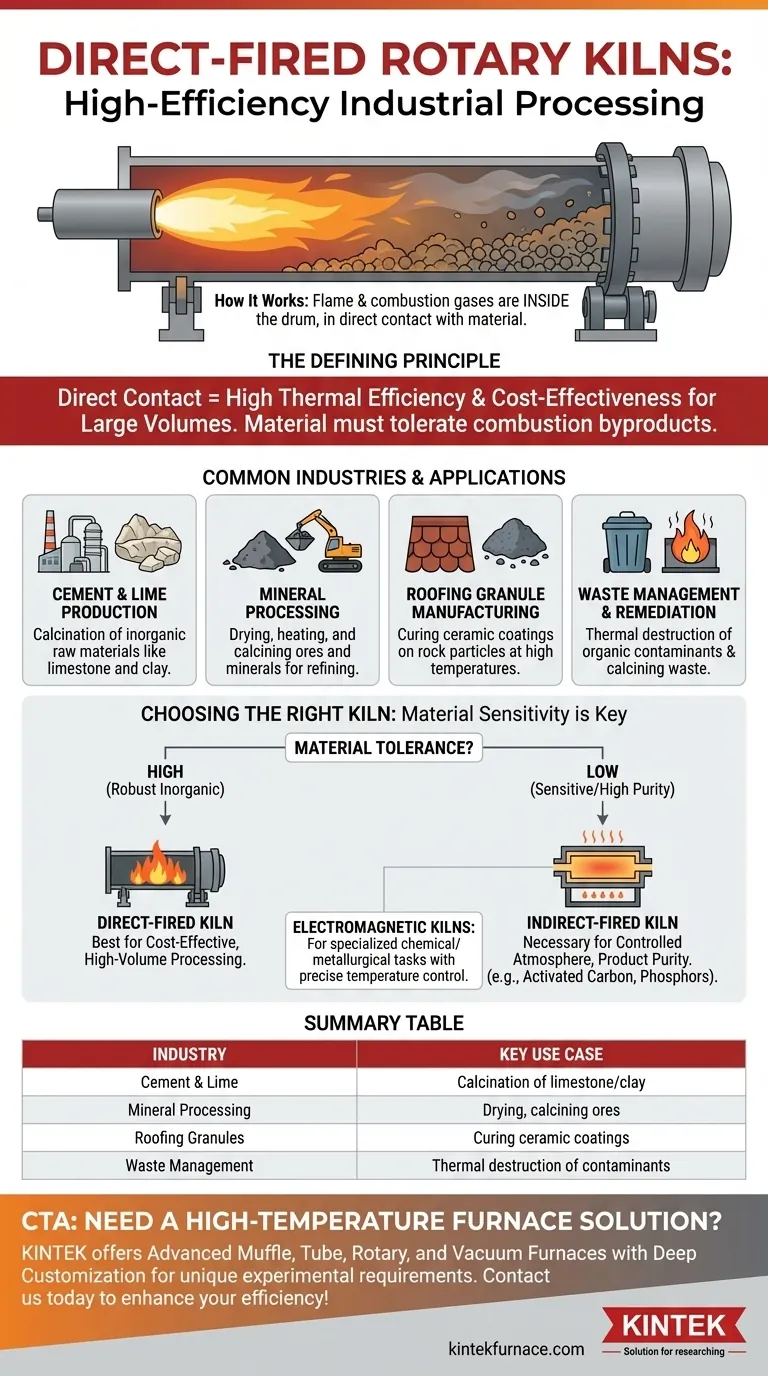
Direct-fired rotary kilns are most commonly used in industries that process large volumes of robust, inorganic materials where cost-effective, high-temperature processing is critical. Key sectors include mineral processing, cement and lime production, roofing granule manufacturing, and certain types of metal recycling and waste management.
The decision to use a direct-fired kiln is not defined by an industry, but by the material being processed. If your material can withstand direct contact with combustion gases without being contaminated, a direct-fired kiln is almost always the more efficient and economical choice.
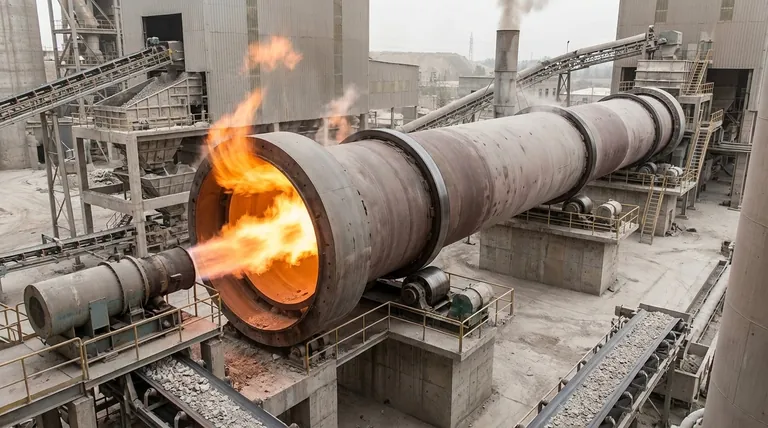

The Defining Principle of Direct-Fired Kilns
A direct-fired rotary kiln is a thermal processing system where the fuel is combusted inside the main rotating cylinder. The flame and hot combustion gases are in direct contact with the material being processed.
How It Works: Direct Contact Heating
As the kiln rotates, the material tumbles through the drum. The burner, located at one end, projects a flame down the length of the kiln, transferring heat directly to the material through both radiation and convection.
The Key Advantage: High Thermal Efficiency
This direct contact allows for rapid and highly efficient heat transfer. It is one of the most effective ways to deliver the immense thermal energy required for large-scale processes like calcination.
The Critical Limitation: Material Tolerance
The primary constraint of a direct-fired kiln is that the material must be able to tolerate exposure to the byproducts of combustion (such as CO₂, H₂O, and trace elements from the fuel) without suffering adverse chemical reactions or contamination.
Common Industries and Applications
The efficiency and simplicity of direct-fired kilns make them the standard choice for several heavy industries.
Cement and Lime Production
This is the most classic application. The raw materials for cement and lime (limestone, clay, shale) are inorganic and require extremely high temperatures for the chemical transformation known as calcination. Direct firing provides the necessary heat in the most economical way.
Mineral Processing
Industries use direct-fired kilns to dry, heat, and calcine a wide variety of ores and minerals. Since these are often bulk materials being prepared for further refining, direct contact with combustion gas is perfectly acceptable and highly cost-effective.
Roofing Granule Manufacturing
To create durable roofing granules, small rock particles are coated and then fired at high temperatures to cure the ceramic coating. A direct-fired kiln provides the intense, uniform heat needed for this curing process on a continuous, high-volume basis.
Waste Management and Remediation
Direct-fired kilns are used to process certain types of waste, such as calcining small waste stones or thermally destroying specific organic contaminants. The high temperatures and oxidizing atmosphere can effectively break down harmful compounds.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Direct vs. Indirect Firing
Choosing the right kiln type is critical and depends entirely on your material's sensitivity.
When to Choose Direct-Fired
A direct-fired kiln is the default choice for high-volume, cost-sensitive processes involving materials that are chemically stable and not susceptible to contamination from combustion gases.
When an Indirect-Fired Kiln is Necessary
An indirect-fired kiln heats the rotating drum from the outside. The material inside never contacts the flame or combustion gases, allowing for a highly controlled, inert, or specific process atmosphere.
This method is essential for high-value or sensitive materials like activated carbon, phosphors, titanates, and specialty chemicals where product purity is paramount or where processes like pyrolysis (heating in the absence of oxygen) are required.
A Note on Electromagnetic Kilns
Electromagnetic induction kilns are a specialized form of indirect heating. They use magnetic fields to heat the kiln shell with extreme precision. They are used in metallurgical and chemical applications where precise temperature control is more important than raw throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by your material's properties and your final product requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, high-volume processing of robust materials: A direct-fired kiln is the industry-standard solution.
- If your primary focus is product purity, processing sensitive materials, or requiring a controlled atmosphere: An indirect-fired kiln is non-negotiable.
- If your primary focus is precision temperature control for specialized chemical or metallurgical tasks: Advanced indirect methods like electromagnetic kilns should be considered.
Ultimately, understanding your material's tolerance for heat and atmospheric contact is the key to selecting the correct thermal processing technology.
Summary Table:
| Industry/Application | Key Use Cases |
|---|---|
| Cement and Lime Production | Calcination of limestone and clay for construction materials |
| Mineral Processing | Drying, heating, and calcining ores and minerals for refining |
| Roofing Granule Manufacturing | Curing ceramic coatings on granules for durability |
| Waste Management | Thermal destruction of contaminants and calcining waste materials |
Need a high-temperature furnace solution tailored to your industrial process? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for industries handling robust materials. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
People Also Ask
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- How do rotary tube furnaces achieve precise temperature control? Master Uniform Heating for Dynamic Processes
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control



















