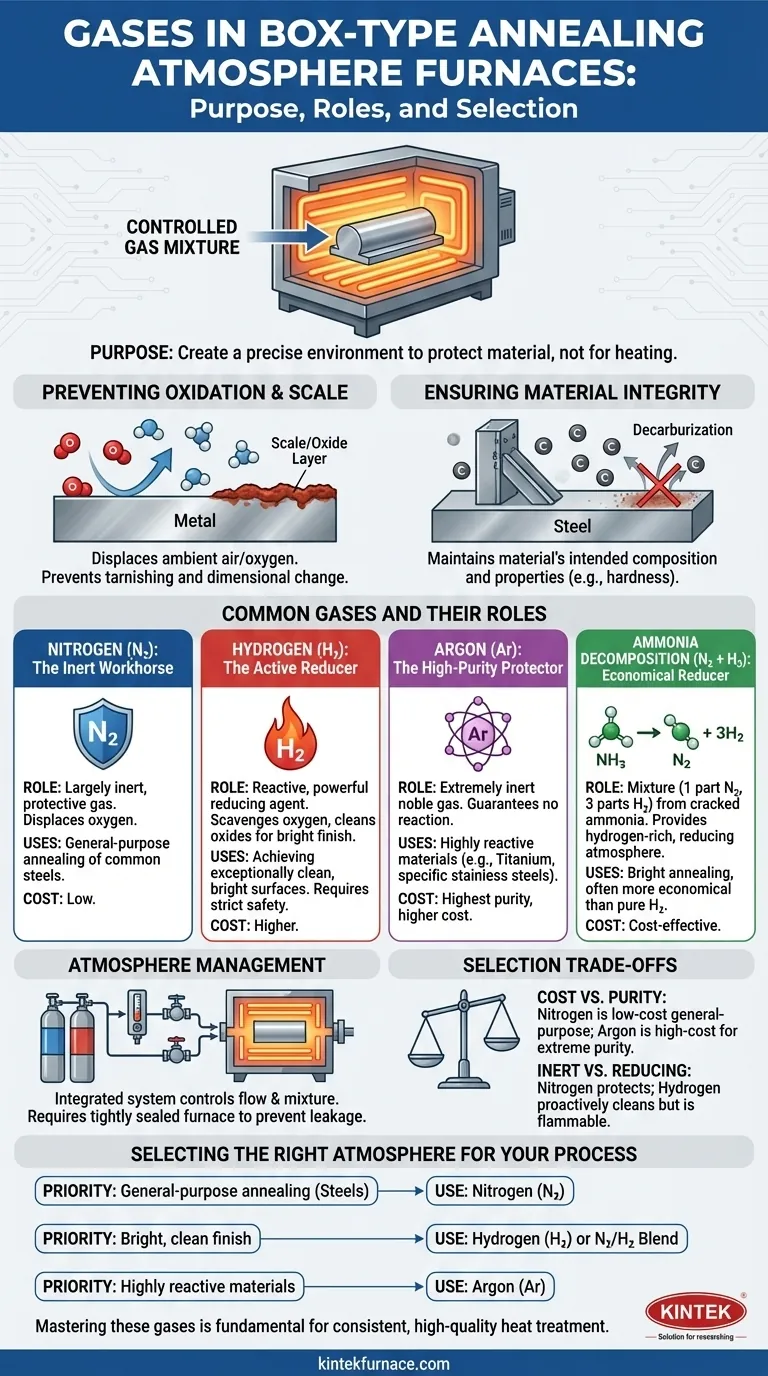
At its core, a box-type annealing atmosphere furnace uses a controlled mixture of specific gases to protect the material being treated. The most common gases introduced are nitrogen (N₂), hydrogen (H₂), argon (Ar), and sometimes ammonia decomposition gas, which is a mixture of nitrogen and hydrogen.
The critical takeaway is that these gases are not used for heating. Their purpose is to create a precisely controlled chemical environment—a protective or reactive atmosphere—that prevents unwanted reactions like oxidation and ensures the final material meets specific metallurgical properties.

The Purpose of a Controlled Atmosphere
When metals are heated to high temperatures, they become highly reactive with the air around them, particularly oxygen. An atmosphere furnace replaces the ambient air with a specific gas or gas mixture to control this environment.
Preventing Oxidation and Scale
The primary goal of an atmosphere is to prevent oxygen from reacting with the hot metal surface. This reaction, known as oxidation, forms a layer of scale or tarnish that can ruin the surface finish and alter the part's dimensions.
A controlled atmosphere displaces the oxygen, blanketing the workpiece in a non-reactive or actively reducing environment.
Ensuring Material Integrity
Beyond just the surface, uncontrolled atmospheres can lead to issues like decarburization in steels, where carbon is stripped from the surface layer, making it softer. A proper atmosphere maintains the material's intended composition and properties.
Common Gases and Their Roles
The choice of gas depends entirely on the material being treated and the desired outcome of the annealing process. Each gas serves a distinct function.
Nitrogen (N₂): The Inert Workhorse
Nitrogen is the most common and cost-effective atmosphere gas. It is largely inert, meaning it does not readily react with most metals, making it an excellent all-purpose protective gas to prevent oxidation.
Hydrogen (H₂): The Active Reducer
Hydrogen is a reactive gas. Instead of just displacing oxygen, it actively scavenges and reacts with any oxygen present. It is a powerful reducing agent, meaning it can strip oxygen from existing oxides on the metal's surface, resulting in an exceptionally clean and bright finish.
Argon (Ar): The High-Purity Protector
Argon is a noble gas, making it even more inert than nitrogen. It is used for materials that are extremely sensitive or that can react with nitrogen at high temperatures, such as titanium and certain stainless steels. Its high purity comes at a higher cost.
Ammonia Decomposition Gas (N₂ + H₂)
This is not a primary gas but a mixture generated on-site by cracking anhydrous ammonia (NH₃) into one part nitrogen and three parts hydrogen. It provides the benefits of a hydrogen-rich atmosphere (bright finish) often more economically than using pure bottled hydrogen.
How the Atmosphere is Managed
Creating and maintaining this precise environment requires an integrated system.
The Atmosphere Control System
This system is the heart of the furnace's function. It consists of a gas source (tanks or generators), flow meters, and regulating valves. These components work together to precisely control the flow rate and mixture of gases entering the furnace chamber.
Furnace Sealing and Integrity
A perfect atmosphere is useless if it leaks out or air leaks in. The furnace is built with a tightly sealed door and robust shell, often made of high-temperature alloy steel, to prevent atmosphere leakage and contamination. This ensures the gas composition inside remains stable throughout the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a gas is a balance of process requirements, material compatibility, and cost.
Cost vs. Purity
Nitrogen is the go-to for general-purpose annealing of common steels due to its low cost and effectiveness. Argon is reserved for specialty applications where its extreme inertness justifies the significantly higher expense.
Inert vs. Reducing (Protective vs. Bright)
An inert gas like nitrogen simply prevents further oxidation. A reducing gas like hydrogen goes a step further by cleaning oxides, but it is also highly flammable and requires more stringent safety systems and operational procedures.
Selecting the Right Atmosphere for Your Process
Your choice of gas directly impacts the quality, finish, and cost of your annealing operation.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose annealing of carbon and alloy steels: A nitrogen-based atmosphere provides excellent protection against oxidation at an economical price point.
- If your primary focus is achieving the brightest, cleanest possible surface finish: A hydrogen or nitrogen/hydrogen blend is the best choice for its active reducing properties.
- If your primary focus is annealing highly reactive materials like titanium or certain stainless steels: Argon is the only option that guarantees a truly inert environment without unwanted reactions.
Ultimately, mastering the use of these gases is fundamental to achieving consistent and high-quality heat treatment results.
Summary Table:
| Gas Type | Role in Furnace | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Nitrogen (N₂) | Inert protective gas | General-purpose annealing of steels |
| Hydrogen (H₂) | Reducing agent for bright finish | Cleaning oxides, achieving high surface quality |
| Argon (Ar) | High-purity inert gas | Annealing reactive materials like titanium |
| Ammonia Decomposition (N₂ + H₂) | Cost-effective reducing mixture | Bright annealing with economic benefits |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's heat treatment capabilities? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With our strong R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored furnace solutions can improve your annealing processes and deliver superior results for your materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does the inert atmosphere heat treating process work? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Material Quality
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- How does an inert atmosphere prevent oxidation? Shield Materials from Oxygen Damage



















