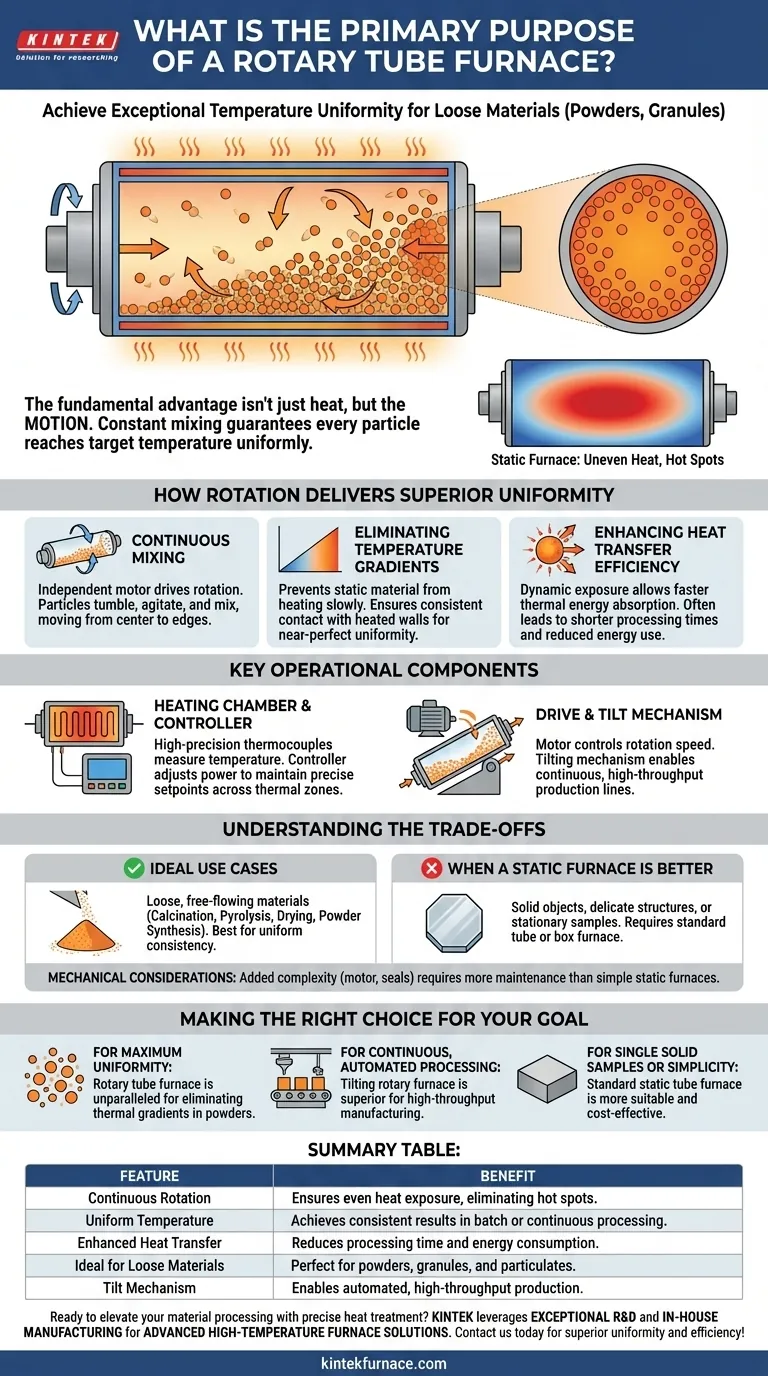
At its core, a rotary tube furnace is engineered for a single, critical purpose: to achieve exceptional temperature uniformity when heat-treating loose materials like powders, granules, or other particulates. By continuously rotating the furnace tube, it ensures every particle is exposed to the heat source evenly, enabling highly consistent physiochemical processing on a batch or continuous basis.
The fundamental advantage of a rotary tube furnace isn't just the heat, but the motion. Unlike static furnaces that can create hot spots, the constant mixing action guarantees that the entire volume of material reaches the target temperature uniformly, leading to more reliable and repeatable results.
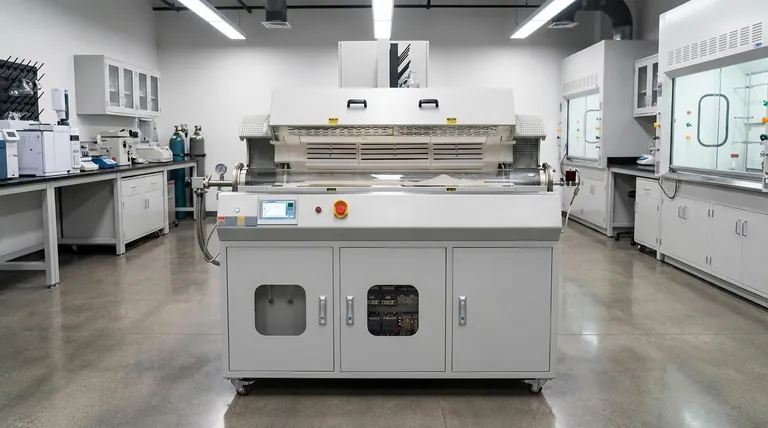

How Rotation Delivers Superior Uniformity
The defining feature of this furnace is its ability to rotate. This simple mechanical action is the key to its unique processing capabilities, solving problems that static heating methods cannot.
The Principle of Continuous Mixing
An independent motor drives the rotation of the circular furnace tube. As the tube rotates, the loose material inside is gently tumbled and mixed.
This constant agitation ensures that particles from the center of the batch are brought to the outer edges, and vice-versa.
Eliminating Temperature Gradients
In a static furnace, material resting at the bottom or in the center heats more slowly than the material near the tube walls. This creates a temperature gradient, resulting in an unevenly processed product.
The rotary action eliminates these gradients. By ensuring every particle has consistent contact with the heated tube wall, the entire sample is maintained at a near-perfectly uniform temperature.
Enhancing Heat Transfer Efficiency
The movement of the material also significantly improves heat transfer. This dynamic exposure to the heat source allows the material to absorb thermal energy more quickly and efficiently than a stationary pile would.
This often leads to shorter processing times and reduced energy consumption for the same outcome.
Key Operational Components
A rotary tube furnace integrates several systems to achieve its precise control over the processing environment. Understanding these components clarifies how it functions.
The Heating Chamber and Controller
The system uses high-precision thermocouples to measure the temperature inside the furnace tube. These sensors feed data back to a temperature controller.
The controller then adjusts the power supplied to the heating elements, ensuring the internal temperature precisely follows the programmed setpoints across one or multiple thermal zones.
The Drive and Tilt Mechanism
The rotation itself is managed by a motor, which can often be set to a constant or variable speed to control the degree of mixing.
Many industrial models also feature a tilting mechanism. By angling the furnace, material can be fed in one end and continuously transported through the heating zone to exit the other, enabling automated, high-throughput production lines.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is not the universal solution for all thermal processing. Its specialized design comes with specific advantages and limitations.
Ideal Use Cases
This furnace excels in applications involving loose, free-flowing materials. Common uses include calcination, pyrolysis, drying, and synthesizing powdered materials where final product consistency is paramount.
If you need to ensure a batch of powder is chemically or physically identical from top to bottom, a rotary furnace is the ideal tool.
When a Static Furnace Is Better
A rotary furnace is unsuitable for processing solid objects, delicate structures, or samples that must remain stationary, such as growing crystals or annealing a silicon wafer.
In these cases, a standard (non-rotating) tube furnace or a box furnace would be the appropriate choice.
Mechanical Considerations
The addition of a motor, rotating seals, and a drive mechanism introduces mechanical complexity. These components require more maintenance than a simple, static furnace, which is a factor to consider in terms of long-term operational cost and reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct furnace type requires aligning the equipment's core function with your specific processing objective.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum uniformity in powders or granules: The rotary tube furnace is unparalleled for eliminating thermal gradients and ensuring a consistent final product.
- If your primary focus is continuous, automated material processing: The tilting capability of an industrial rotary furnace makes it the superior choice for high-throughput manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is heat-treating a single, solid sample or you require a simpler setup: A standard, static tube furnace is more suitable and cost-effective for your application.
By understanding that the value lies in its rotational mixing, you can confidently determine if a rotary tube furnace is the right tool to achieve your processing goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Continuous Rotation | Ensures even heat exposure for all particles, eliminating hot spots |
| Uniform Temperature | Achieves consistent results in batch or continuous processing |
| Enhanced Heat Transfer | Reduces processing time and energy consumption |
| Ideal for Loose Materials | Perfect for powders, granules, and particulates |
| Tilt Mechanism | Enables automated, high-throughput production lines |
Ready to elevate your material processing with precise heat treatment? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our rotary tube furnaces, part of a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, are designed for superior uniformity and efficiency. With strong deep customization capabilities, we can precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your lab's performance and deliver reliable, repeatable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control



















