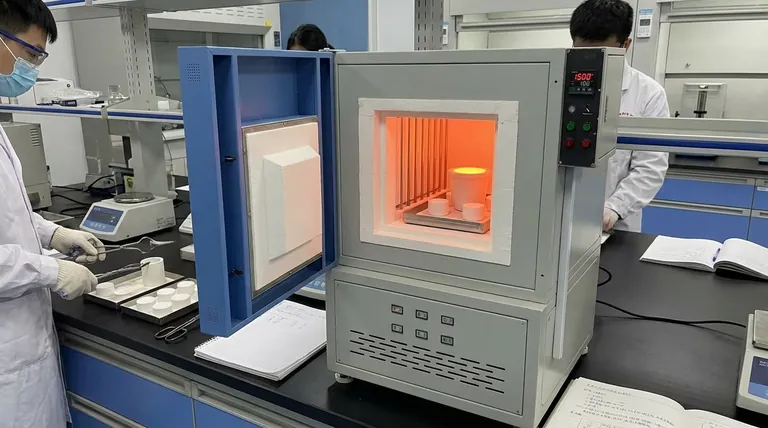
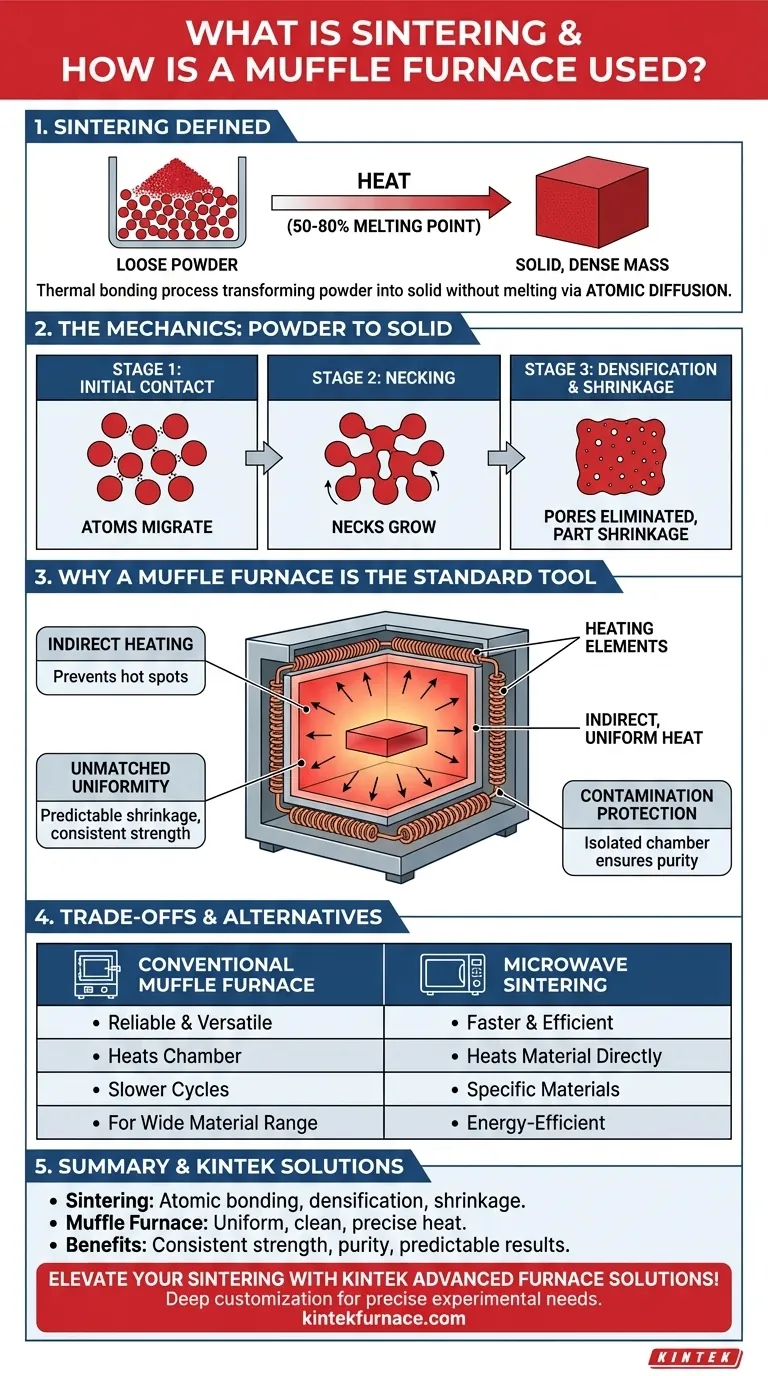
At its core, sintering is a thermal bonding process that transforms loose powder into a solid, dense mass without melting it. It achieves this by heating the material to a temperature high enough to cause atoms to diffuse across the particles' boundaries, effectively welding them together. A muffle furnace is the instrument of choice for this task because its design provides the extremely uniform, controlled, and contaminant-free heat necessary for the process to succeed.
Sintering is not about melting; it's about fusing particles together through atomic motion. The muffle furnace is the ideal environment for this because its isolated chamber delivers the precise, clean, and uniform heat required to create a strong, consistent final product.

The Mechanics of Sintering: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a cornerstone of powder metallurgy and ceramic production. The process fundamentally alters a material's microstructure, turning a collection of individual grains into a cohesive, functional part.
The Role of Temperature
The key to successful sintering is maintaining a temperature that is typically 50% to 80% of the material's absolute melting point.
This temperature is the "sweet spot" where atoms have enough energy to move, but not so much that the bulk material liquefies. Precise temperature control is non-negotiable.
Atomic Diffusion and "Necking"
At the sintering temperature, atoms begin to migrate from the bulk of the particles to the points of contact between them.
This atomic movement builds small "necks," or bridges, at these contact points. Over time, these necks grow wider, pulling the particles closer together and eliminating the empty spaces (pores) between them.
The Result: Densification and Shrinkage
As the necks grow and pores are eliminated, the overall material becomes denser and stronger.
A direct and expected consequence of this densification is shrinkage. A component, such as a zirconia dental crown, will shrink significantly—often up to 20-25%—as it is sintered, a factor that must be precisely accounted for in the initial design.
Why a Muffle Furnace is the Standard Tool
A muffle furnace is not just any oven. Its specific design is engineered to overcome the primary challenges of high-temperature material processing.
The Principle of Indirect Heating
The name "muffle" refers to the furnace's core feature: an isolated inner chamber (the muffle) that contains the material being heated.
The heating elements are located outside this chamber. They heat the chamber's walls, which then radiate heat uniformly onto the workpiece. This indirect heating is crucial for preventing hot spots and ensuring even processing.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
Because heat radiates from all surfaces of the inner chamber, the material is heated evenly from all directions.
This uniformity is essential for predictable shrinkage and for developing consistent strength throughout the final part. Uneven heating would cause warping, internal stresses, and weak points.
Protection from Contamination
The muffle acts as a barrier, separating the workpiece from the heating elements and any potential byproducts of combustion or element degradation.
This ensures the purity of the material is maintained, which is critical for applications in high-strength ceramics, medical implants, and electronic components.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While the muffle furnace is a reliable workhorse, it's important to understand its operational characteristics in the context of other technologies.
The Limitation of Conventional Sintering
Traditional muffle furnaces operate by heating the entire chamber, a process which can be relatively slow and consume significant energy. The ramp-up and cool-down cycles can extend the total processing time considerably.
The Rise of Microwave Sintering
A more modern alternative, the microwave sintering furnace, uses a different heating principle. It uses microwave energy that couples directly with the material itself, generating heat from within.
Key Differences: Speed and Efficiency
Microwave sintering is often much faster and more energy-efficient because it heats the material directly rather than the entire furnace chamber. However, conventional muffle furnaces remain exceptionally versatile, reliable, and are often better suited for larger parts or a wider variety of materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right heating technology depends entirely on your project's specific priorities.
- If your primary focus is process reliability and material versatility: A conventional muffle furnace is the established, robust choice for a wide range of metals, composites, and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is speed and energy efficiency for specific materials: A microwave sintering furnace may be the superior option, especially for advanced ceramic applications where its heating characteristics are a known advantage.
- If your primary focus is achieving specific material properties: Precise control over the temperature cycle—including heating rate, hold time, and cooling rate—is the most critical factor, a core strength of modern, programmable muffle furnaces.
Ultimately, understanding the relationship between the sintering process and the tool you use empowers you to consistently achieve your desired material outcomes.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Details |
|---|---|
| Sintering Process | Thermal bonding of powders without melting, via atomic diffusion and necking, leading to densification and shrinkage. |
| Muffle Furnace Role | Provides uniform, controlled, and contaminant-free heating with indirect heating for precise temperature management. |
| Key Benefits | Ensures consistent strength, predictable shrinkage, and material purity for metals, ceramics, and composites. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 50-80% of material's melting point for effective sintering. |
Elevate your sintering processes with KINTEK's advanced furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering reliable, contaminant-free results for materials like ceramics and metals. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your sintering outcomes and boost efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the core function of a muffle furnace in biomass activation? Optimize Carbonization & Pore Development
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in HZSM-5 preparation? Master Catalytic Activation
- Why is a high-temperature muffle furnace used for Ni-BN powder preheating? Achieve defect-free coating density.
- What is the function of a high-temperature muffle furnace in ZnO-SP preparation? Master Nanoscale Synthesis Control
- What is the critical role of a high-temperature muffle furnace in converting biomass into Fe-N-BC?



















