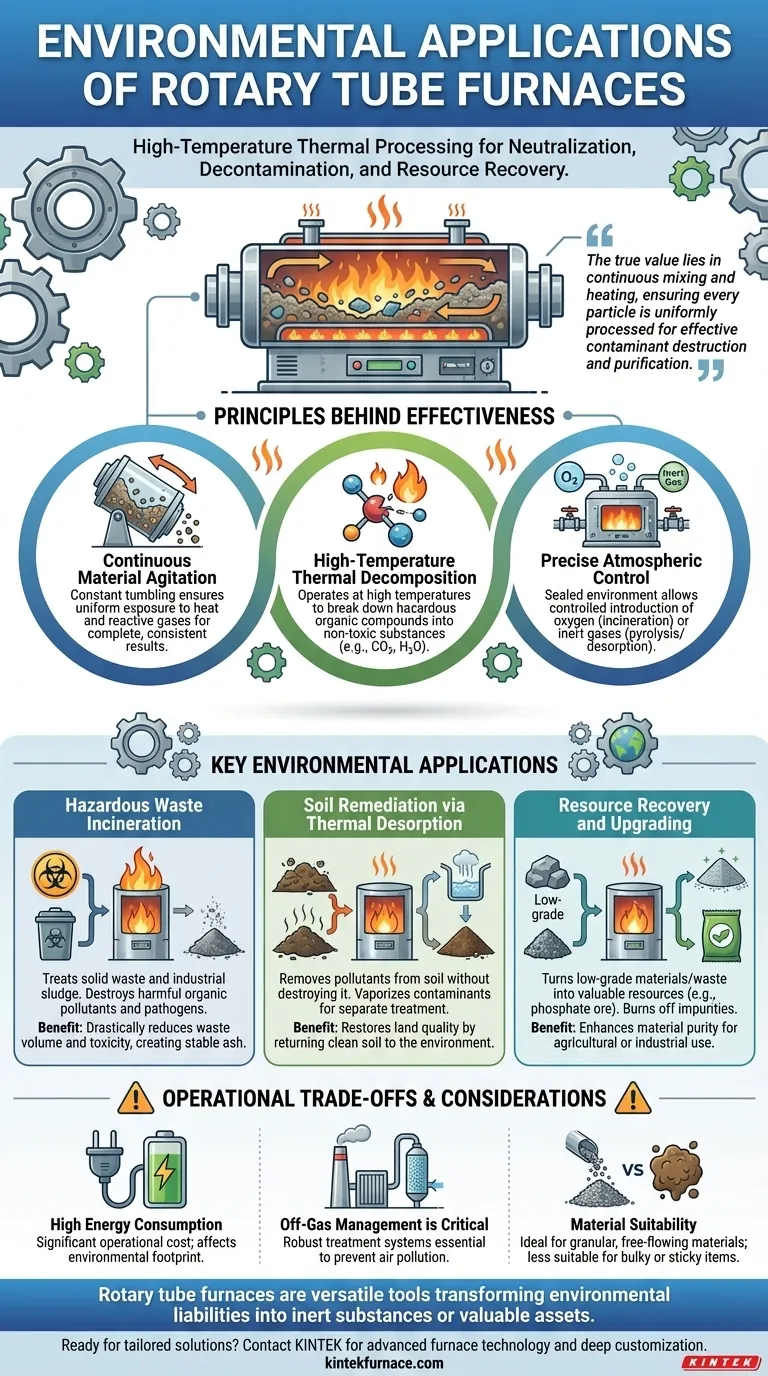
At their core, rotary tube furnaces serve critical environmental functions by using high-temperature thermal processing to neutralize hazardous materials, decontaminate soil, and recover valuable resources from waste streams. Their primary applications include the incineration of solid waste and sludge, the thermal desorption of pollutants from soil, and the upgrading of materials like phosphate ore.
The true value of a rotary tube furnace in environmental applications lies in its unique ability to continuously mix and heat loose or powdered materials. This ensures every particle is uniformly processed, making it exceptionally effective at destroying contaminants and purifying materials.
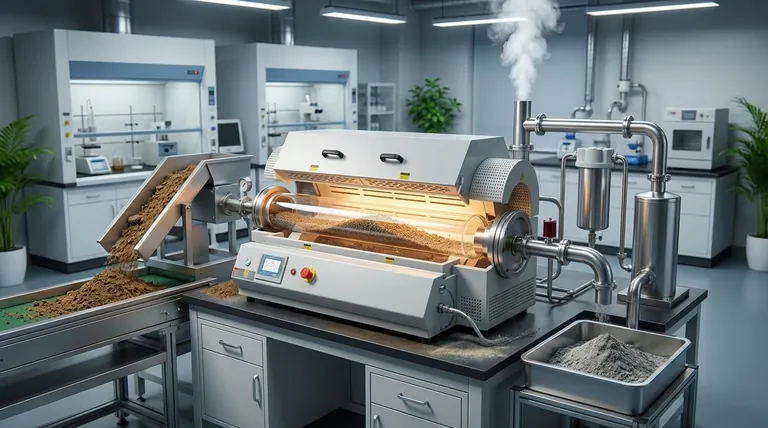

The Principles Behind Their Environmental Effectiveness
A rotary tube furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; its design provides specific advantages that are crucial for treating environmental contaminants effectively.
Continuous Material Agitation
The slow rotation of the furnace tube constantly tumbles the material being processed. This ensures that every particle is uniformly exposed to the heat and any reactive gases inside the furnace.
This agitation is vital for achieving complete and consistent results, whether you are burning waste or vaporizing contaminants from soil particles.
High-Temperature Thermal Decomposition
These furnaces operate at temperatures high enough to facilitate incineration, a process that breaks down hazardous organic compounds into simpler, non-toxic substances like carbon dioxide and water.
This capability is fundamental for destroying pathogens in sludge or toxic chemicals in industrial waste, significantly reducing their environmental impact.
Precise Atmospheric Control
The sealed environment of the furnace tube allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere. You can introduce oxygen for complete combustion (incineration) or use an inert gas to heat materials without burning them (pyrolysis or desorption).
This control is the key to tailoring the process to the specific material and desired outcome, such as separating a contaminant from soil without destroying the soil itself.
Key Environmental Applications Explained
The core principles of agitation, heat, and control enable several high-impact environmental solutions.
Hazardous Waste Incineration
Rotary tube furnaces are used to treat solid waste and industrial sludge. The high-temperature incineration process destroys harmful organic pollutants and pathogens.
This drastically reduces the volume and toxicity of the waste, transforming it into a more stable and manageable ash.
Soil Remediation via Thermal Desorption
For contaminated soil, the goal is often to remove pollutants without destroying the soil. A rotary furnace can heat the soil to a specific temperature that vaporizes contaminants like hydrocarbons or mercury.
These vaporized pollutants are then collected and treated in a separate off-gas system. The clean soil can be returned to the environment, restoring land quality.
Resource Recovery and Upgrading
These furnaces can also turn low-grade materials or waste byproducts into valuable resources. For example, they are used to upgrade phosphate ores for fertilizer production.
By heating the ore in a controlled process (calcination), impurities are burned off, which enhances the ore's purity and makes it suitable for agricultural use.
Understanding the Operational Trade-offs
While powerful, using a rotary tube furnace involves important considerations and requires a comprehensive system design.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures required for incineration or calcination is energy-intensive. This represents a significant operational cost and an important factor in the overall environmental footprint of the process.
Off-Gas Management is Critical
Thermal processing creates exhaust gases that may contain pollutants, particulates, or acid gases. A robust off-gas treatment system—including scrubbers and filters—is essential to prevent air pollution and ensure regulatory compliance.
Material Suitability
Rotary furnaces are ideal for processing granular, loose, and free-flowing materials. They are less suitable for very large, bulky items or extremely sticky materials that can cake onto the furnace walls and impede the tumbling action.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting this technology depends entirely on the problem you need to solve. Your primary objective will determine which of the furnace's capabilities is most important.
- If your primary focus is waste destruction and volume reduction: The furnace's ability to achieve complete, high-temperature incineration is its most critical feature.
- If your primary focus is decontamination of soil or materials: The precise control over temperature and atmosphere for thermal desorption without combustion is the most valuable aspect.
- If your primary focus is creating value from low-grade resources: The furnace's efficiency in driving chemical changes like calcination to purify and upgrade materials is its key benefit.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace is a versatile and powerful tool for transforming environmental liabilities into inert substances or valuable assets.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hazardous Waste Incineration | High-temperature destruction of pollutants | Reduces toxicity and volume of waste |
| Soil Remediation | Thermal desorption of contaminants | Removes pollutants without soil destruction |
| Resource Recovery | Upgrading materials like phosphate ore | Converts waste into valuable resources |
Ready to enhance your environmental processing with tailored solutions? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you're focused on waste destruction, soil decontamination, or resource recovery, we can help you achieve superior results. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can benefit your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















