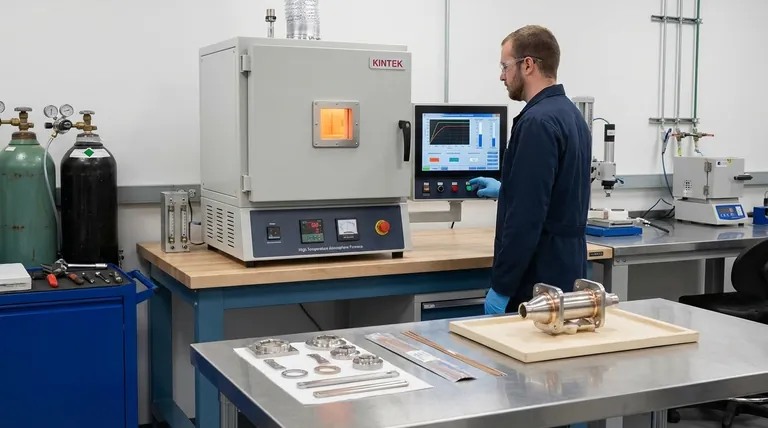
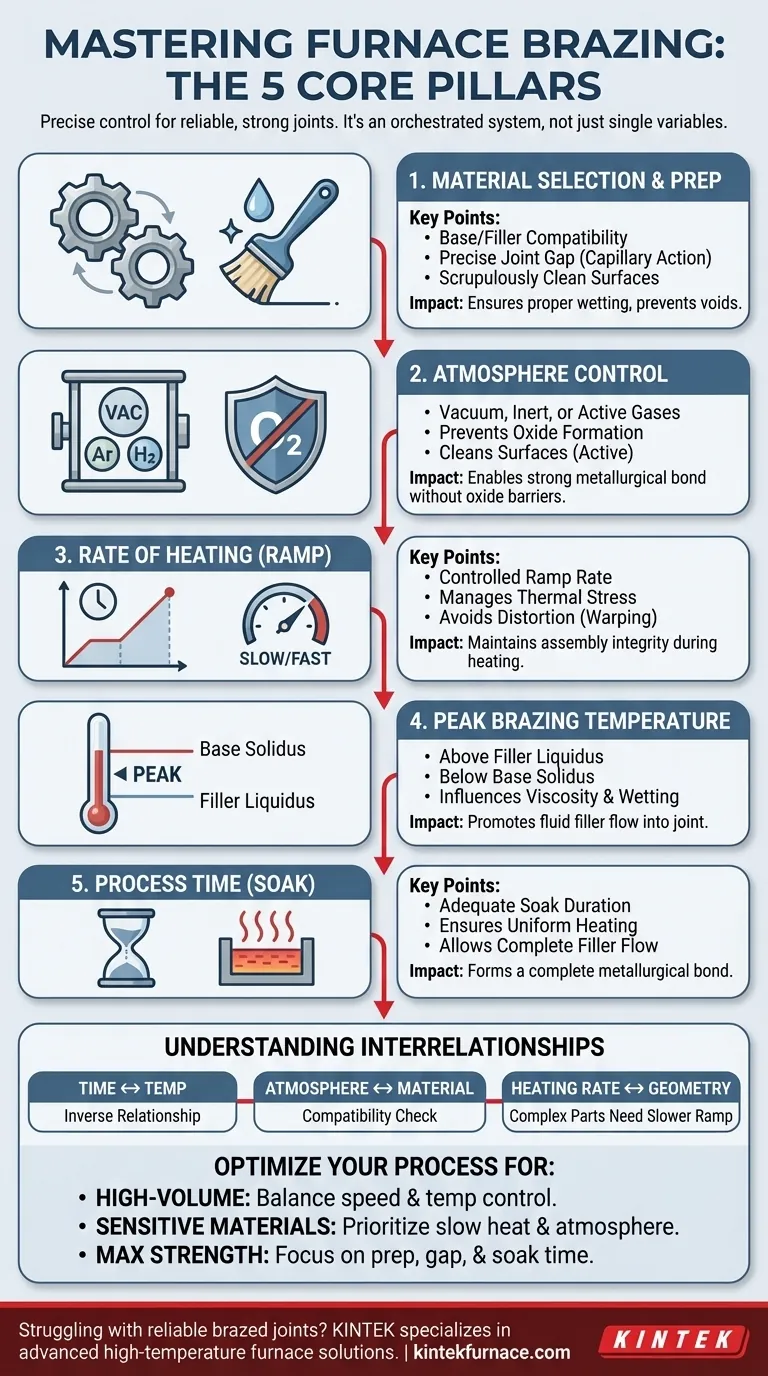
To ensure a reliable furnace braze joint, you must precisely control five interrelated factors: the materials selected, the furnace atmosphere, the rate of heating, the peak brazing temperature, and the total process time. Success depends on managing how these variables interact to create a clean environment where the filler metal can flow properly and form a strong metallurgical bond.
Achieving a perfect braze is not about optimizing a single variable in isolation. It is about orchestrating the entire system—the materials, atmosphere, and thermal profile—to work in harmony.

The Five Pillars of Furnace Brazing
A reliable brazing process is built on the careful management of five core elements. Each one plays a distinct and critical role in the final quality of the joint.
Material Selection and Preparation
The process begins long before the parts enter the furnace. The base metals and the braze filler metal must be compatible.
Proper joint design is equally crucial. The gap between the parts must be engineered precisely to allow the filler metal to be drawn in through capillary action but not so large that it fails to fill completely.
Finally, all parts must be scrupulously clean. Contaminants like oils, grease, or heavy oxides will prevent the filler metal from wetting the base metal surfaces, leading to voids and a failed joint.
Atmosphere Control
The furnace atmosphere is one of the most critical process controls. Its primary job is to prevent the formation of oxides on the base and filler metals as they heat up.
Different atmospheres are used for different materials. A vacuum is excellent for reactive metals like titanium. Inert atmospheres (like argon) are protective, while active atmospheres (like hydrogen blends) can chemically reduce surface oxides, effectively cleaning the parts during the cycle.
Without proper atmosphere control, oxides will act as a barrier, stopping the filler metal from flowing and bonding to the base material.
Rate of Heating
The speed at which the assembly is heated, known as the ramp rate, must be controlled to manage thermal stress.
Heating too quickly can cause thin sections to heat much faster than thick sections, leading to thermal distortion or warping of the assembly.
Conversely, a ramp rate that is too slow can be inefficient and may lead to undesirable metallurgical changes in the base materials before the brazing temperature is even reached.
Peak Brazing Temperature
The peak temperature is the specific temperature at which the assembly is held to perform the braze. This temperature must be high enough to melt the filler metal completely (above its liquidus temperature) but remain safely below the melting point of the base metals (their solidus temperature).
Temperature directly influences the filler metal's viscosity and its ability to wet the base materials. A properly selected peak temperature ensures the filler flows fluidly into the joint via capillary action.
Process Time
Process time, or soak time, refers to the duration the assembly is held at the peak brazing temperature.
This time must be long enough for the entire assembly, including the thickest sections, to reach a uniform temperature. It also allows sufficient time for the filler metal to flow completely throughout the joint and form a proper metallurgical bond.
Understanding the Interrelationships
The five pillars of brazing do not exist in a vacuum; they are deeply interconnected. Changing one variable forces adjustments in others.
The Time-Temperature Relationship
Time and temperature have an inverse relationship. A slightly higher peak temperature might allow for a shorter process time because the filler metal will be more fluid. However, this increases the risk of distortion or damage to heat-sensitive base materials.
Atmosphere and Material Compatibility
The choice of atmosphere is dictated by the materials being joined. Brazing stainless steels, for example, often requires a dry hydrogen atmosphere to reduce the tough chromium oxides that form. Using the wrong atmosphere for your material will guarantee a failed joint.
Heating Rate and Part Geometry
Complex assemblies with varying thicknesses demand a slower, more deliberate heating rate. This ensures the entire part reaches the peak temperature uniformly, preventing the issues of thermal stress and ensuring the filler metal flows into areas that might otherwise lag behind in temperature.
Optimizing Your Brazing Process
Your ideal process parameters depend entirely on your specific goal. Use these principles to guide your decisions.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production: Balance a faster heating rate and shorter process time with precise temperature control to ensure quality without sacrificing throughput.
- If your primary focus is joining dissimilar or sensitive materials: Prioritize slower heating rates and meticulous atmosphere control to manage thermal stresses and prevent unwanted reactions.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and integrity: Concentrate on pristine material preparation, precise joint gap control, and verifying complete filler flow through adequate time at temperature.
Mastering how these fundamental variables interact is the key to transforming furnace brazing from an art into a reliable and repeatable science.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Control Points | Impact on Joint Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Base/filler metal compatibility, joint gap, cleanliness | Ensures proper wetting and capillary action, prevents voids |
| Atmosphere Control | Use of vacuum, inert, or active gases | Prevents oxide formation, enables strong metallurgical bonds |
| Heating Rate | Controlled ramp to manage thermal stress | Reduces distortion and warping in assemblies |
| Peak Temperature | Above filler liquidus, below base solidus | Promotes fluid filler flow and complete joint filling |
| Process Time | Adequate soak for uniform heating and bonding | Allows full filler metal flow and bond formation |
Struggling to achieve reliable brazed joints in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored for precision brazing. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our deep customization capabilities ensure your furnace meets unique experimental needs, enhancing joint quality and process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can optimize your brazing process and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
People Also Ask
- How does a mixed gas flow control system maintain stability during high-temperature nitriding? Precision Gas Ratios
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















