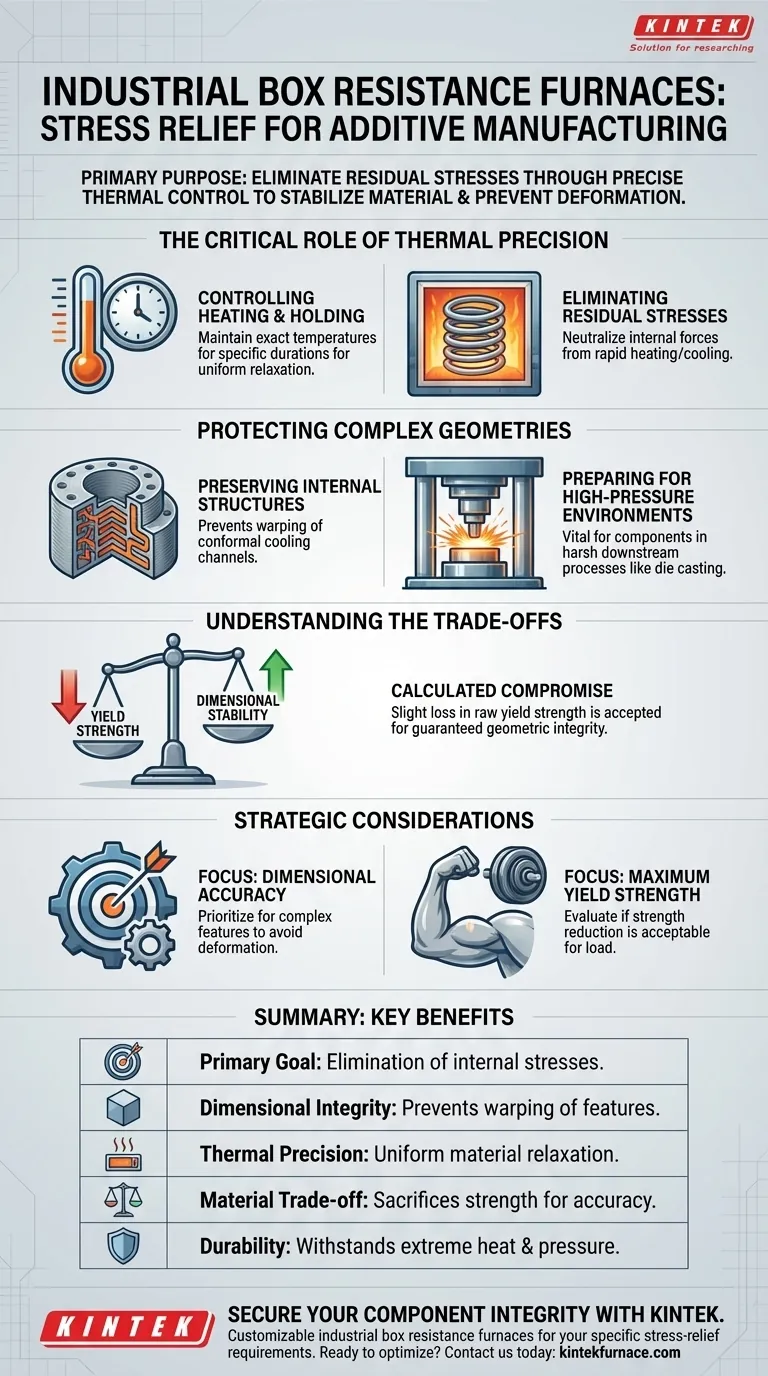
The primary purpose of using industrial box resistance furnaces for additive manufacturing components is to eliminate residual stresses through precise thermal control. By rigorously managing heating temperatures and holding times, these furnaces stabilize the material structure, preventing deformations that would otherwise compromise the component during subsequent high-pressure applications.
Core Takeaway: Additive manufacturing inherently creates internal material tension. Stress relief heat treatment sacrifices a degree of raw yield strength to ensure the dimensional stability and structural integrity required for complex features, such as internal cooling channels, to survive future manufacturing steps.

The Critical Role of Thermal Precision
Controlling Heating and Holding
Industrial box resistance furnaces are selected for this task because of their ability to deliver consistent and precise heat.
To effectively relieve stress, the equipment must maintain exact temperatures for specific durations (holding times).
This precision is necessary to uniformly relax the material without inducing new thermal gradients.
Eliminating Residual Stresses
The additive manufacturing process involves rapid heating and cooling, which locks residual stresses into the metal.
If left untreated, these internal forces act like a compressed spring waiting to release.
The furnace provides the thermal environment needed to neutralize these forces before the part is put into service.
Protecting Complex Geometries
Preserving Internal Structures
Many additive components, such as molds or dies, feature intricate internal designs like conformal cooling channels.
These channels are highly susceptible to warping if residual stresses are not removed.
Heat treatment ensures these invisible, critical pathways remain open and dimensionally accurate.
Preparing for High-Pressure Environments
This treatment is particularly vital for components intended for harsh downstream processes, such as high-pressure die casting.
During die casting, the component is exposed to extreme heat and crushing pressure.
Without prior stress relief, the component would likely deform or fail unexpectedly under these conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Yield Strength vs. Dimensional Stability
It is important to acknowledge that this heat treatment alters the mechanical properties of the material, specifically aluminum alloys.
The process often results in a reduction of the material's yield strength.
However, this is a calculated compromise: the slight loss in strength is accepted to gain the essential guarantee of dimensional stability and geometric integrity.
Strategic Considerations for Heat Treatment
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Deciding on the parameters for stress relief requires balancing mechanical requirements with geometric precision.
- If your primary focus is Dimensional Accuracy: Prioritize this treatment to ensure complex internal features, like cooling channels, do not deform during use.
- If your primary focus is Maximum Yield Strength: Evaluate if the reduction in strength caused by thermal relaxation is acceptable for your specific application load.
Ultimately, the goal is to transform a printed shape into a reliable, engineering-grade component capable of withstanding industrial rigors.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Benefit for Additive Manufacturing Components |
|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Elimination of internal residual stresses and material stabilization. |
| Dimensional Integrity | Prevents warping of complex features like internal cooling channels. |
| Thermal Precision | Precise heating and holding times ensure uniform material relaxation. |
| Material Trade-off | Sacrifices a degree of raw yield strength for improved geometric accuracy. |
| Durability | Prepares components to withstand extreme heat and high-pressure environments. |
Secure Your Component Integrity with KINTEK
Don't let residual stresses compromise your additive manufacturing success. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized industrial box resistance furnaces—all customizable to your specific stress-relief requirements. Whether you are protecting intricate internal cooling channels or prepping components for high-pressure die casting, our thermal solutions ensure the dimensional stability and reliability your projects demand.
Ready to optimize your heat treatment process? Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your lab!
Visual Guide
References
- Dirk Lehmhus, M. Dalgiç. Combining Metal Additive Manufacturing and Casting Technology: High Performance Cooling Channels for Electric Powertrain Components. DOI: 10.1002/adem.202500445
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature muffle furnace play in g-C3N4 catalyst synthesis? Precision Pyrolysis Solutions
- What role does a laboratory muffle furnace play in the fluorination roasting stage of NdFeB waste recovery?
- What is the significance of the calcination process? Engineering SrMo1-xNixO3-δ Nanocrystals via Muffle Furnace
- How does a muffle furnace differ from a pusher furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- What is the primary application of a muffle furnace in coal tar processing? Optimize Your Pyrolysis Results
- Why is a muffle furnace essential for Sn:ZnO nanopowders? Achieve Perfect Crystal Structure and Purity
- What are the environmental conditions for a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe, Accurate High-Temperature Operations
- What role does a high-temperature laboratory furnace play in BaTiO3? Master Dislocation Injection & Plasticity



















