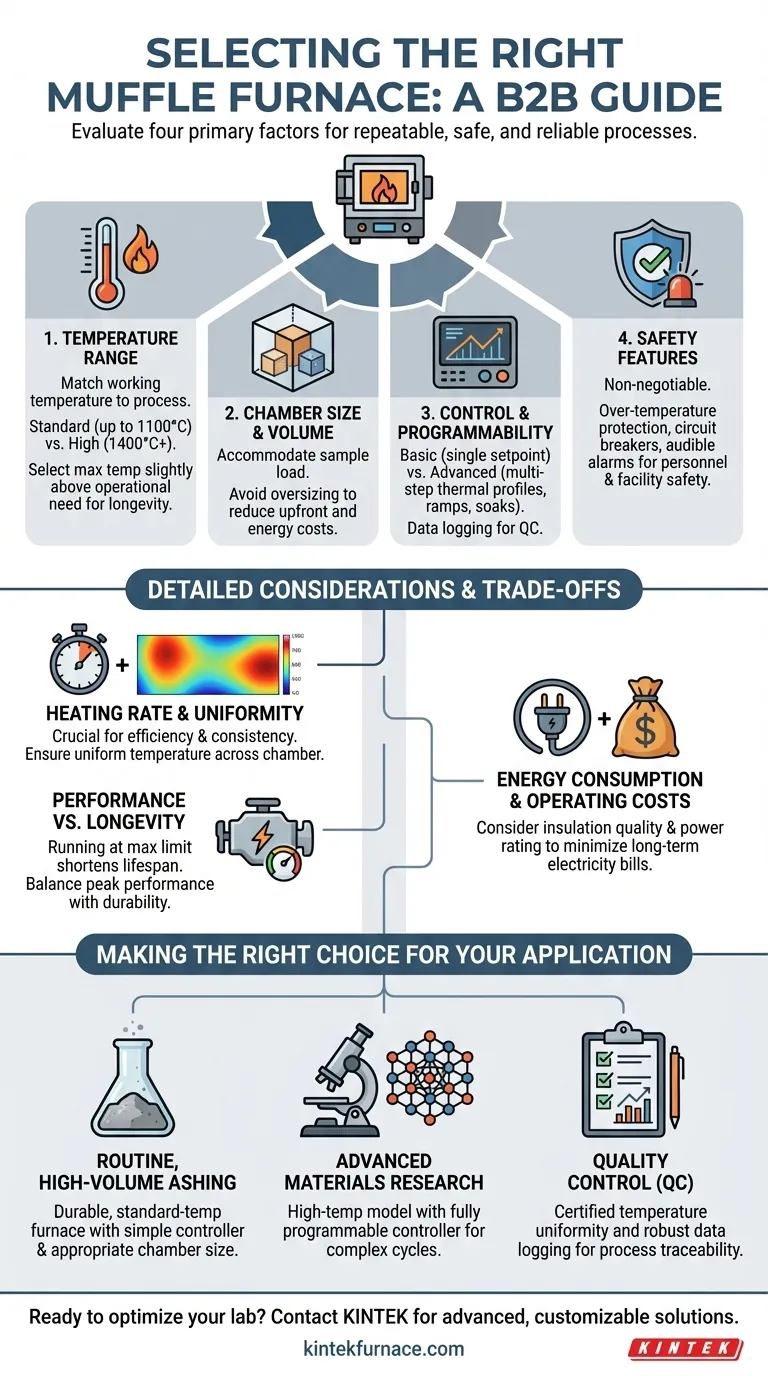
To select the right muffle furnace, you must evaluate four primary factors: the required temperature range for your application, the necessary chamber size, the level of control and programmability you need, and the essential safety features. These elements work together to ensure your processes are repeatable, your samples are protected, and your lab operates safely.
The goal is not to buy the furnace with the highest temperature or most features, but to precisely match the equipment's capabilities to your specific scientific or industrial application. An improper choice can compromise research reliability, waste energy, and introduce unnecessary safety risks.

Defining Your Core Technical Requirements
The performance specifications of a muffle furnace directly dictate its suitability for your work. Misjudging these requirements is the most common and costly mistake.
Operating Temperature Range
The single most important factor is the working temperature. The furnace must be able to consistently achieve and maintain the heat required for your specific process.
Standard furnaces typically operate up to 1100°C, which is sufficient for many ashing or heat-treating applications. However, testing certain polymers or advanced materials may demand temperatures of 1400°C or higher.
For longevity, select a furnace with a maximum temperature slightly above your typical operating temperature. Constantly running equipment at its absolute limit will shorten its lifespan.
Chamber Size and Volume
The internal chamber dimensions determine your sample throughput. You must choose a size that can accommodate your typical sample load without being excessively large.
An oversized chamber not only has a higher upfront cost but also consumes significantly more energy to heat and maintain temperature. This can lead to higher long-term operating costs.
Heating Rate and Temperature Uniformity
Heating rate, or rise time, is the time it takes for the furnace to reach its target temperature. This is a critical factor for process efficiency, especially in high-throughput environments.
Equally important is temperature uniformity. For reliable results, you must ensure that all samples within the chamber are exposed to the same temperature. Ask manufacturers for data on temperature variation across the chamber volume.
Evaluating Control and Programmability
The furnace's controller is its brain. The level of sophistication you need depends entirely on the complexity of your thermal processes.
Basic vs. Advanced Controllers
A basic controller allows you to set a single target temperature and a process time. This is often sufficient for straightforward applications like determining ash content.
Advanced programmable controllers allow you to create complex, multi-step thermal profiles with different ramps (rate of temperature change) and soaks (holding at a temperature for a set time). This is essential for materials science, ceramics, and advanced research.
Data Logging and Monitoring
For quality control and research purposes, the ability to monitor and log temperature data is critical. This provides an auditable record that the process was performed to specification.
Modern furnaces may offer digital outputs or connectivity options to export this data for analysis, which is a key feature for labs operating under strict quality management systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Imperatives
Selecting a furnace involves balancing performance with practical constraints like budget, safety, and long-term operating costs.
Performance vs. Longevity
There is a direct trade-off between pushing a furnace to its maximum performance and its expected lifespan. A furnace that can hold its maximum temperature for about an hour is robust, but doing so daily will cause faster wear on heating elements and insulation.
The Critical Role of Safety Features
Safety features are non-negotiable. Your furnace must be equipped with over-temperature protection, which automatically shuts down the unit if it exceeds a preset maximum temperature.
Look for other essential features like electrical circuit breakers and audible alarms. These systems protect not only your valuable samples but, more importantly, your personnel and facility.
Energy Consumption and Operating Costs
A furnace's upfront price is only part of its total cost. Consider the quality of insulation and the power rating of the heating elements.
A well-insulated furnace will maintain its temperature with less energy, reducing your electricity bills over the life of the equipment. This long-term operating cost should be a key factor in your decision.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, your specific use case must guide your selection. Evaluate your needs against these common scenarios.
- If your primary focus is routine, high-volume ashing: A durable, standard-temperature (1100°C) furnace with a simple controller and appropriate chamber size for your throughput is the most cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is advanced materials research: Prioritize a high-temperature model with a fully programmable controller that allows for complex, multi-step thermal cycles.
- If your primary focus is quality control with strict audit needs: Select a furnace with certified temperature uniformity and robust data logging capabilities to ensure process traceability and compliance.
A methodical evaluation of your specific application is the only way to ensure your investment serves you safely and reliably for years to come.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations |
|---|---|
| Operating Temperature Range | Must match application needs; standard up to 1100°C, high-temp up to 1400°C+ for longevity |
| Chamber Size and Volume | Choose based on sample throughput; avoid oversized to reduce energy costs |
| Heating Rate and Uniformity | Critical for efficiency and reliable results; check manufacturer data for variations |
| Control and Programmability | Basic for simple tasks, advanced for complex profiles with ramps and soaks |
| Safety Features | Essential for protection; includes over-temperature protection, circuit breakers, alarms |
| Energy Consumption | Consider insulation quality and power rating to minimize long-term operating costs |
Ready to optimize your lab with the perfect muffle furnace? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Don't compromise on reliability—contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your processes with durable, efficient equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the study of biochar regeneration and reuse? Unlock Sustainable Water Treatment



















