At its core, the difference between Sub-Atmospheric Chemical Vapor Deposition (SACVD) and Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) comes down to the energy source used to drive the chemical reaction. PECVD uses plasma to enable reactions at low temperatures, making it ideal for heat-sensitive materials. In contrast, SACVD uses a specific combination of thermal energy and pressure to achieve high-quality, conformal films at high deposition rates, but it requires higher temperatures.
The fundamental choice between these two processes is a trade-off between your substrate's temperature tolerance and your need for throughput and film conformality. PECVD prioritizes low temperature, while SACVD prioritizes deposition speed and gap-fill performance.
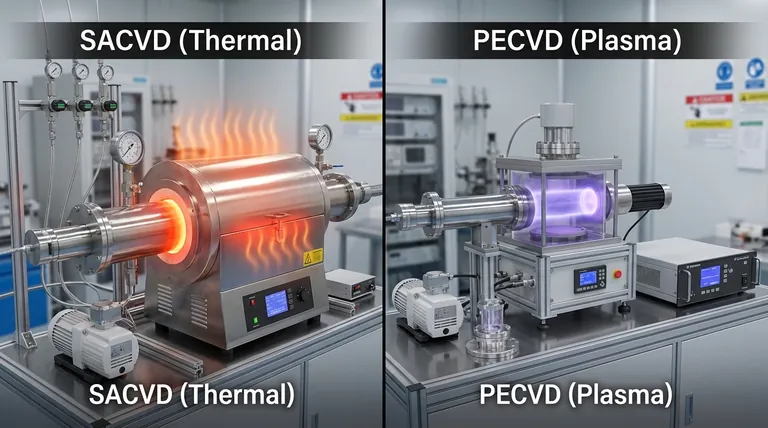
The Core Mechanism: How Energy is Supplied
To select the right process, you must first understand how each one initiates the thin-film deposition. The "energy source" is the defining factor that dictates the process window and ideal applications for each technique.
PECVD: Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
PECVD uses an electric field to ionize precursor gases, creating a plasma. This plasma is a highly energetic soup of ions, electrons, and free radicals.
These reactive species, not high heat, provide the energy needed to break down precursor molecules and deposit a thin film onto the substrate. This allows the process to run at much lower temperatures, typically from room temperature to around 350°C.
SACVD: Sub-Atmospheric Chemical Vapor Deposition
SACVD is a thermal process. It does not use plasma. Instead, it relies on carefully controlled heat and pressure to drive the chemical reaction.
The "Sub-Atmospheric" name refers to running the process at pressures below atmospheric levels but often higher than in other vacuum-based CVD methods. This specific pressure regime, combined with temperatures typically higher than PECVD, is optimized to enhance precursor transport and surface reactions, leading to excellent film properties.
Key Process Differentiators
The difference in energy source leads to distinct advantages and disadvantages in key performance metrics that directly impact manufacturing.
Operating Temperature
This is the most critical distinction. PECVD is the low-temperature champion, essential for depositing films on substrates that cannot withstand high heat, such as polymers or devices with previously fabricated low-melting-point metal layers.
SACVD operates at higher temperatures (e.g., 400°C to 650°C). While lower than some conventional CVD processes, it is significantly hotter than PECVD and can be destructive to temperature-sensitive structures.
Deposition Rate and Throughput
SACVD is engineered for high deposition rates. Its thermal and pressure-driven chemistry is highly efficient, making it a workhorse for applications where manufacturing throughput is a primary concern.
PECVD can have variable deposition rates, but it is generally not chosen when maximum speed is the sole objective. The focus is on enabling deposition that would otherwise be impossible due to thermal constraints.
Film Quality and Conformality
SACVD is renowned for its excellent conformality and gap-fill capability. The process conditions are tuned to ensure the film deposits evenly over complex, high-aspect-ratio topography, such as deep trenches between metal lines in an integrated circuit.
PECVD can produce high-quality films, but their conformality is often inferior to that of high-temperature thermal processes like SACVD. The primary benefit of PECVD is its low-temperature capability, which sometimes comes at the cost of film density or step coverage.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method is never about finding a "perfect" solution. It's about accepting a set of trade-offs that align with your primary goal.
The Temperature vs. Throughput Dilemma
This is the central trade-off. If your device has a strict thermal budget, you must use PECVD. In doing so, you may sacrifice some deposition speed or gap-fill performance.
If your substrate can handle the heat and your priority is fast, conformal gap-fill, SACVD is the superior choice.
Plasma-Induced Damage
A significant consideration for PECVD is the risk of plasma damage. The energetic ions that enable low-temperature deposition can physically bombard the substrate, potentially damaging sensitive electronic structures already present on the wafer. Thermal processes like SACVD do not have this risk.
Precursor Chemistry
Because SACVD relies on specific thermal reactions (e.g., using ozone and TEOS for silicon dioxide), its precursor chemistry is often more constrained. The powerful nature of plasma allows PECVD to utilize a wider range of precursor gases, as the plasma can break down molecules that might not react efficiently in a purely thermal process.
How to Choose the Right Process
Your application requirements will provide a clear answer. Use the following guide to make a definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is depositing on temperature-sensitive materials: PECVD is your only viable choice, as it protects the underlying substrate from thermal damage.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput gap-fill for non-sensitive structures: SACVD is the superior option, delivering excellent conformality at high deposition rates.
- If your primary focus is minimizing any risk of process-induced device damage: A thermal process like SACVD is inherently safer, as it avoids the energetic ion bombardment associated with plasma.
- If your primary focus is film quality on a robust substrate that can tolerate heat: SACVD will generally produce a more conformal and dense film than a low-temperature PECVD process.
By understanding the fundamental role of the energy source, you can confidently select the deposition technology that best aligns with your specific material, thermal, and manufacturing requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | SACVD (Sub-Atmospheric CVD) | PECVD (Plasma-Enhanced CVD) |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | Thermal Energy | Plasma (Electric Field) |
| Operating Temperature | High (400°C - 650°C) | Low (Room Temp - 350°C) |
| Primary Advantage | High Deposition Rate & Conformality | Low-Temperature Processing |
| Ideal For | High-throughput gap-fill on robust substrates | Temperature-sensitive materials & devices |
Struggling to Choose Between SACVD and PECVD for Your Lab?
Selecting the right deposition technology is critical to your research and development success. The choice hinges on your specific substrate, thermal budget, and performance requirements for film conformality and throughput.
KINTEK can be your partner in precision. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide advanced CVD solutions, including PECVD systems, tailored to your unique experimental needs. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace or system is optimized for your specific application, whether you require low-temperature processing or high-speed, conformal deposition.
Let's optimize your process together. Contact our experts today to discuss your requirements and discover the perfect KINTEK solution for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does chemical vapour deposition (CVD) differ from PVD? Key Differences in Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What is PECVD specification? A Guide to Choosing the Right System for Your Lab
- What are the classifications of CVD based on vapor characteristics? Optimize Your Thin Film Deposition Process
- What parameters control the quality of PECVD-deposited films? Master Key Variables for Superior Film Properties
- How does PECVD contribute to semiconductor manufacturing? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Film Deposition



















