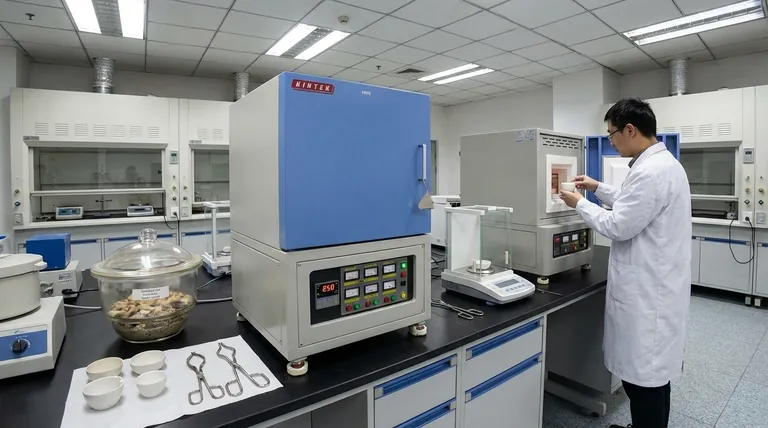
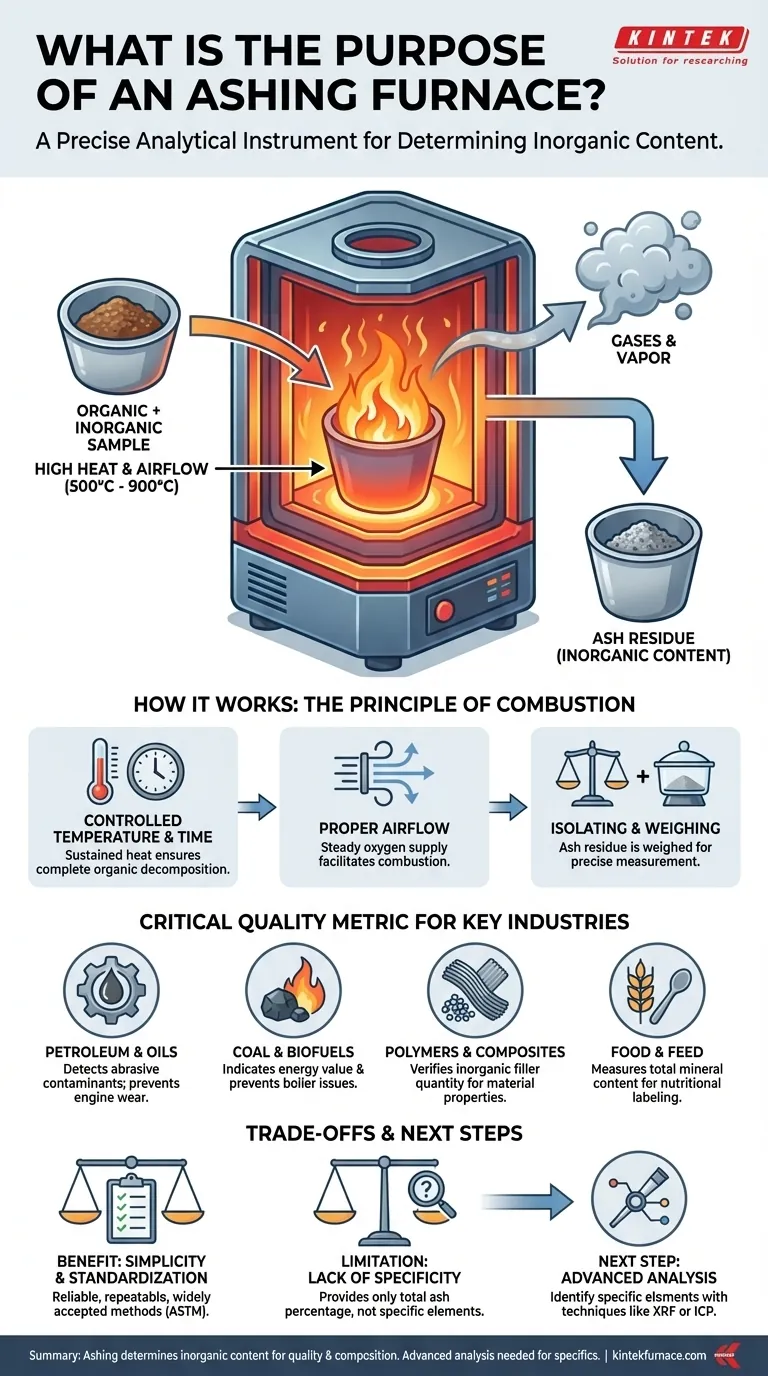
At its core, an ashing furnace serves a single, critical purpose: to determine the amount of inorganic, non-combustible content within a sample. The furnace operates at very high temperatures to completely burn away all organic material, leaving behind only the "ash." This remaining ash is then weighed to provide a quantitative measure of the original sample's composition.
An ashing furnace is not simply for incineration; it is a precise analytical instrument. Its function is to isolate the inorganic residue (ash) to assess a material's purity, identify the quantity of inorganic fillers, or verify its composition against quality and safety standards.

How an Ashing Furnace Works: The Principle of Combustion
The process of ashing is a form of gravimetric analysis, meaning it relies on measuring mass. The furnace provides a highly controlled environment to ensure the results are accurate and repeatable.
The Role of Controlled Temperature
An ashing furnace heats a sample to a specific temperature, typically between 500°C and 900°C, and holds it there for a set period. This sustained, high heat ensures the complete combustion and thermal decomposition of all organic and volatile components.
The Importance of Airflow
Proper airflow is critical. The furnace introduces a steady supply of air (oxygen) to facilitate the combustion process. This converts the sample's organic matter into gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor, which are then vented from the chamber.
Isolating and Weighing the Ash
After the combustion cycle is complete, the only thing remaining in the crucible is the ash. This residue consists of minerals, salts, metallic compounds, and any other inorganic material that does not burn. The crucible is cooled in a desiccator and then weighed precisely to determine the ash content percentage.
Why Ash Content is a Critical Quality Metric
The amount of ash is a vital data point across many industries. It is a direct indicator of material purity, composition, and quality.
For Petroleum and Lubricating Oils
In fuels and lubricants, ash is considered a contaminant. It often represents abrasive solids or metallic compounds. High ash content can lead to engine deposits, increased wear, and reduced performance, making this test essential for quality control.
For Coal and Biofuels
The ash content of a fuel like coal directly relates to its energy value. More ash means less combustible material, resulting in lower energy output per kilogram. It also impacts boiler operation, as high ash can cause fouling and slagging.
For Polymers and Composites
In the plastics industry, ashing is used to determine the quantity of inorganic fillers, such as glass fiber, talc, or calcium carbonate. These fillers are intentionally added to modify a polymer's properties (e.g., strength, stiffness, or cost), and ashing verifies that the correct amount was used.
For Food and Feed
In food science, ash content represents the total mineral content of a product. This measurement is a fundamental part of nutritional analysis and is required for accurate labeling. It serves as an overall indicator of the food's inorganic nutrient profile.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the ashing process has specific characteristics that are important to understand.
The Benefit: Simplicity and Standardization
Ashing is a straightforward, reliable, and widely accepted method for determining total inorganic content. Standardized procedures, such as those from ASTM, ensure that results are comparable and repeatable across different labs.
The Limitation: Lack of Specificity
A standard ashing test provides a single number: the total percentage of ash. It does not, by itself, tell you what specific elements or compounds make up that ash. It cannot distinguish between a beneficial mineral and a toxic heavy metal.
The Next Step: Advanced Analysis
For a detailed elemental breakdown, the ash produced by the furnace is often just the first step. The residue must then be analyzed using more sophisticated techniques, such as X-ray Fluorescence (XRF) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) spectroscopy, to identify the specific elements present.
Applying This to Your Analysis Goal
Your reason for performing an ash test will determine how you interpret the results.
- If your primary focus is quality control for fuels or oils: Use ashing to quickly verify that inorganic contaminant levels are within specified limits.
- If your primary focus is composition in plastics or composites: Use ashing to determine the precise percentage of inorganic filler material, confirming the product meets its design specifications.
- If your primary focus is nutritional analysis of food: Use ashing as the standard method to measure the total mineral content for regulatory compliance and labeling.
- If your primary focus is identifying specific contaminants: View ashing as a preparatory step; the resulting ash must then be analyzed by more advanced spectroscopic methods to identify individual elements.
Ultimately, understanding the purpose of ashing allows you to move from simply measuring a sample's remains to interpreting what those remains signify about its quality and character.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Determines inorganic, non-combustible content by burning organic material and weighing the ash residue. |
| Key Industries | Petroleum, coal/biofuels, polymers/composites, food/feed. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 500°C to 900°C for complete combustion. |
| Critical Factors | Controlled temperature, proper airflow, and precise weighing for accuracy. |
| Benefits | Simple, standardized method for assessing purity, composition, and quality. |
| Limitations | Provides total ash percentage only; advanced analysis needed for specific elements. |
Need a reliable ashing furnace for your lab? KINTEK specializes in high-temperature furnace solutions, including ashing furnaces, designed for precise and repeatable results. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Enhance your quality control and analytical processes—contact us today to discuss how we can support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- How is the thermal stability of KBaBi compounds evaluated? Discover Precise XRD & Heat Treatment Limits
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control



















