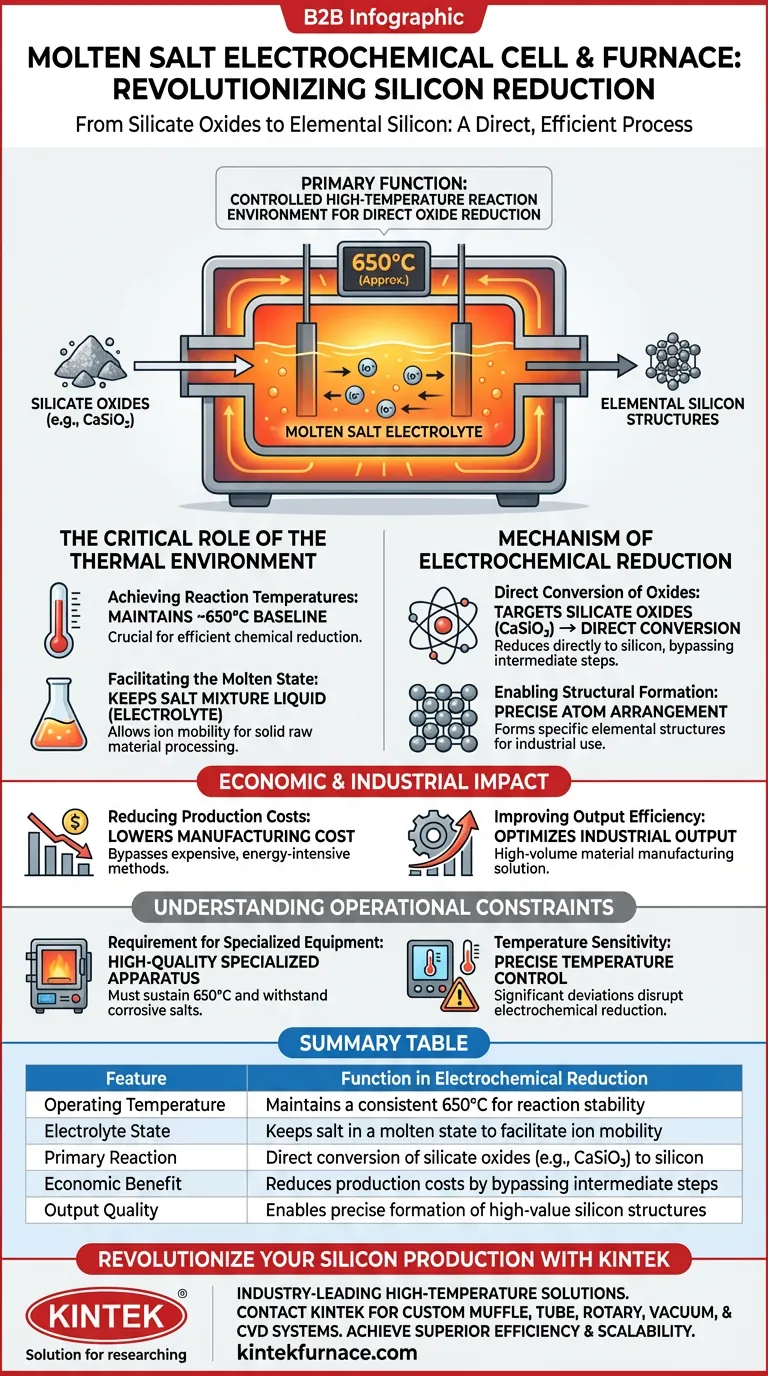
The primary function of a molten salt electrochemical cell is to create a controlled high-temperature reaction environment capable of converting silicate oxides directly into elemental silicon. By maintaining a steady temperature of approximately 650°C, the furnace enables the specific electrochemical conditions required to reduce complex materials, such as calcium silicate (CaSiO3), into usable silicon structures.
While standard extraction methods can be complex, the molten salt furnace solves the efficiency challenge by providing a specialized medium for direct oxide reduction. This approach significantly lowers production costs while improving the scalability of silicon material manufacturing.

The Critical Role of the Thermal Environment
Achieving Reaction Temperatures
The fundamental purpose of the furnace is to establish and maintain a thermal baseline of approximately 650°C.
This specific temperature is critical for the process. Without this consistent heat, the chemical reduction of silicate materials cannot occur efficiently.
Facilitating the Molten State
The furnace ensures the salt mixture remains in a liquid, molten state.
This molten system acts as the electrolyte necessary for the reaction. It allows for the mobility of ions required to process solid raw materials into elemental forms.
Mechanism of Electrochemical Reduction
Direct Conversion of Oxides
The electrochemical cell, operating within this furnace, targets silicate oxides like calcium silicate (CaSiO3).
It facilitates a direct conversion process. Rather than requiring multiple intermediate steps, the system reduces these oxides straight into elemental silicon structures.
Enabling Structural Formation
The environment provided by the furnace allows for the precise arrangement of silicon atoms.
This results in the formation of specific elemental structures desirable for industrial applications, derived directly from the raw silicate inputs.
Economic and Industrial Impact
Reducing Production Costs
Utilizing this specialized furnace equipment drives down the overall cost of manufacturing.
By enabling direct electrochemical reduction, the process bypasses more expensive, energy-intensive traditional methods of silicon extraction.
Improving Output Efficiency
The combination of the furnace and the electrochemical cell optimizes industrial output.
This system increases the efficiency of silicon production, making it a viable solution for high-volume material manufacturing.
Understanding the Operational Constraints
Requirement for Specialized Equipment
Success in this process is strictly tied to the quality of the furnace equipment.
Standard thermal units are insufficient; the process requires specialized apparatus capable of sustaining the 650°C environment while withstanding the corrosive nature of molten salts.
Temperature Sensitivity
The process relies on precise temperature control.
Deviating significantly from the 650°C target can disrupt the electrochemical reduction, preventing the effective conversion of calcium silicate into elemental silicon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology aligns with your manufacturing objectives, consider the following:
- If your primary focus is cost reduction: Leverage molten salt electrolysis to lower operational expenses by bypassing multi-step extraction processes.
- If your primary focus is raw material flexibility: Adopt this method to process silicate oxides (like CaSiO3) directly, turning abundant raw materials into high-value elemental silicon.
By controlling the thermal and electrochemical environment, you unlock a more direct, efficient path to silicon production.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Electrochemical Reduction |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature | Maintains a consistent 650°C for reaction stability |
| Electrolyte State | Keeps salt in a molten state to facilitate ion mobility |
| Primary Reaction | Direct conversion of silicate oxides (e.g., CaSiO3) to silicon |
| Economic Benefit | Reduces production costs by bypassing intermediate steps |
| Output Quality | Enables precise formation of high-value silicon structures |
Revolutionize Your Silicon Production with KINTEK
Are you looking to optimize your electrochemical reduction processes? KINTEK provides industry-leading high-temperature solutions tailored for specialized lab and industrial needs. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to withstand the corrosive nature of molten salts and maintain precise thermal control.
Whether you are processing calcium silicate or developing advanced elemental silicon structures, our technical team is ready to help you achieve superior efficiency and scalability. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique project requirements!
Visual Guide
References
- Xinyu Chen, Lin Zeng. Advancing high‐performance one‐dimensional Si/carbon anodes: Current status and challenges. DOI: 10.1002/cnl2.118
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- How does an ultra-high vacuum preparation chain assist in the preparation of RCu samples? Ensure Pristine Data
- What is the importance of a vacuum drying oven in In2O3/C electrode prep? Ensure High-Accuracy Battery Testing
- Why is a multi-stage vacuum evaporation system utilized in FMDS treatment? Maximize Efficiency and Resource Recovery
- What is the function of a laboratory vacuum drying oven in W-Ni2P@NiFe LDH/NF preparation? Optimize Electrocatalysts
- What technical advantages do vacuum drying ovens offer for NH2-MIL-125? Preserve MOF Integrity with Precision Drying
- What are the key advantages of using continuous vacuum furnaces in metal heat treatment? Boost Efficiency and Quality
- What is a vacuum furnace and what are its main advantages? Discover Superior Material Processing
- What are the critical steps in the vacuum arc furnace process? Achieve Unmatched Metal Purity and Performance



















