In semiconductor manufacturing, a vertical tube furnace is a critical piece of equipment used for high-temperature thermal processing of silicon wafers. It provides the precisely controlled environment needed for essential steps like annealing, diffusion, oxidation, and chemical vapor deposition (CVD), which are fundamental to building integrated circuits.
The choice of a vertical furnace is not arbitrary; its design is a direct solution to the semiconductor industry's demand for extreme process uniformity. The vertical orientation provides superior temperature control and leverages gravity for consistent gas flow, resulting in higher quality and more reliable chip production.
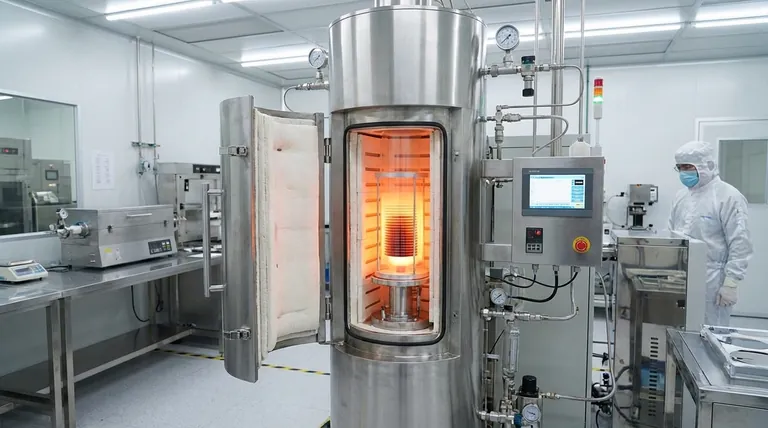

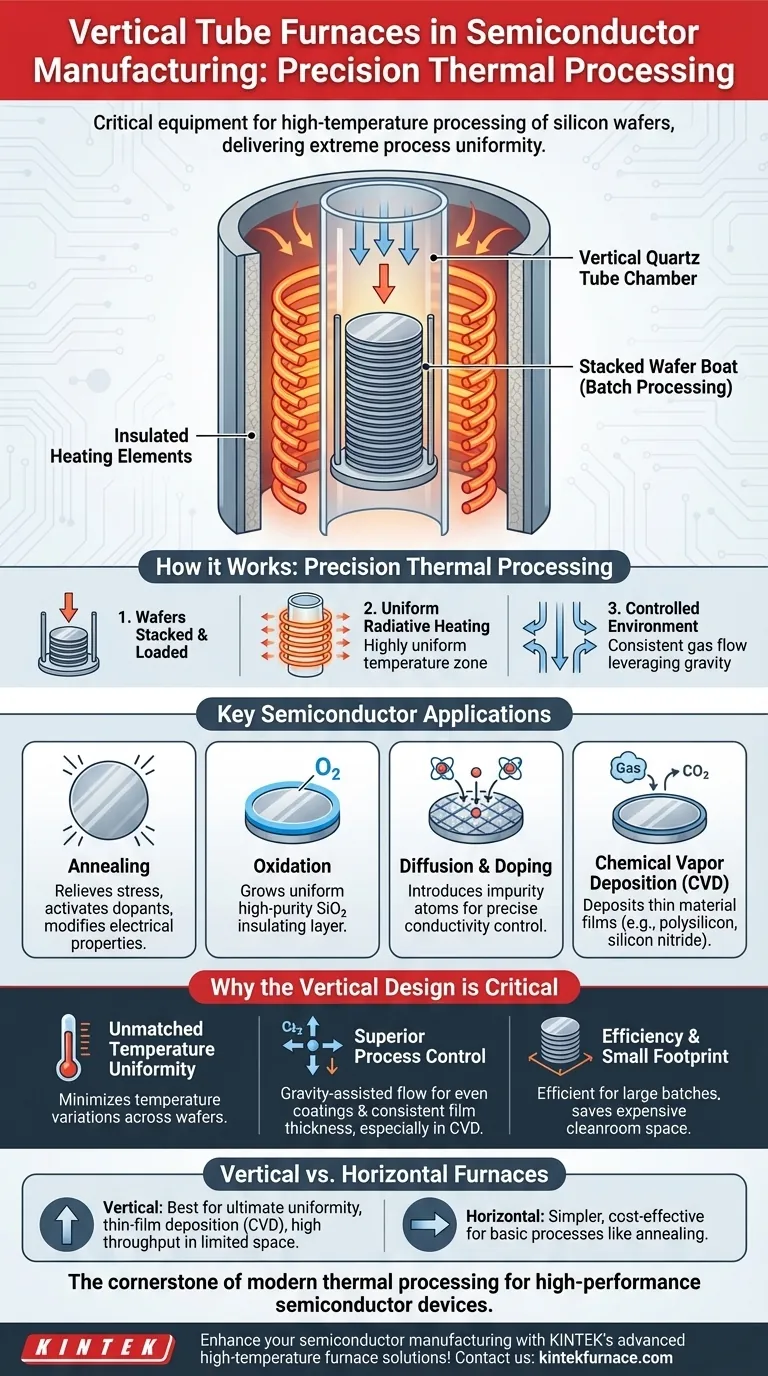
The Core Function: Precision Thermal Processing
A vertical tube furnace is designed for one primary purpose: to heat wafers to a specific temperature, for a specific duration, within an exceptionally stable environment. This precision is non-negotiable in fabricating modern microelectronics.
How a Vertical Tube Furnace Works
The furnace consists of a vertically oriented quartz tube that serves as the processing chamber. Wafers are stacked in a carrier, often called a "boat," and loaded into the bottom of the tube.
Heating elements surround the exterior of the quartz tube. This configuration allows for highly efficient and uniform radiative heat transfer to the wafers inside, ensuring every wafer—and every part of each wafer—experiences the same thermal conditions.
Key Semiconductor Applications
Vertical furnaces are essential for several thermal processes that define a semiconductor's properties.
- Annealing: This process heats wafers to relieve stress in the crystal lattice or to activate implanted dopants, which modifies the silicon's electrical properties.
- Oxidation: Wafers are heated in an oxygen-rich environment to grow a thin, uniform layer of high-purity silicon dioxide (SiO₂), a critical insulating material.
- Diffusion & Doping: This involves introducing impurity atoms (dopants) into the silicon wafer at high temperatures, precisely controlling its conductivity in specific regions.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Process gases are introduced into the tube, where they react at high temperatures and deposit a thin film of material, such as polysilicon or silicon nitride, onto the wafer surface.
Why the Vertical Design is Critical
The vertical orientation offers distinct advantages that are vital for the nanometer-scale precision required in chip manufacturing. It is a deliberate engineering choice driven by the need for process control.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
By stacking wafers vertically and surrounding them with heating elements, a highly uniform temperature zone is created along the length of the tube. This minimizes temperature variations between wafers and across the surface of a single wafer, which is essential for consistent device performance.
Superior Process Control with Gravity
In processes like CVD, gravity is a significant asset. Process gases introduced into the chamber flow more uniformly down and around the vertically stacked wafers. This prevents gas depletion and ensures every wafer receives an even coating, leading to consistent film thickness.
Efficiency in Batch Processing
Vertical furnaces are incredibly efficient for processing large batches of wafers simultaneously. The vertical "boat" carrier system simplifies automated loading and unloading. Furthermore, the vertical design has a much smaller footprint than a comparable horizontal furnace, saving expensive cleanroom floor space.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
While powerful, the vertical furnace is not the only option for thermal processing. Understanding its relationship to other furnace types clarifies its specific role.
Vertical vs. Horizontal Furnaces
Horizontal tube furnaces were the industry standard for many years and are still used for certain applications. They are often simpler and can be suitable for processes like basic annealing or sintering where the ultimate level of uniformity is less critical.
However, for advanced thin-film deposition and processes requiring the tightest control, the vertical furnace's superior temperature uniformity and gravity-assisted gas flow make it the preferred choice in modern fabrication facilities.
Process-Specific Furnace Designs
Different thermal processes can demand specialized equipment. For instance, graphite tube furnaces are specifically designed for ultra-high temperature applications like graphene growth or preparing carbon nanotubes, which operate beyond the limits of standard quartz tubes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a vertical furnace is driven by the specific requirements of the manufacturing process.
- If your primary focus is ultimate uniformity and thin-film deposition (CVD): The vertical furnace's superior temperature control and gravity-assisted flow make it the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing throughput in a limited space: The vertical furnace's high batch capacity and small footprint offer a significant operational advantage.
- If your primary focus is a simpler thermal process like basic annealing: A horizontal furnace may be a sufficient and more cost-effective solution.
Ultimately, the vertical furnace is the cornerstone of modern thermal processing because its design directly enables the precision and repeatability required to manufacture high-performance semiconductor devices.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | Relieves stress and activates dopants | Improves electrical properties |
| Oxidation | Grows silicon dioxide layer | Provides critical insulation |
| Diffusion & Doping | Introduces impurities into silicon | Controls conductivity precisely |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) | Deposits thin films on wafers | Enables uniform coating and device layering |
Enhance your semiconductor manufacturing with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable products like Vertical Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, delivering superior temperature control and process uniformity. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your thermal processing and boost production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















