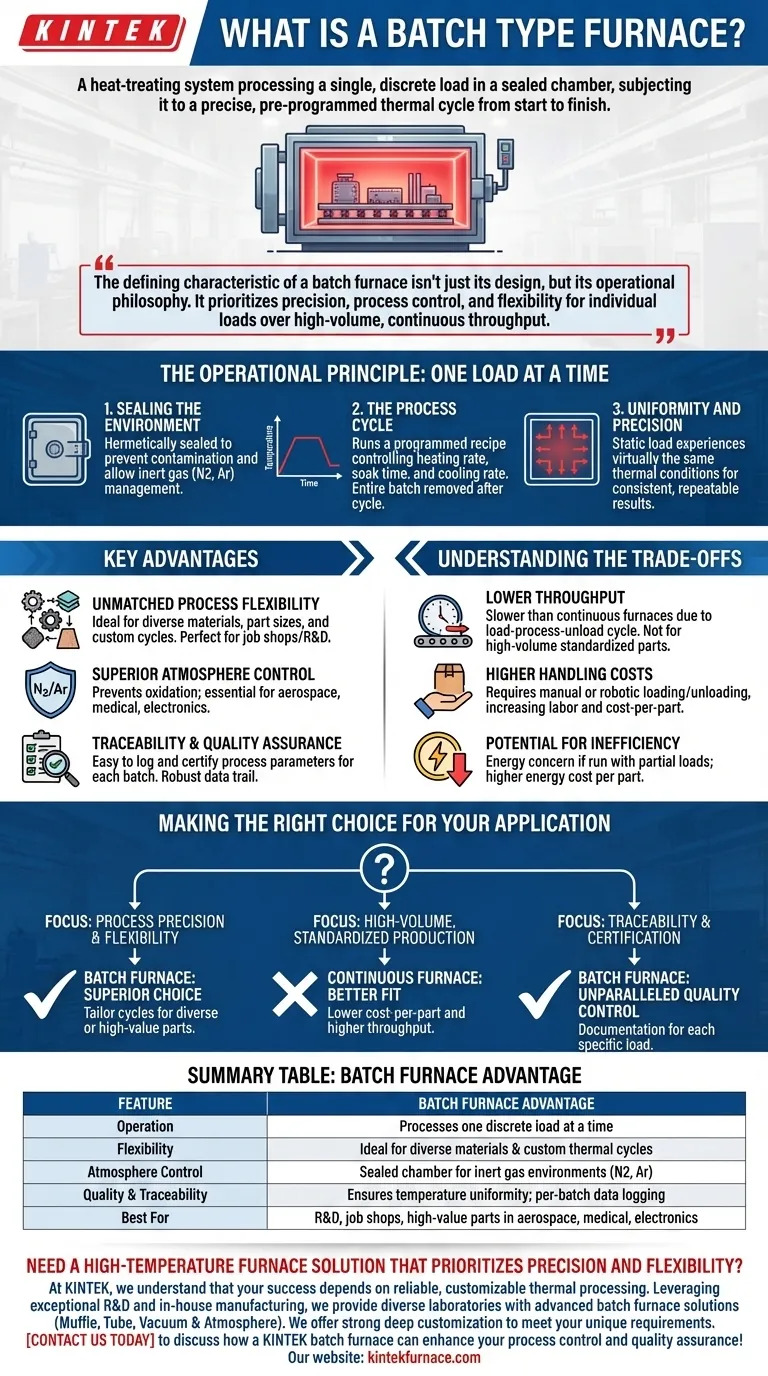
At its core, a batch furnace is a heat-treating system designed to process a single, discrete load of material at a time within a sealed chamber. Unlike continuous furnaces that move parts through different temperature zones, a batch furnace treats the entire load as one unit, subjecting it to a precise, pre-programmed thermal cycle from start to finish.
The defining characteristic of a batch furnace isn't just its design, but its operational philosophy. It prioritizes precision, process control, and flexibility for individual loads over the high-volume, continuous throughput of other furnace types.

The Operational Principle: One Load at a Time
The "batch" method is a deliberate choice centered on control. The entire process revolves around loading a group of parts, sealing the chamber, and executing a specific thermal recipe.
Sealing the Environment
Once the furnace door is closed, the heating chamber is hermetically sealed from the outside environment.
This seal is critical. It prevents contamination and allows for the precise management of the internal atmosphere, such as using inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation on sensitive parts.
The Process Cycle
A typical cycle involves loading the parts, sealing the door, and running a programmed recipe. This recipe controls the rate of heating, the "soak" time at a specific temperature, and the rate of cooling.
After the cycle is complete, the entire batch is removed. This start-and-stop nature is fundamental to its operation.
Uniformity and Precision
Because the entire load is static within the sealed chamber, a batch furnace can achieve exceptional temperature uniformity. Every part in the batch experiences virtually the same thermal conditions, ensuring consistent and repeatable results.
Key Advantages of the Batch Approach
Choosing a batch furnace provides distinct advantages for specific manufacturing and processing goals, particularly where quality and customization are paramount.
Unmatched Process Flexibility
The greatest strength of a batch furnace is its versatility. You can run an annealing process for one batch of steel and immediately follow it with a completely different tempering cycle for another.
This makes it ideal for job shops or R&D environments that handle a wide variety of materials, part sizes, and heat treatment specifications.
Superior Atmosphere Control
The sealed chamber allows for unparalleled control over the furnace atmosphere. This is essential for processing high-value or sensitive materials common in the aerospace, medical, and electronics industries.
By preventing oxygen exposure, batch furnaces ensure parts emerge clean and free of scale or discoloration.
Traceability and Quality Assurance
Because each load is a discrete, traceable event, it is easy to log and certify the exact process parameters for every part in that batch.
This provides a robust data trail for quality control, which is often a strict requirement for critical components used in certified applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technology is a universal solution. The strengths of a batch furnace come with inherent limitations that are important to understand.
Lower Throughput
The most significant trade-off is production volume. The load-process-unload cycle is inherently slower than a continuous furnace that processes parts without interruption.
For high-volume, standardized production of a single part type, a batch furnace is often not the most efficient choice.
Higher Handling Costs
Each batch requires manual or robotic loading and unloading. This introduces labor and handling time into the process, which can increase the overall cost-per-part compared to a fully automated continuous line.
Potential for Inefficiency
Energy efficiency can be a concern if the furnace is frequently run with partial loads. Heating the entire thermal mass of the furnace for a small number of parts can lead to a higher energy cost per part produced.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace technology requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is process precision and flexibility: A batch furnace is the superior choice, allowing you to tailor heat treatment cycles for diverse or high-value parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, standardized production: A continuous furnace will almost always provide a lower cost-per-part and higher throughput for a consistent product stream.
- If your primary focus is traceability and certification: The discrete nature of batch processing provides unparalleled quality control and documentation for each specific load.
Ultimately, selecting a batch furnace is a strategic decision to prioritize control and quality over sheer production volume.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Batch Furnace Advantage |
|---|---|
| Operation | Processes one discrete load at a time |
| Flexibility | Ideal for diverse materials and custom thermal cycles |
| Atmosphere Control | Sealed chamber for inert gas environments (e.g., nitrogen, argon) |
| Quality & Traceability | Ensures temperature uniformity and provides per-batch data logging |
| Best For | R&D, job shops, and high-value parts in aerospace, medical, and electronics industries |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution that prioritizes precision and flexibility?
At KINTEK, we understand that your success depends on reliable, customizable thermal processing. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced batch furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, and Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, is complemented by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental and production requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how a KINTEK batch furnace can enhance your process control and quality assurance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the function of a vacuum sintering furnace in the SAGBD process? Optimize Magnetic Coercivity and Performance
- Why is a vacuum environment essential for sintering Titanium? Ensure High Purity and Eliminate Brittleness
- How does pressure application in a vacuum hot press furnace facilitate sintering of copper composites? Optimize Density
- Why is a vacuum hot press sintering furnace required for nanocrystalline ceramics? Preserve Structure with Pressure
- What role does a vacuum hot pressing furnace play in TiBw/TA15 synthesis? Enhance In-Situ Composite Performance



















