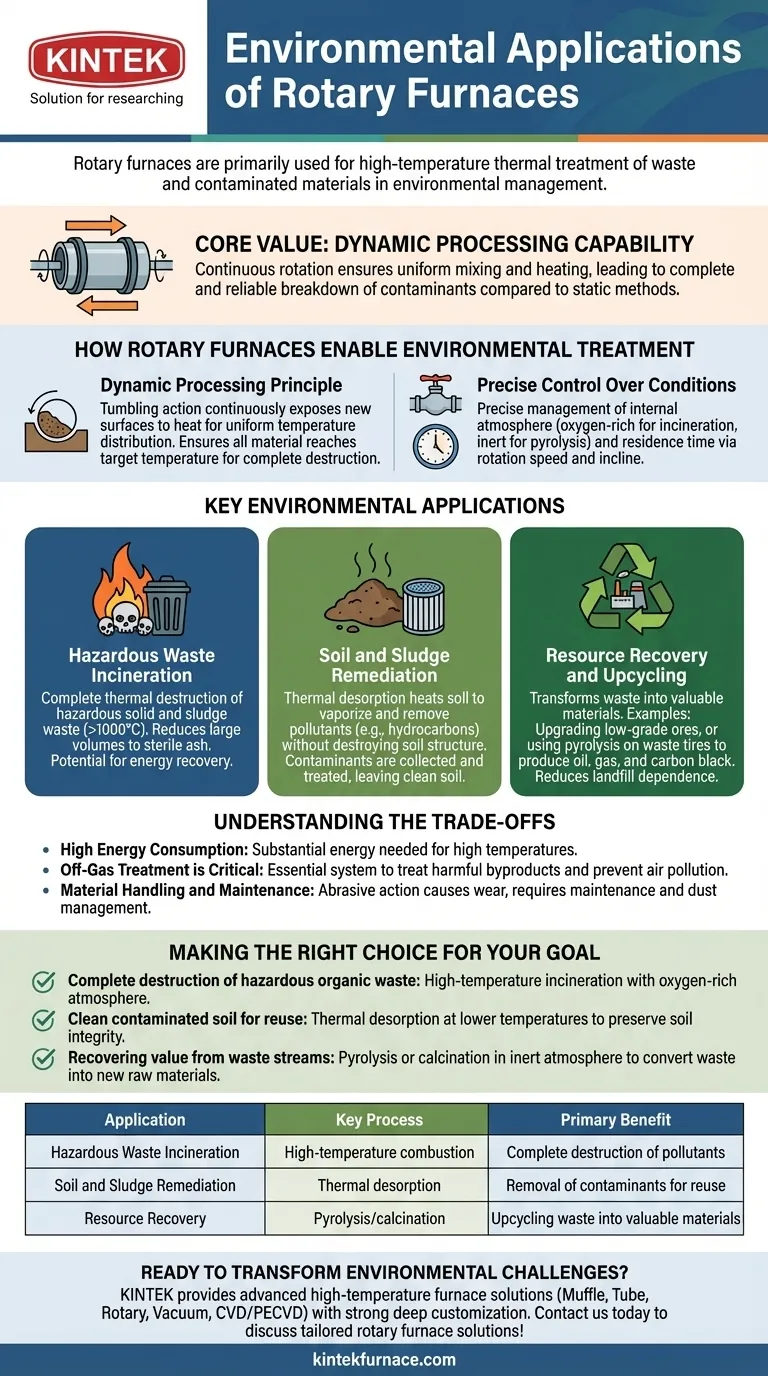
In environmental management, rotary furnaces are primarily used for high-temperature thermal treatment of waste and contaminated materials. Their key applications include the complete destruction of hazardous waste through incineration, the remediation of contaminated soil via thermal desorption, and the recovery of valuable resources from industrial byproducts.
The core value of a rotary furnace in environmental applications lies in its dynamic processing capability. The continuous rotation ensures every particle of material is uniformly mixed and heated, leading to a more complete and reliable breakdown of contaminants compared to static heating methods.

How Rotary Furnaces Enable Environmental Treatment
The effectiveness of a rotary furnace stems from its fundamental design—a rotating cylindrical vessel. This simple mechanical principle provides two critical advantages for processing complex and often hazardous materials.
The Principle of Dynamic Processing
The tumbling action inside the furnace continuously exposes new surfaces of the material to the heat source. This ensures uniform temperature distribution throughout the entire batch.
Unlike a static furnace where the outer layers can insulate the core, a rotary furnace guarantees that all material reaches the target temperature. This is essential for the complete destruction of pollutants.
This constant mixing also promotes thorough interaction between the material and the controlled atmosphere inside the furnace, accelerating the desired chemical reactions.
Precise Control Over Process Conditions
Rotary furnaces allow for precise management of the internal atmosphere. An oxygen-rich environment can be used for complete combustion (incineration), while an inert or oxygen-starved atmosphere is used for processes like pyrolysis.
Furthermore, operators can control the residence time—how long the material stays in the furnace—by adjusting the rotation speed and the incline of the tube. This control is vital for ensuring contaminants are held at a specific temperature long enough to be fully neutralized.
Key Environmental Applications in Detail
The unique capabilities of rotary furnaces make them suitable for several specific, high-impact environmental tasks.
Hazardous Waste Incineration
For solid and sludge waste containing hazardous organic compounds (like PCBs, dioxins, or solvents), high-temperature incineration is often the most effective disposal method.
The rotary furnace's uniform heating ensures the waste reaches temperatures (often >1000°C) that guarantee the complete thermal destruction of these pollutants. The process reduces a large volume of hazardous material into a small, sterile, and often non-hazardous ash. In some systems, the heat generated is captured to produce energy.
Soil and Sludge Remediation
A process called thermal desorption is used to clean contaminated soil or industrial sludge. The goal is not to destroy the soil but to remove the pollutants from it.
The furnace heats the soil to a temperature high enough to vaporize the contaminants (such as petroleum hydrocarbons or mercury) but low enough to avoid destroying the soil structure itself. These vaporized pollutants are then collected and treated in a separate off-gas system, leaving behind clean, reusable soil.
Resource Recovery and Upcycling
Rotary furnaces are powerful tools for a circular economy, helping to recover value from materials once considered waste.
This includes upgrading low-grade phosphate ores to improve their purity for fertilizer production or using pyrolysis to break down waste tires into oil, gas, and carbon black. By transforming industrial byproducts into valuable raw materials, these furnaces help reduce landfill dependence and conserve natural resources.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, rotary furnace systems come with significant operational complexities and considerations that must be managed.
High Energy Consumption
Achieving and maintaining the high temperatures required for incineration or thermal treatment demands a substantial amount of energy. This represents a major operational cost and must be factored into the overall environmental footprint of the process.
Off-Gas Treatment is Critical
The thermal process transforms solid waste into ash and gas. This off-gas can contain harmful byproducts, such as heavy metals, acid gases, and newly formed dioxins. A complex and robust off-gas treatment system—including scrubbers, filters, and afterburners—is not optional; it is essential for preventing air pollution.
Material Handling and Maintenance
The abrasive nature of the tumbling action can cause significant wear and tear on the furnace's internal refractory lining, requiring regular maintenance and replacement. It can also generate fine dust, which must be carefully managed both within the system and in the final material handling stages.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The specific thermal process you use in a rotary furnace depends entirely on your end goal for the material.
- If your primary focus is complete destruction of hazardous organic waste: High-temperature incineration with an oxygen-rich atmosphere is the most direct and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is to clean contaminated soil for reuse: Thermal desorption at lower temperatures is the correct application to preserve the soil's integrity while removing volatile pollutants.
- If your primary focus is recovering value from waste streams: Pyrolysis (in an inert atmosphere) or calcination may be the ideal process to convert waste into new raw materials.
Ultimately, the rotary furnace is a versatile technology that transforms environmental liabilities into manageable outputs.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Hazardous Waste Incineration | High-temperature combustion | Complete destruction of pollutants |
| Soil and Sludge Remediation | Thermal desorption | Removal of contaminants for reuse |
| Resource Recovery | Pyrolysis/calcination | Upcycling waste into valuable materials |
Ready to transform your environmental challenges into opportunities? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored rotary furnace solutions can enhance your waste treatment and resource recovery processes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What is the basic construction of a rotary tube furnace? Key Components for Uniform Heating
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs



















