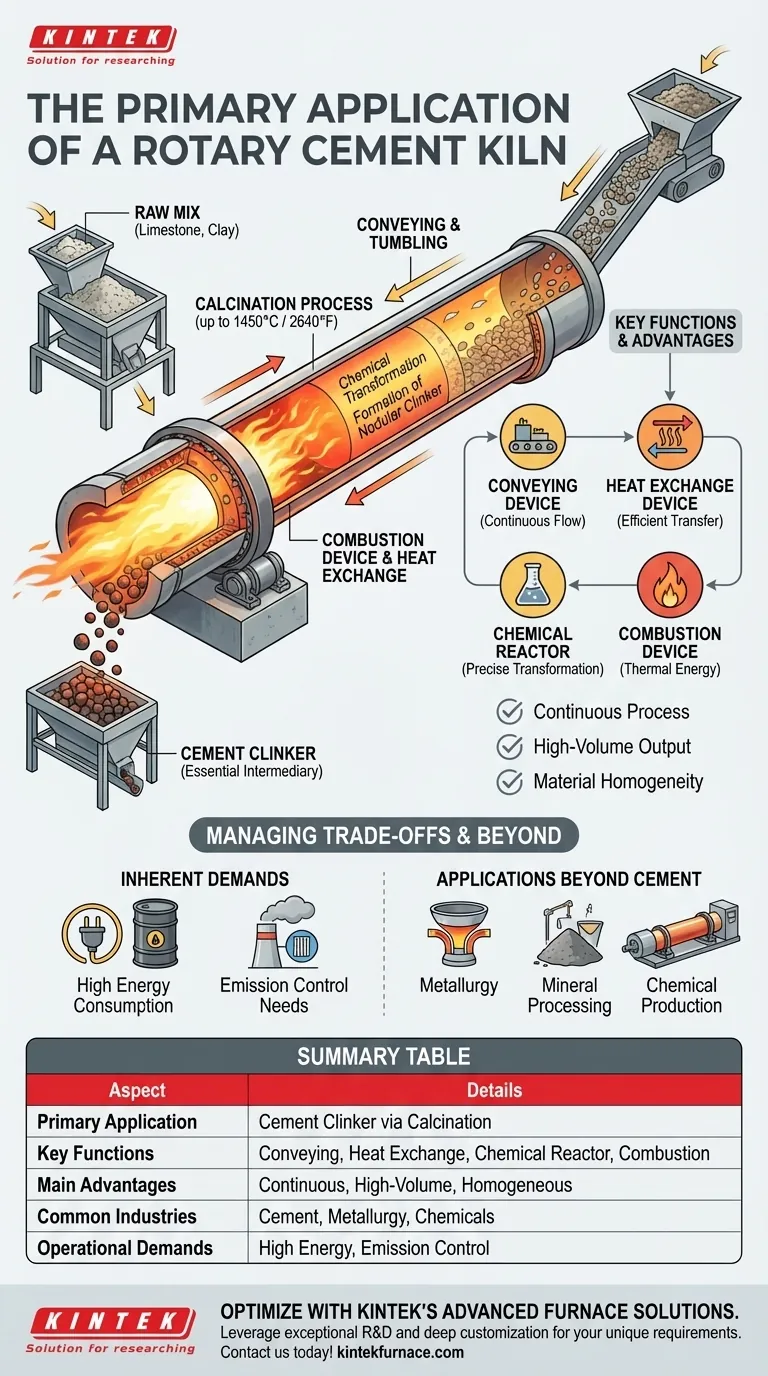
The primary application of a rotary cement kiln is the production of cement clinker, the essential intermediary material used to manufacture all modern cement. This high-temperature process, known as calcination, chemically transforms a mixture of limestone, clay, and other materials into the nodular, marble-sized clinker that forms the basis of concrete.
A rotary kiln is not merely a furnace; it is a dynamic chemical reactor. Its core purpose is to use extreme heat and continuous motion to facilitate a precise chemical transformation, converting raw ingredients into a new material with the specific properties required for cement.

The Kiln's Role in Cement Production
The rotary kiln is often called the "heart" of the cement plant because it is the central piece of equipment responsible for the most critical phase change in the entire manufacturing process.
From Raw Mix to Clinker
A finely ground raw mix is fed into the upper end of a long, gently sloped, rotating steel cylinder. As the kiln slowly turns, the material gradually tumbles down toward the lower, hotter end.
This journey exposes the material to increasingly high temperatures, often reaching up to 1450°C (2640°F). This intense heat drives off water, decomposes the limestone into calcium oxide, and fuses the materials into new compounds, forming the clinker.
More Than a Furnace: Its Four Functions
A rotary kiln serves four distinct roles simultaneously:
- Conveying Device: The rotation and incline of the kiln continuously move material from the feed end to the discharge end.
- Heat Exchange Device: It efficiently transfers heat from the burner flame and hot gases to the material bed.
- Chemical Reactor: It provides the high-temperature environment needed for the essential chemical reactions of calcination to occur.
- Combustion Device: The lower end houses a powerful burner that provides the thermal energy required for the entire system.
The Importance of Uniform Processing
The slow, constant rotation is critical. It ensures homogeneity by continuously mixing the material, preventing hot spots and guaranteeing that every particle is exposed to the same temperature profile. This results in a final clinker product with highly consistent quality.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While indispensable for cement manufacturing, rotary kilns come with inherent operational demands that must be managed.
Why Rotary Kilns Dominate
The rotary kiln design offers several key advantages that make it the industry standard. It facilitates a continuous process, allowing for a constant, high-volume flow of material. Its design is also flexible, capable of producing various types of cement, including Portland, white, and pozzolana cement.
The Inherent Demands: Energy and Emissions
The primary trade-off is immense energy consumption. Maintaining temperatures over 1400°C requires a significant amount of fuel.
Consequently, modern kilns are engineered for maximum thermal efficiency, often with preheaters and precalciners to minimize heat loss. They also require sophisticated emission control systems, such as filters and gas scrubbers, to manage the byproducts of combustion and calcination.
Applications Beyond Cement
While "cement kiln" is in the name, the underlying rotary kiln technology is used in other industries for high-temperature material processing.
Electric rotary kilns, for example, are used in metallurgy, mineral processing, and chemical production. They are ideal for processes requiring precise temperature control for oxidation, reduction reactions, or roasting granular materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the kiln's function helps clarify its application in various industrial contexts.
- If your primary focus is large-scale cement production: The traditional, fuel-fired rotary kiln is the established industry standard for its ability to produce high volumes of homogenous clinker continuously.
- If your primary focus is specialized material processing: An electric rotary kiln may be superior for its precise temperature control, which is critical for specific chemical reactions in metallurgy or advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is operational efficiency: The kiln's design for continuous heat exchange and material flow is paramount to minimizing energy loss and ensuring product consistency.
Ultimately, the rotary kiln's genius lies in its ability to transform simple raw materials into the building blocks of our modern world through a continuous, controlled, and highly efficient thermal process.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Primary Application | Production of cement clinker via calcination at up to 1450°C |
| Key Functions | Conveying, heat exchange, chemical reactor, combustion |
| Main Advantages | Continuous process, high-volume output, material homogeneity |
| Common Industries | Cement production, metallurgy, mineral processing, chemicals |
| Operational Demands | High energy consumption, requires emission control systems |
Optimize Your Industrial Processes with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in cement production, metallurgy, or chemical processing, our expertise ensures enhanced efficiency, precise temperature control, and consistent results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can tailor a solution for your specific needs and drive your projects forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does automated control in electric rotary kilns benefit industrial processes? Achieve Unmatched Precision & Efficiency
- What are the uses of rotary kilns in the building materials industry besides cement clinker? Key Applications Explained
- Why is a Rotary Kiln specifically suitable for treating high-carbon FMDS? Turn Waste Carbon into a Resource
- What advantages do electrically heated rotary kilns offer in temperature control? Achieve Precision and Uniformity for Superior Results
- How does the raw meal move inside the rotary kiln? Master Controlled Flow for Efficient Processing















