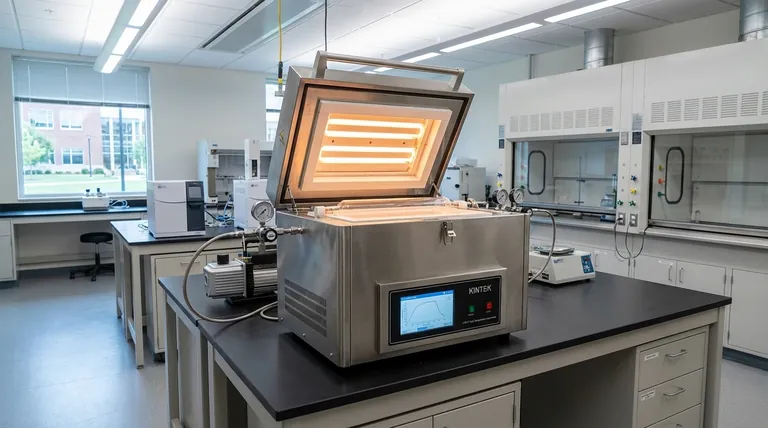
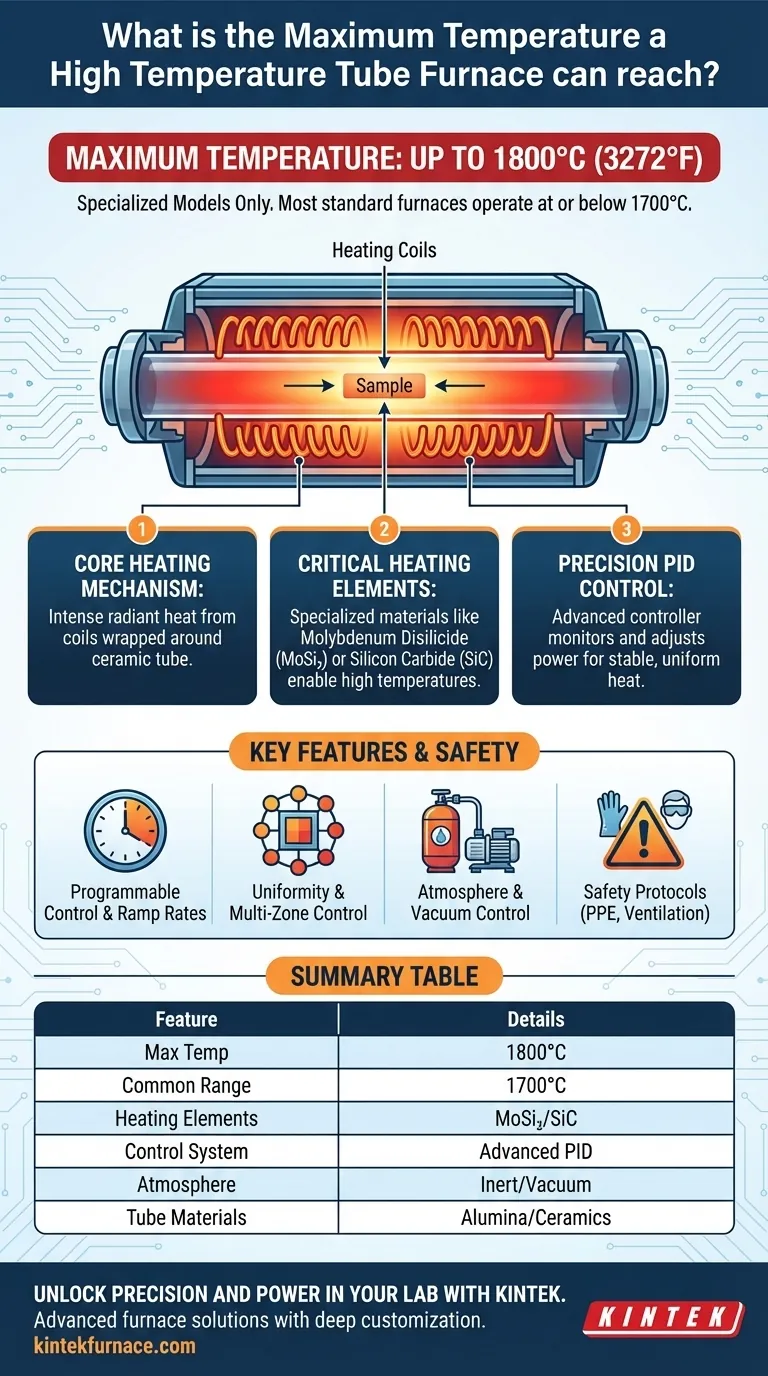
In short, a high-temperature tube furnace can reach a maximum temperature of 1800°C (3272°F). However, this figure represents the upper limit for specialized models. The vast majority of standard high-temperature furnaces operate at or below 1700°C, with the exact maximum temperature being a defining feature that varies significantly from one model to another.
The maximum temperature of a tube furnace is not just a single number, but a result of its specific design, heating elements, and control system. Understanding these components is critical to selecting the right instrument and operating it safely and effectively.

How Tube Furnaces Achieve High Temperatures
A high-temperature tube furnace is an electric heater designed for precise thermal processing of materials. Its performance is determined by the synergy between its heating mechanism, element materials, and control system.
The Core Heating Mechanism
At its heart, the furnace is a simple concept. It consists of a cylindrical ceramic tube that contains the sample. Heating coils are wrapped around this tube, and when a high electrical current is passed through them, they generate intense, radiant heat.
The Critical Role of Heating Elements
The material used for the heating coils is the primary factor that dictates the furnace's maximum temperature. Different materials have different thermal limits. While standard models may use certain alloys, furnaces capable of reaching 1700°C or 1800°C rely on specialized materials like Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) or Silicon Carbide (SiC) elements.
Precision Temperature Control
Achieving a high temperature is only half the battle; maintaining it with stability is crucial. These furnaces use an advanced PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller. This system continuously monitors the temperature via high-resolution thermocouples and makes tiny adjustments to the power, ensuring the heat remains exceptionally stable and uniform.
Key Features That Define Performance
Beyond raw temperature, several features determine a furnace's suitability for a specific research or production task. These capabilities allow for highly repeatable and complex thermal processes.
Programmable Control and Ramp Rates
Modern furnaces are fully programmable. Users can define a precise temperature profile, including the ramp rate (how quickly it heats up), the soak time (how long it holds a temperature), and the cooling rate.
Uniformity and Multi-Zone Control
For larger samples, maintaining a perfectly even temperature across the entire heating zone is a challenge. Advanced models solve this with multi-zone control, using several independent sets of heating coils and sensors along the tube to ensure thermal uniformity.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Control
Many chemical processes are sensitive to oxygen. Tube furnaces are designed to be sealed, allowing users to connect gas lines to create an inert atmosphere (like Nitrogen or Argon) or connect a pump to create a vacuum.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Protocols
Operating equipment at such extreme temperatures requires a clear understanding of its limitations and the associated safety procedures. This is non-negotiable for operator safety and experimental success.
Not All Models Are Created Equal
It is critical to remember that an "1800°C furnace" is a specialized piece of equipment. Do not assume any tube furnace can reach this level. Always confirm the manufacturer's specified maximum operating temperature and never exceed it.
The Importance of Tube Material
The process tube itself must be able to withstand the target temperature. Common quartz tubes are only suitable for lower temperatures (around 1100°C), while higher temperatures demand tubes made from high-purity alumina or other advanced ceramics.
Essential Safety Measures
Working with these furnaces demands strict adherence to safety protocols. Always wear heat-resistant gloves and safety goggles. Ensure the area is well-ventilated, especially when processing materials that could release gases. Only trained personnel should operate the furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on your primary goal. The "best" furnace is the one that meets your specific technical requirements for temperature, control, and atmosphere.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures: You must select a specialized furnace explicitly rated for 1700°C or 1800°C, which will be equipped with the appropriate advanced heating elements.
- If your primary focus is precision and repeatability: Prioritize a furnace with a multi-zone PID controller and a fully programmable interface to ensure your thermal profiles are executed perfectly every time.
- If your primary focus is processing sensitive materials: Ensure the model you choose has the necessary ports and seals to support a vacuum or the specific inert gas atmosphere your work requires.
Ultimately, understanding your own process requirements is the key to leveraging the full power of a high-temperature tube furnace.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | Up to 1800°C (3272°F) for specialized models |
| Common Operating Range | Up to 1700°C for standard models |
| Key Heating Elements | Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂), Silicon Carbide (SiC) |
| Control System | Advanced PID for precise temperature stability |
| Atmosphere Options | Inert gases (e.g., Nitrogen, Argon), vacuum |
| Tube Materials | Alumina or advanced ceramics for high temperatures |
Unlock Precision and Power in Your Lab with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need to reach extreme temperatures up to 1800°C, ensure uniform heating, or handle sensitive materials under controlled atmospheres, we deliver reliable, tailored solutions that enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can elevate your research and production processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency



















