In short, the primary finishing processes that follow metal casting from an induction furnace are trimming, cleaning, machining, and surface treatment. These steps are essential for transforming a raw, solidified casting into a functional, precise component that meets all engineering specifications. The use of an induction furnace significantly improves the initial quality of the cast, which in turn makes these finishing processes more efficient and predictable.
The core principle to understand is that finishing is not a separate activity but an integral part of the casting system. While an induction furnace produces a superior initial part with fewer defects, the finishing stage is still the critical final step that guarantees the part's required precision, appearance, and performance.

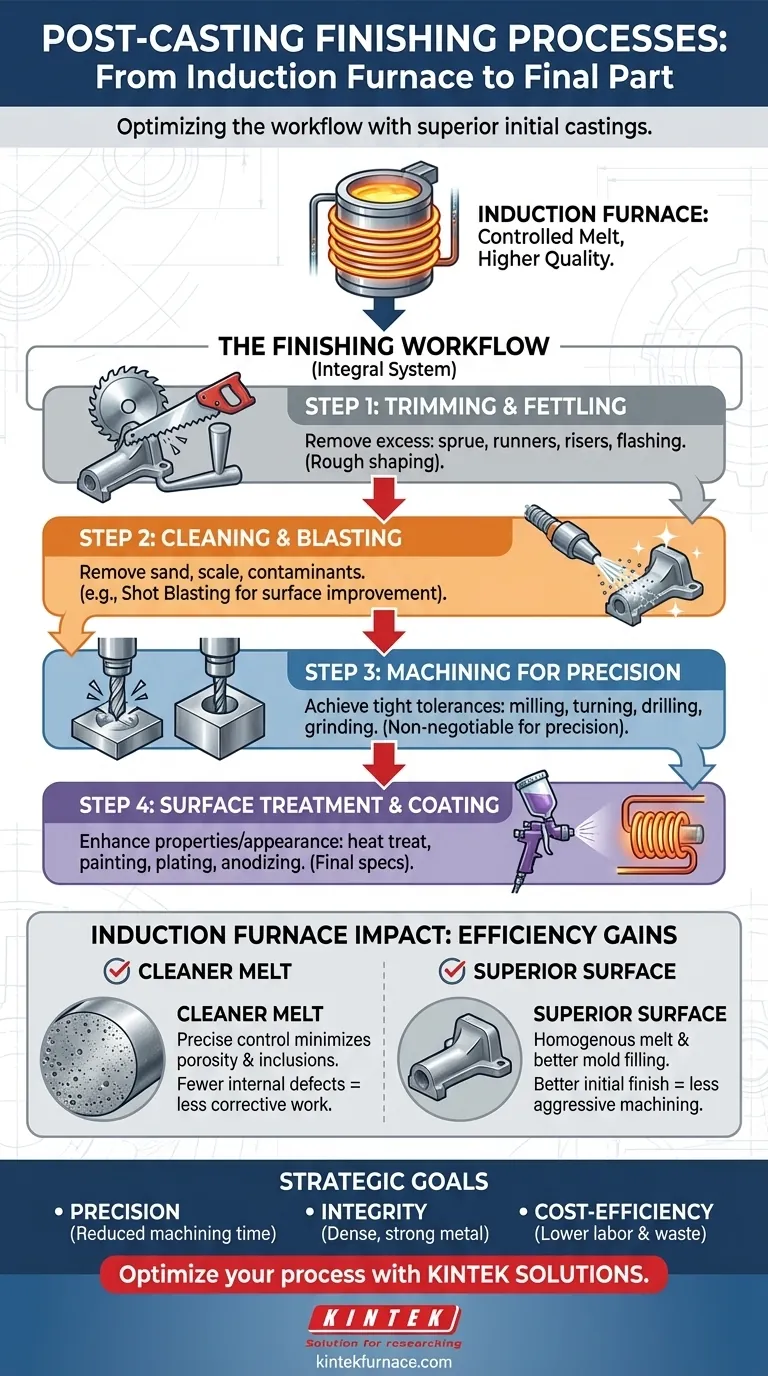
From Raw Casting to Finished Part: The Finishing Workflow
Once molten metal solidifies in a mold, the resulting object is a "raw casting." It is close to the final shape but lacks the precision and refinement needed for most applications. The following sequence of finishing operations bridges that gap.
Step 1: Trimming and Fettling
The first step involves removing excess material that is part of the casting process but not the final product. This is a rough-shaping stage.
These materials include the sprue (the channel where metal entered the mold), runners (channels that distribute metal), risers (reservoirs of molten metal that prevent shrinkage voids), and any flashing (thin metal that leaked between mold halves).
Step 2: Cleaning and Blasting
After trimming, the casting's surface must be thoroughly cleaned. This process removes residual molding sand, scale from oxidation, and other surface contaminants.
Shot blasting is a common and highly effective method. It involves propelling small metallic or ceramic particles at high velocity against the casting's surface, which scours it clean and can also improve its fatigue resistance through a process called shot peening.
Step 3: Machining for Precision
Casting is not a perfectly precise process. To achieve tight dimensional tolerances required for parts to fit and function correctly, machining is almost always necessary.
Operations like milling, turning, drilling, and grinding are used to create flat surfaces, precise holes, and other features that cannot be formed accurately by casting alone.
Step 4: Surface Treatment and Coating
The final stage involves applying treatments to enhance the part's properties or appearance. This is entirely dependent on the part's end-use.
These treatments can be functional, such as heat treatment to improve strength, or aesthetic and protective, such as painting, plating, powder coating, or anodizing to prevent corrosion and provide a finished look.
Why Induction Furnaces Impact the Finishing Stage
The choice of melting furnace has a direct impact on the amount and complexity of the finishing work required. Induction furnaces are valued for producing higher-quality initial castings, which streamlines the subsequent steps.
The Benefit of a Cleaner Melt
Induction furnaces offer precise temperature and chemistry control. This control minimizes the formation of oxides and prevents gas absorption into the molten metal.
The result is a casting with significantly fewer internal defects like porosity (gas bubbles) or inclusions (impurities). A denser, more solid casting is stronger and requires less corrective work later.
Superior Surface Finish from the Start
The electromagnetic stirring action inherent to induction furnaces creates a homogenous melt temperature. This, combined with precise pouring control, results in better mold filling.
This leads to a raw casting with a better initial surface finish and enhanced dimensional accuracy. A smoother "as-cast" surface may require less aggressive blasting or machining to meet final specifications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While advanced casting methods improve efficiency, it's crucial to have a realistic perspective on the role of finishing.
Finishing Is Not Optional
Even with a perfect melt from an induction furnace, no casting process can consistently produce parts that meet the tight tolerances of modern engineering without machining.
The goal of using an induction furnace isn't to eliminate finishing but to make it more predictable, faster, and less wasteful. Knowing the initial casting is high-quality allows for more efficient machining setups and reduces rejection rates.
The Cost of Quality
The higher efficiency of an induction furnace—less energy used, less material wasted, and faster melts—translates directly to cost savings.
A significant portion of these savings is realized in the finishing department. When you need to machine less material off every part, you save time, reduce tool wear, and generate less scrap, lowering the total cost of production.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The finishing strategy must align with the primary objective for the component.
- If your primary focus is dimensional accuracy: Acknowledge that precision machining is non-negotiable, but a high-quality initial casting from an induction furnace will drastically reduce the time and cost to achieve it.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity: The clean, dense metal produced by an induction furnace provides a superior starting point, minimizing internal defects that could compromise the part's strength.
- If your primary focus is cost-efficiency: Investing in a controlled melting process like induction casting directly reduces downstream labor, tooling costs, and material waste in the finishing stages.
Ultimately, viewing casting and finishing as an integrated system, where the quality of one stage directly impacts the efficiency of the next, is the key to producing a superior final part.
Summary Table:
| Finishing Process | Key Steps | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Trimming and Fettling | Remove sprue, runners, risers, flashing | Eliminate excess material from casting |
| Cleaning and Blasting | Shot blasting, surface scouring | Remove contaminants and improve fatigue resistance |
| Machining | Milling, turning, drilling, grinding | Achieve precise dimensional tolerances |
| Surface Treatment | Heat treatment, painting, plating, coating | Enhance strength, corrosion resistance, and appearance |
Ready to optimize your metal casting and finishing processes? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and achieve superior part quality with our tailored solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum induction melting technology and why is it important? Achieve High-Purity Metals for Critical Applications
- How does the Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) process work? Achieve Superior Metal Purity and Control
- What are the common applications of Vacuum Induction Melting? Essential for High-Performance Metals and Alloys
- What are the core functions of the High Vacuum Induction Melting (VIM) furnace? Optimize DD5 Superalloy Purification
- How has vacuum smelting impacted the development of superalloys? Unlock Higher Strength and Purity



















