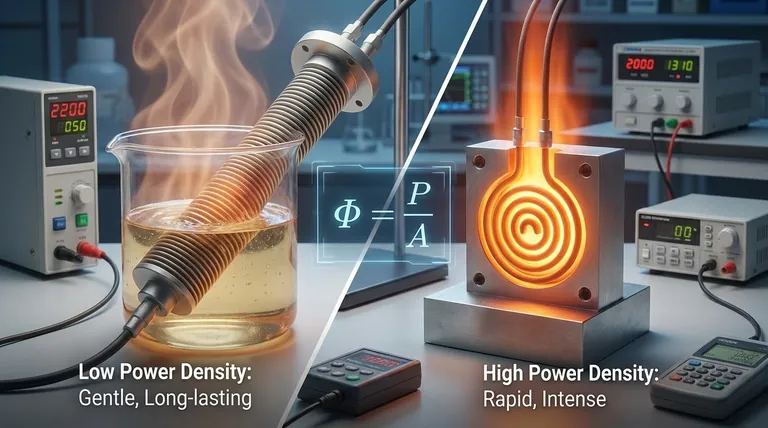
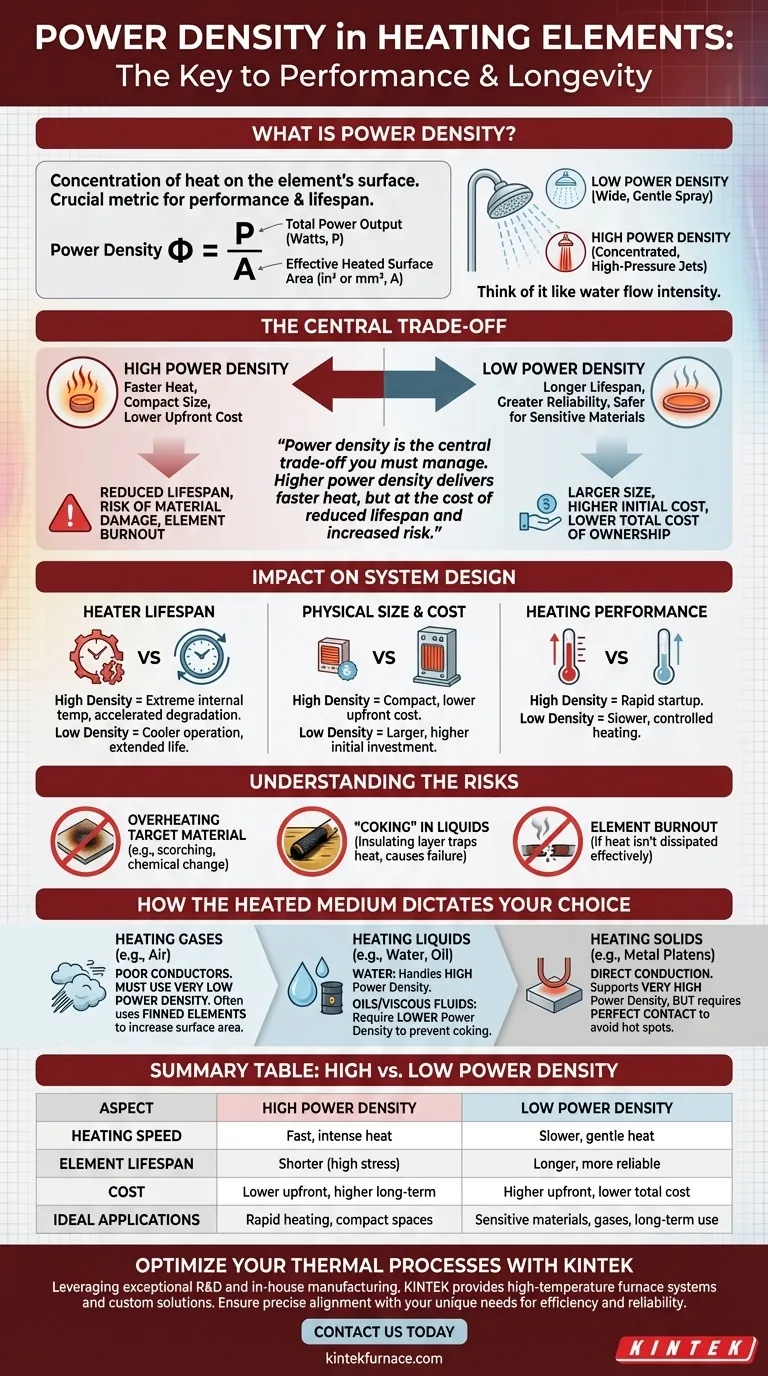
In the world of thermal engineering, power density is the single most important metric for defining a heating element's performance and longevity. It quantifies the concentration of heat on the element's surface. Power density (Φ) is calculated by dividing the heater's total power output in watts (P) by its effective heated surface area (A), typically expressed in watts per square inch or square millimeter.
Power density is not just a technical specification; it is the central trade-off you must manage. A higher power density delivers faster, more intense heat from a smaller element, but often at the cost of reduced lifespan and an increased risk of damaging the material being heated.
The Core Principle: Heat Flux and Concentration
Understanding the Formula
The calculation for power density is straightforward: Φ = P / A.
Think of it like a showerhead. The total water flow (Power) is constant, but you can change its intensity. A wide, gentle spray is low power density, while a few concentrated, high-pressure jets are high power density.
Why It's a Critical Metric
Power density directly determines the heating element's own surface temperature. An element with high power density will run significantly hotter than a low-density element of the same wattage.
This surface temperature dictates the rate and intensity of heat transfer, which directly impacts everything from system reliability to the integrity of the product you are heating.
How Power Density Impacts System Design
Heater Lifespan and Reliability
This is the most direct consequence. A higher power density forces the element's internal resistance wire to operate at extreme temperatures, accelerating its degradation and leading to a shorter service life.
Conversely, a low power density element operates at a cooler, less stressful temperature, ensuring greater reliability and a significantly longer operational lifespan.
Physical Size and Cost
High power density allows you to get more heat out of a smaller physical element. This can be an advantage in tight spaces and often results in a lower upfront cost for the heater itself.
Low-density heaters require a larger surface area to dissipate the same amount of wattage, making them physically bigger and often more expensive to manufacture.
Heating Performance
A high-density heater transfers heat very rapidly due to its high surface temperature. This is useful for applications requiring a quick startup or a rapid temperature increase.
However, this intensity can be a major disadvantage if the surrounding material cannot absorb the heat fast enough.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Power Density Dilemma
The Risk of Overheating the Target Material
A high power density element can easily scorch, burn, or chemically alter the medium it is heating.
For example, using a high-density heater in oil can cause "coking"—where the oil burns onto the element surface. This creates an insulating layer, which traps heat and quickly leads to element failure.
The Cost vs. Longevity Equation
High-density heaters are often cheaper upfront but can lead to higher long-term costs due to frequent replacement and process downtime.
Low-density heaters have a higher initial investment but provide superior reliability, protecting both the process and the equipment for a lower total cost of ownership.
The Danger of Element Burnout
If the heat generated by a high-density element is not drawn away effectively, the element's temperature will rise uncontrollably, leading to premature burnout.
This is a common failure mode when heating gases or when there is poor contact between the heater and a solid surface.
How the Heated Medium Dictates Your Choice
The material you are heating is the most important factor in selecting the appropriate power density. Each medium has a different capacity to absorb heat.
Heating Gases (e.g., Air)
Gases are poor conductors of heat. To heat them effectively without the element destroying itself, you must use a very low power density. This is often achieved with finned elements that dramatically increase the surface area.
Heating Liquids (e.g., Water, Oil)
Water is an excellent medium for heat transfer and can handle high power densities.
Oils and other viscous fluids, however, require significantly lower power densities to prevent chemical breakdown and coking.
Heating Solids (e.g., Metal Platens)
Direct conduction into a solid can support very high power densities, provided there is perfect, uniform contact between the heater and the solid. Any air gaps will act as insulators, creating hot spots that cause immediate failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is rapid heating in a compact space: A higher power density element may be suitable, but you must ensure the target material can withstand the intense heat without damage.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and process stability: Always opt for a lower power density element, even if it has a higher initial cost and a larger footprint.
- If you are heating a sensitive material like oil or plastic: You must use a low power density element to prevent scorching, degradation, and catastrophic system failure.
- If you are heating a gas like air: A low power density element, often with fins to increase surface area, is non-negotiable for effective and safe operation.
Ultimately, choosing the correct power density is about balancing speed, cost, and reliability to ensure the integrity of your entire thermal system.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | High Power Density | Low Power Density |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Speed | Fast, intense heat | Slower, gentle heat |
| Element Lifespan | Shorter due to high stress | Longer, more reliable |
| Cost | Lower upfront, higher long-term | Higher upfront, lower total cost |
| Ideal Applications | Rapid heating in compact spaces | Sensitive materials, gases, long-term use |
Optimize your thermal processes with KINTEK's advanced heating solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with high-temperature furnace systems like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can benefit your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Chairside Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Furnace with Transformer for Ceramic Restorations
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Vacuum Press Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes SIC heating elements superior for high-temperature applications? Unlock Efficiency and Durability
- Why is silicon carbide resistant to chemical reactions in industrial furnaces? Unlock Durable High-Temp Solutions
- What are the properties and capabilities of Silicon Carbide (SiC) as a heating element? Unlock Extreme Heat and Durability
- What makes silicon carbide heating elements resistant to chemical corrosion? Discover the Protective Oxide Layer
- Why are SiC heating elements considered environmentally friendly? Discover Their Eco-Efficiency & Lifespan Insights



















