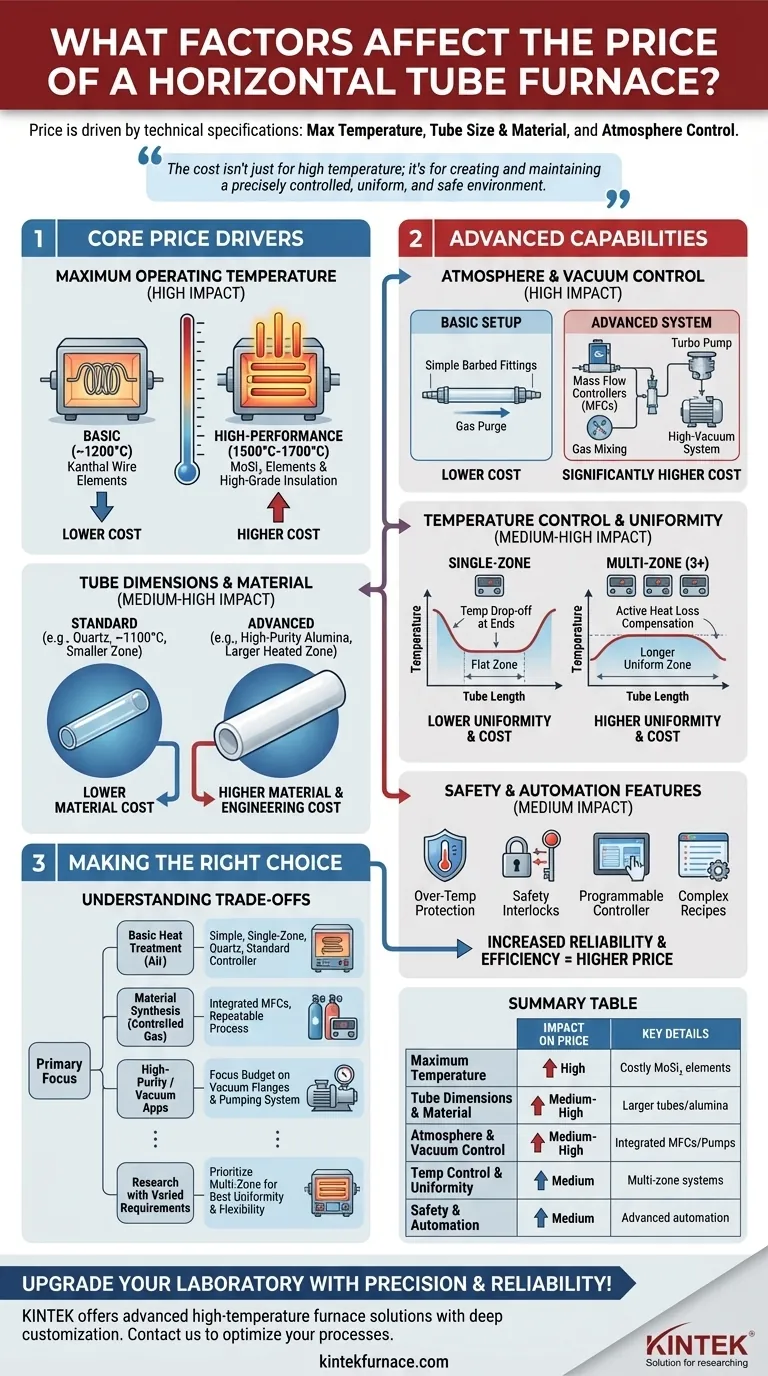
The price of a horizontal tube furnace is determined by a clear set of technical specifications. Its maximum temperature, the size and material of its processing tube, and the sophistication of its atmosphere control system are the primary drivers of cost. These factors can cause prices to range from a few thousand dollars for a basic, low-temperature unit to tens of thousands for a high-performance, multi-zone system with advanced gas and vacuum capabilities.
The cost of a tube furnace isn't just about achieving a high temperature; it's about paying for the ability to create and maintain a precisely controlled, uniform, and safe processing environment. Understanding this distinction is the key to selecting the right instrument and justifying its cost.
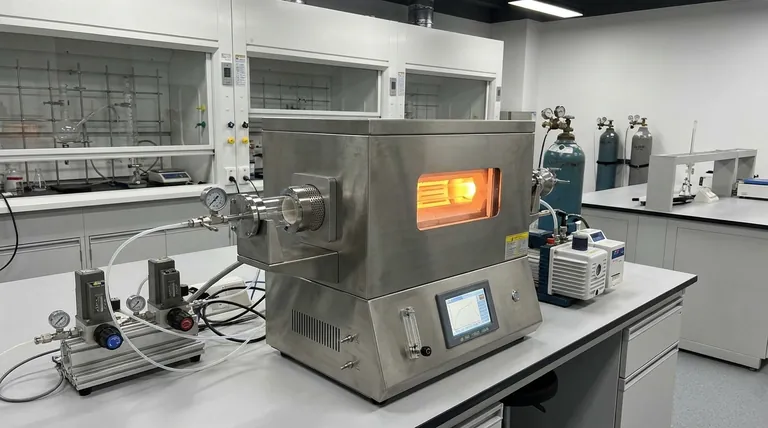

The Core Price Drivers: From Temperature to Size
The foundational specifications of the furnace account for the most significant portion of its cost. Higher performance in these basic areas requires more advanced materials and engineering.
Maximum Operating Temperature
The single biggest factor influencing price is the maximum temperature. Furnaces are built with different heating elements and insulation materials designed for specific temperature ranges.
A furnace rated for 1200°C often uses robust Kanthal (FeCrAl) wire elements. Moving up to 1500°C or 1700°C requires significantly more expensive Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi₂) elements and higher-grade ceramic fiber insulation, dramatically increasing the unit's cost.
Tube Dimensions and Material
The physical size of the furnace chamber and the tube it's designed to hold directly impacts material costs. A furnace with a larger heated zone requires more heating elements, insulation, and a larger steel shell.
The process tube itself is a critical component. A simple quartz tube is suitable for many applications up to ~1100°C in non-reactive environments. However, processes requiring higher temperatures or chemical resistance necessitate more expensive high-purity alumina tubes or specialized alloy tubes.
Advanced Capabilities That Define High-End Models
Beyond the basics of temperature and size, the furnace's ability to control its internal environment is what separates entry-level models from advanced scientific instruments.
Atmosphere and Vacuum Control
The ability to process a sample in an inert atmosphere or under vacuum is a common requirement that adds significant cost.
A basic setup may only have simple barbed fittings for purging with gas. A more advanced and expensive system will include mass flow controllers (MFCs) for precise, repeatable gas mixing and a fully integrated high-vacuum system with turbo pumps, which substantially increases the price and complexity.
Temperature Control and Uniformity
All tube furnaces have a temperature controller, but their quality varies. A basic, single-zone furnace uses one controller and one set of heating elements, which can result in temperature drop-off near the ends of the tube.
High-end models often feature three or more heating zones, each with its own controller. This allows the system to actively compensate for heat loss at the ends, creating a much longer and more uniform flat temperature zone, which is critical for consistent results in research and quality control.
Safety and Automation Features
Safety is paramount in high-temperature equipment. Standard features like over-temperature protection and safety interlocks that shut off power when the furnace is opened are built into reputable models.
More advanced automation, such as programmable controllers that can run complex temperature recipes without supervision, adds to the cost but also to the repeatability and efficiency of your process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing capability against budget. Being aware of common pitfalls can prevent costly mistakes.
Over-Specifying vs. Future-Proofing
It is tempting to buy a furnace with the highest possible specifications. However, purchasing a 1700°C furnace for a process that will never exceed 1000°C is an inefficient use of funds, as the high-temperature components will go unused.
Conversely, consider your future needs. If there's a reasonable chance your research will require higher temperatures or gas control in the next year or two, investing in that capability now can be more cost-effective than buying a second furnace later.
The Hidden Cost of Poor Uniformity
A cheaper furnace may advertise a high maximum temperature, but if its uniform hot zone is very short or inconsistent, your experimental results will suffer. The cost of failed experiments, wasted materials, and lost time can quickly exceed the initial savings from buying a lower-quality unit.
Supplier Reputation and Support
A portion of the price reflects the manufacturer's reputation, the quality of their technical support, and the warranty they provide. A reliable supplier offers peace of mind and expert assistance, which is invaluable when troubleshooting a complex process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select a furnace by matching its features directly to your application's requirements.
- If your primary focus is basic heat treatment or annealing in air: A simple, single-zone furnace with a quartz tube and a standard controller offers the most cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis under controlled gas flow: Invest in a system with integrated mass flow controllers to ensure your process is repeatable and your results are reliable.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing or vacuum applications: The quality of the vacuum-tight flanges and the pumping system will be the main cost driver; this is where you should focus your budget.
- If your primary focus is research with varied requirements: Prioritize a multi-zone furnace to achieve the best temperature uniformity, providing flexibility for different sample types and process conditions.
Ultimately, a well-informed choice aligns the furnace's capabilities directly with your specific processing needs, ensuring every dollar invested contributes to reliable and accurate results.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Price | Key Details |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Temperature | High | Higher temps (e.g., 1500°C+) use costly elements like MoSi₂, increasing price significantly. |
| Tube Dimensions & Material | Medium to High | Larger tubes and materials like alumina vs. quartz raise costs due to more materials and engineering. |
| Atmosphere & Vacuum Control | High | Integrated systems with mass flow controllers and vacuum pumps add complexity and expense. |
| Temperature Control & Uniformity | Medium to High | Multi-zone systems for better uniformity cost more but ensure consistent results. |
| Safety & Automation Features | Medium | Advanced automation and safety interlocks increase price for improved reliability and efficiency. |
Upgrade your laboratory with precision and reliability! At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization capabilities to meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're in research, material synthesis, or quality control, our furnaces deliver precise temperature control, uniform heating, and enhanced safety—ensuring accurate results and cost-efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your processes and support your goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















