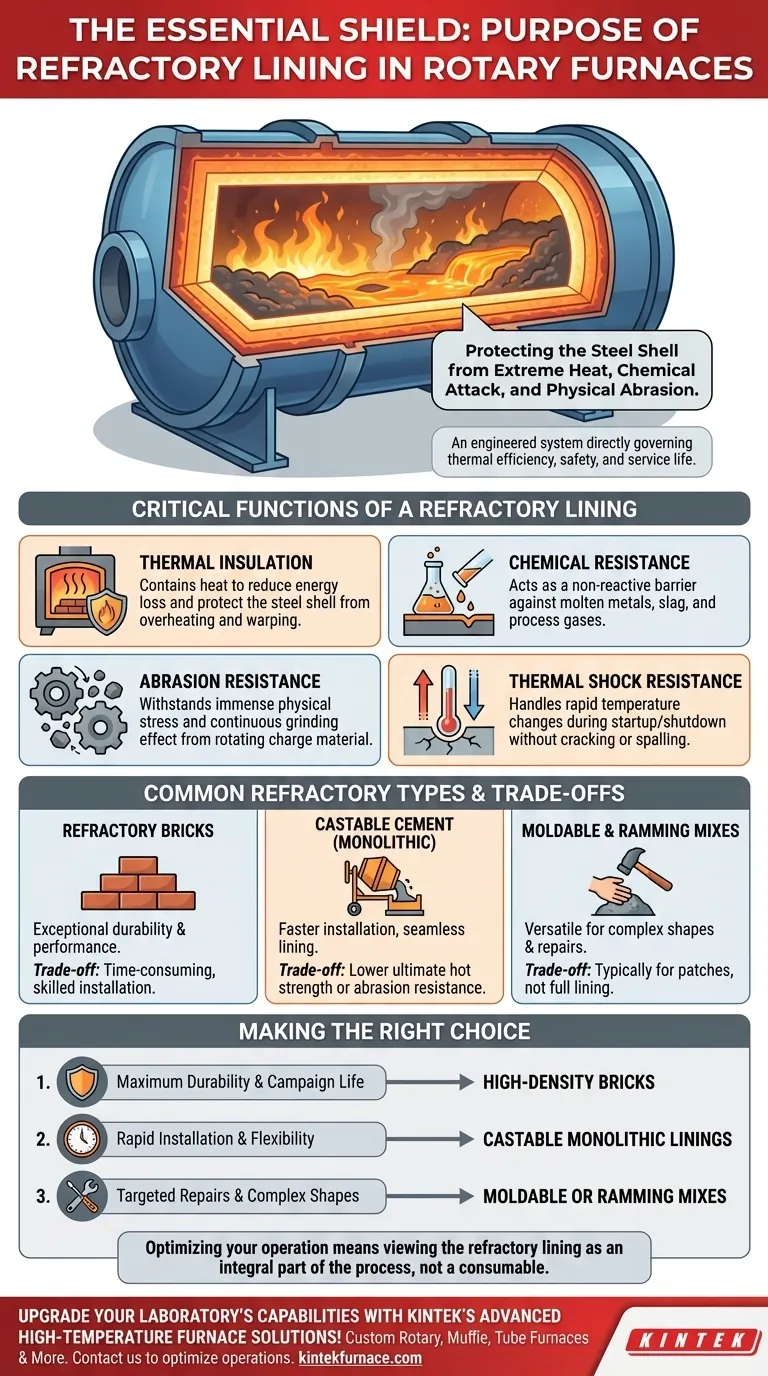
At its core, a refractory lining is the essential shield for the steel shell of a rotary furnace. Its primary purpose is to protect the furnace structure from the destructive forces within—extreme heat, chemical attack from molten materials, and the physical abrasion caused by the rotating charge. Without it, a furnace would fail in a matter of minutes.
A refractory lining is not merely a protective layer; it is an engineered system that directly governs the furnace's thermal efficiency, operational safety, and overall service life. The choice of material is a critical decision that balances performance, cost, and installation complexity.
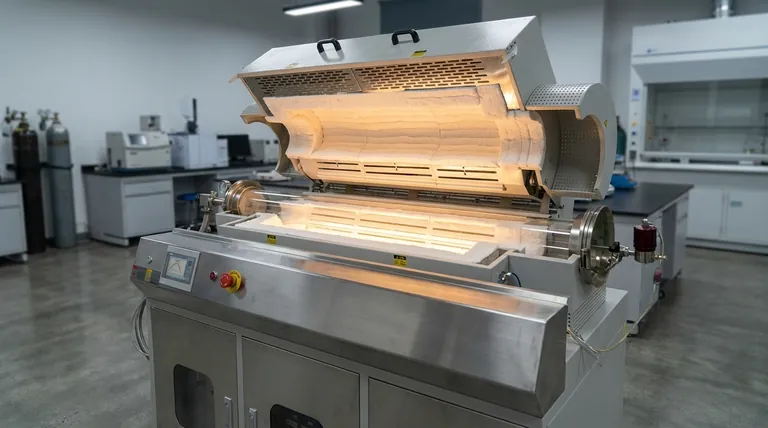

The Critical Functions of a Refractory Lining
To understand the importance of refractory materials, we must break down their specific duties inside the hostile environment of a rotary furnace.
Thermal Insulation
The most obvious function is containing heat. A proper lining minimizes the heat that escapes through the furnace's steel shell.
This thermal containment is crucial for two reasons: it dramatically reduces fuel consumption by keeping energy focused on the process, and it protects the structural integrity of the steel shell from overheating and warping.
Chemical Resistance
Molten metals, slag, and process gases are highly corrosive. The refractory lining acts as a non-reactive barrier between these corrosive agents and the furnace shell.
The material selection is critical here, as different refractories are designed to resist specific chemical compositions, whether they are acidic or basic in nature.
Abrasion Resistance
In a rotary furnace, the charge material (like scrap metal or ore) is constantly tumbling as the furnace turns. This creates immense physical stress and a continuous grinding effect.
The lining must be hard and durable enough to withstand this constant abrasion, preventing the charge from wearing through the protective layer and reaching the shell.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnaces are not always operating at a constant temperature. They go through heating and cooling cycles during startup, shutdown, and charging.
Refractory materials must be able to withstand these rapid temperature changes—known as thermal shock—without cracking, spalling, or failing.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Common Refractory Types
There is no single "best" refractory material; the optimal choice depends on the specific application, budget, and operational goals. Each type involves a set of trade-offs.
Refractory Bricks
Bricks are a traditional and highly effective lining material known for their exceptional durability and performance under extreme conditions.
However, their primary trade-off is installation. Laying refractory bricks is a time-consuming process that requires highly skilled masons, making it a more expensive and slower option upfront.
Castable Cement (Monolithic Linings)
Castable refractories are like a high-temperature concrete. They are mixed with water and then poured or gunned into place, forming a single, seamless (monolithic) lining.
This method is much faster than bricking and is excellent for creating smooth linings without joints, which can be weak points. The trade-off may be in ultimate hot strength or abrasion resistance compared to some premium, high-fired bricks.
Moldable and Ramming Mixes
These materials have a clay-like consistency and are installed by being rammed or hammered into place.
Their main advantage is versatility. They are ideal for creating complex shapes, patching worn-out areas, or making emergency repairs. They are typically used for specific sections or repairs rather than for a full furnace lining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct refractory system is a balance of performance requirements and logistical constraints. The decision should be driven by your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum campaign life and durability: High-density, high-alumina refractory bricks are often the superior choice despite the higher installation cost.
- If your primary focus is rapid installation and operational flexibility: Castable monolithic linings provide an excellent balance of performance and speed.
- If your primary focus is targeted repairs or lining complex shapes: Moldable or ramming mixes offer the versatility needed for patching and custom-formed sections.
Ultimately, viewing the refractory lining as an integral part of the process, not just a consumable, is the key to optimizing your entire furnace operation.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Thermal Insulation | Contains heat to reduce energy loss and protect the steel shell from overheating. |
| Chemical Resistance | Acts as a barrier against corrosive molten materials and gases. |
| Abrasion Resistance | Withstands physical wear from tumbling charge materials in the rotating furnace. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Handles rapid temperature changes during heating and cooling cycles without damage. |
Upgrade your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and durability. Don't let furnace inefficiencies hold you back—contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can protect your equipment and optimize your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What are the main structural components of a rotary furnace? Explore Key Parts for Efficient Material Processing



















