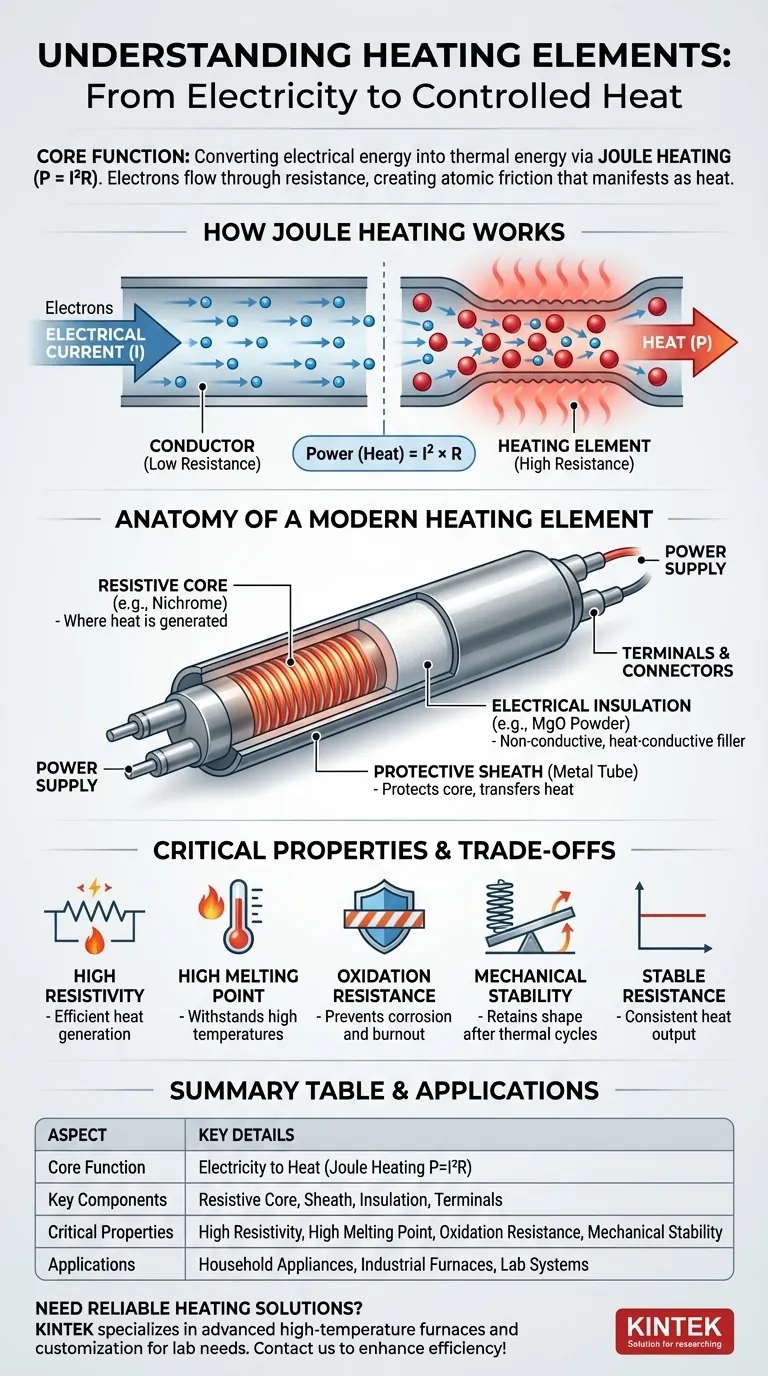
At its core, a heating element's function is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy, or heat. This transformation is achieved through a principle known as Joule heating, which occurs when electrical current flowing through a material encounters resistance. This resistance effectively creates atomic-level friction, which manifests as heat.
A heating element is not merely a wire that gets hot. It is an engineered component designed to intentionally resist the flow of electricity in a controlled, safe, and durable manner to produce a specific amount of heat.
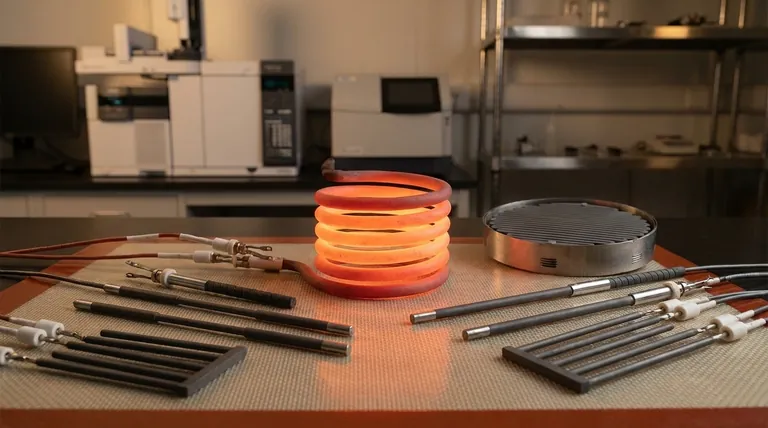

The Core Principle: How Joule Heating Works
The function of a heating element is rooted in a fundamental law of physics. Understanding this process reveals why specific materials and designs are necessary.
The Flow of Electricity Meets Resistance
When you apply a voltage, you create a flow of electrons—an electrical current. In a perfect conductor, these electrons would flow with no opposition. However, all materials have some degree of electrical resistance.
From Friction to Heat
As electrons move through the resistive material of a heating element, they collide with the atoms of that material. These constant collisions impede the electrons' flow and transfer their kinetic energy to the atoms, causing them to vibrate more rapidly. This increased atomic vibration is what we perceive as heat.
Quantifying the Heat
This relationship is described by Joule's first law, often expressed as P = I²R. This formula shows that the power (P), or heat generated per second, is proportional to the square of the current (I) multiplied by the material's resistance (R). This makes resistance the most critical design factor for a heating element.
Anatomy of a Modern Heating Element
A complete heating element is a system of components working together, not just the resistive material itself.
The Resistive Core
This is the heart of the element where heat is generated. It's typically a wire or ribbon made of a specialized alloy, like Nichrome (a nickel-chromium blend), which has high resistance.
The Protective Sheath
The core is often encased in a metal tube or sheath. This sheath protects the resistive core from moisture, physical damage, and oxidation, which would otherwise cause it to degrade quickly at high temperatures.
The Electrical Insulation
A crucial, non-conductive material like magnesium oxide (MgO) powder is typically used to fill the space between the core and the sheath. This powder is a brilliant insulator of electricity, preventing shorts, but an excellent conductor of heat, allowing thermal energy to transfer efficiently to the outer sheath.
Terminals and Connectors
These are the components that safely connect the resistive core to the external power supply, completing the circuit.
Understanding the Trade-offs: What Makes a Good Element?
Selecting or designing a heating element involves balancing several key properties. A failure in any one of these areas can lead to poor performance or a short operational life.
High Resistivity
The material must have high electrical resistance to generate significant heat efficiently. A low-resistance material would require an impractically large current to get hot and would function more like a simple conductor.
High Melting Point
This is non-negotiable. The element must be able to operate at its intended high temperature without melting, softening, or deforming.
Resistance to Oxidation
At high temperatures, most metals react with oxygen in the air and corrode or burn out. Effective heating elements form a stable, protective outer layer of oxide that prevents further degradation, ensuring a long service life.
Mechanical Stability
The material must remain strong and not become brittle or warp after thousands of heating and cooling cycles. It needs to maintain its shape and integrity to function reliably.
A Stable Resistance
Ideally, the material's resistance should not change drastically as its temperature changes. A stable resistance (known as a low temperature coefficient of resistance) ensures a consistent and predictable heat output.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding these principles allows you to evaluate the quality and suitability of heating elements in any context, from a household appliance to an industrial furnace.
- If your primary focus is longevity: Prioritize elements with superior oxidation resistance and mechanical stability, as these properties directly combat wear and tear from high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is consistent performance: An element with a low temperature coefficient of resistance is critical, as it ensures the heat output remains stable and predictable across its operating range.
- If your primary focus is safety and efficiency: Pay close attention to the quality of the insulation (like MgO) and the integrity of the outer sheath, as these components prevent electrical hazards and direct heat effectively.
Ultimately, a superior heating element is a sophisticated system where material science and engineering converge to create controlled heat reliably and safely.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Core Function | Converts electrical energy to heat via Joule heating (P = I²R) |
| Key Components | Resistive core (e.g., Nichrome), protective sheath, electrical insulation (e.g., MgO), terminals |
| Critical Properties | High resistivity, high melting point, oxidation resistance, mechanical stability, stable resistance |
| Applications | Household appliances, industrial furnaces, and other high-temperature systems |
Need a reliable heating solution for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are silicon carbide heating elements essential in high-temperature industries? Unlock Reliable, Extreme Heat Solutions
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights
- What are the properties and applications of silicon carbide (SiC)? Unlock High-Temperature Performance
- What are the advantages of using high purity green silicon carbide powder in heating elements? Boost Efficiency and Lifespan



















