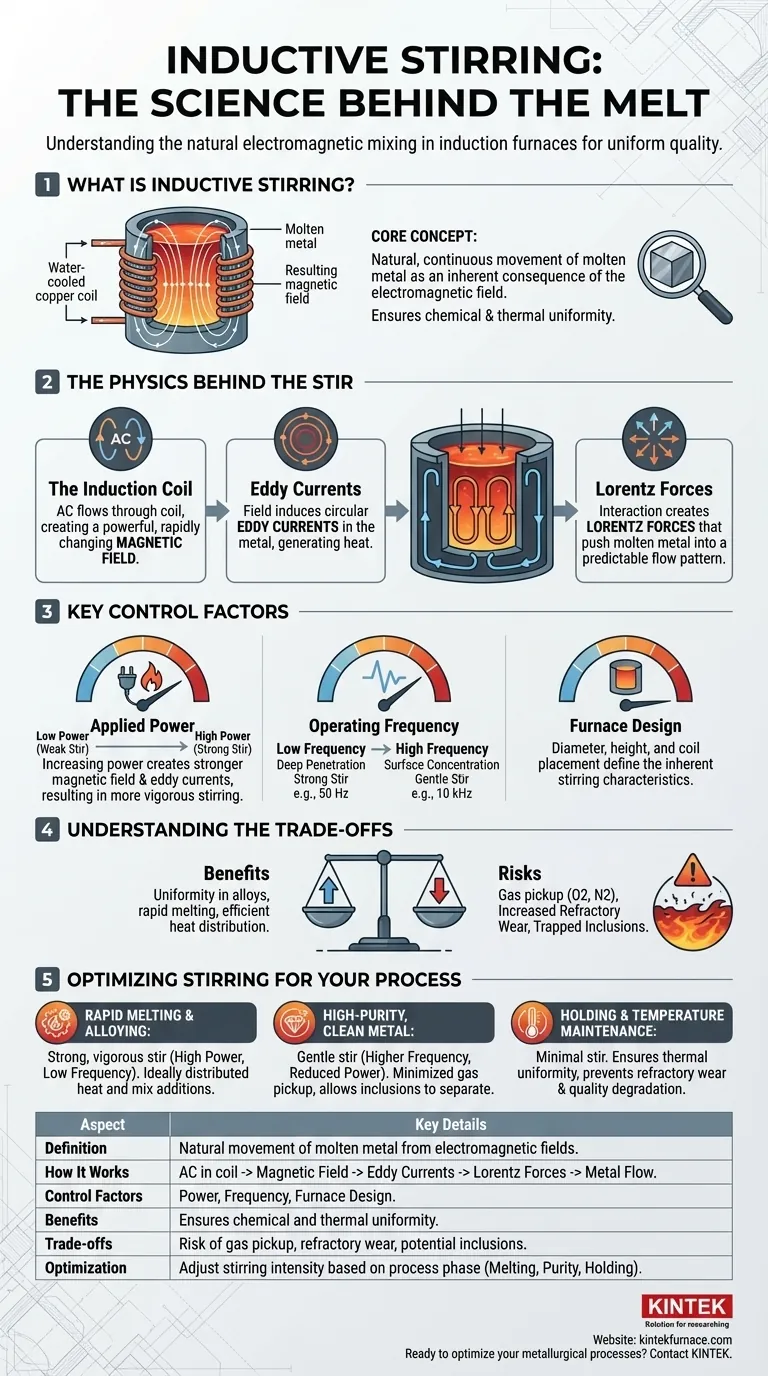
At its core, inductive stirring is the natural, continuous movement of molten metal that occurs within an induction furnace. This self-mixing action is not a separate feature but an inherent consequence of the electromagnetic field used to heat the metal. It plays a critical role in creating a chemically and thermally uniform liquid bath, which is essential for producing high-quality alloys.
The key insight is that induction heating doesn't just melt the metal; it simultaneously creates forces that stir it. Understanding how to control these forces transforms this phenomenon from a simple side effect into a powerful tool for metallurgical process control.
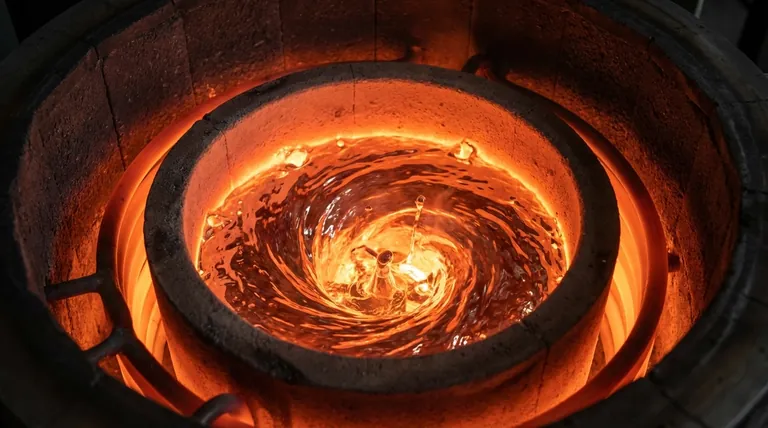

The Physics Behind the Stir: How It Works
To understand inductive stirring, you must first understand how an induction furnace heats metal. The stirring is a direct result of the same physical principles that generate the heat.
The Role of the Induction Coil
An induction furnace uses a coil of water-cooled copper tubing. A powerful alternating current (AC) flows through this coil, generating a strong, rapidly changing magnetic field in the space within and around it.
Creating Eddy Currents
This changing magnetic field passes through the metal charge placed inside the furnace. According to Faraday's law of induction, the magnetic field induces circular electrical currents within the metal. These are known as eddy currents. The resistance of the metal to the flow of these currents generates immense heat, causing the metal to melt.
Lorentz Forces: From Current to Motion
This is the crucial step that causes stirring. The induced eddy currents are now flowing within the same primary magnetic field that created them. The interaction between this magnetic field and the electrical currents generates a physical force known as the Lorentz force.
These forces push the molten metal, creating a predictable flow pattern. The metal is typically forced downwards in the center of the furnace and upwards along the outer walls, resulting in two distinct recirculation loops.
Key Factors Controlling Stirring Intensity
The vigor of the stirring is not fixed; it can be controlled by adjusting several key operational parameters.
Applied Power
The relationship here is direct and intuitive. Increasing the electrical power supplied to the coil creates a stronger magnetic field and induces stronger eddy currents. This results in more powerful Lorentz forces and, consequently, a more vigorous stirring action.
Operating Frequency
The frequency of the alternating current is a critical control lever.
- Low Frequencies (e.g., 50/60 Hz) penetrate deeper into the molten bath, generating strong Lorentz forces throughout the melt. This results in a very strong stirring action.
- High Frequencies (e.g., 1,000 to 10,000 Hz) tend to concentrate the eddy currents near the surface of the melt. This is highly efficient for heating but produces a much gentler stirring action.
Furnace Design and Coil Geometry
The physical design of the furnace—its diameter, height, and the specific shape and placement of the induction coil—fundamentally defines the shape and intensity of the magnetic field. This means the inherent stirring characteristics are "baked in" to the furnace's design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While beneficial, vigorous inductive stirring is not always desirable. It introduces critical trade-offs that must be managed.
Risk of Gas Pickup
A highly turbulent surface increases the contact area between the molten metal and the furnace atmosphere. This can accelerate the absorption of unwanted gases like oxygen and nitrogen, potentially leading to defects in the final cast product.
Increased Refractory Wear
The constant flow of hot, liquid metal acts like an abrasive, eroding the refractory lining of the furnace. A more aggressive stir accelerates this wear, increasing maintenance costs and downtime.
Potential for Inclusions
While stirring helps mix alloys, excessive turbulence can prevent non-metallic impurities (inclusions) from floating to the surface where they can be skimmed off. Instead, the turbulence can drag them back down and trap them within the melt, reducing the cleanliness of the metal.
Optimizing Stirring for Your Process
Controlling stirring intensity is about matching the action to the metallurgical goal. There is no single "best" level of stirring; it depends entirely on the process phase and the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is rapid melting and alloying: A strong, vigorous stir created by high power and low frequency is ideal to quickly distribute heat and mix in alloy additions.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, clean metal: A gentle stir is preferred to minimize gas pickup and allow inclusions to separate. This may involve using higher frequencies or reducing power after the initial melt-down.
- If your primary focus is maintaining temperature in a holding furnace: Only a minimal stir is needed to ensure thermal uniformity, preventing both excessive refractory wear and degradation of metal quality.
By understanding these principles, you can actively manage inductive stirring, turning it from an automatic occurrence into a precise and valuable process variable.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Details |
|---|---|
| Definition | Natural movement of molten metal from electromagnetic fields in induction furnaces, enabling self-mixing. |
| How It Works | AC in coil creates magnetic field, inducing eddy currents and Lorentz forces that drive metal flow. |
| Control Factors | Power (higher = stronger stir), Frequency (low = deep stir, high = gentle stir), Furnace Design. |
| Benefits | Ensures chemical and thermal uniformity, essential for high-quality alloy production. |
| Trade-offs | Risk of gas pickup, increased refractory wear, potential inclusion trapping with excessive stirring. |
| Optimization | Adjust stirring intensity based on process phase: strong for melting/alloying, gentle for purity, minimal for holding. |
Ready to optimize your metallurgical processes with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored equipment like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and quality. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- Why is a Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace essential? Unlock Purity for Aerospace and Semiconductors
- How does vacuum melting technology contribute to sustainability? Boost Durability and Recycling Efficiency
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity
- What is the purpose of vacuum melting, casting and re-melting equipment? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications



















