At its core, the primary challenge Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition (MPCVD) faces is a fundamental trade-off between its slow, highly-controlled growth rate and the demands of scalable industrial production. While renowned for producing high-purity diamond films, MPCVD is often limited by physical constraints, thermal requirements, and the intricate balance between deposition speed and the final quality of the diamond.
The central challenge of MPCVD is not a single weakness, but a series of interconnected trade-offs. The decision to use it hinges on balancing the need for exceptional diamond quality and purity against the practical limitations of growth speed, substrate compatibility, and physical scale.

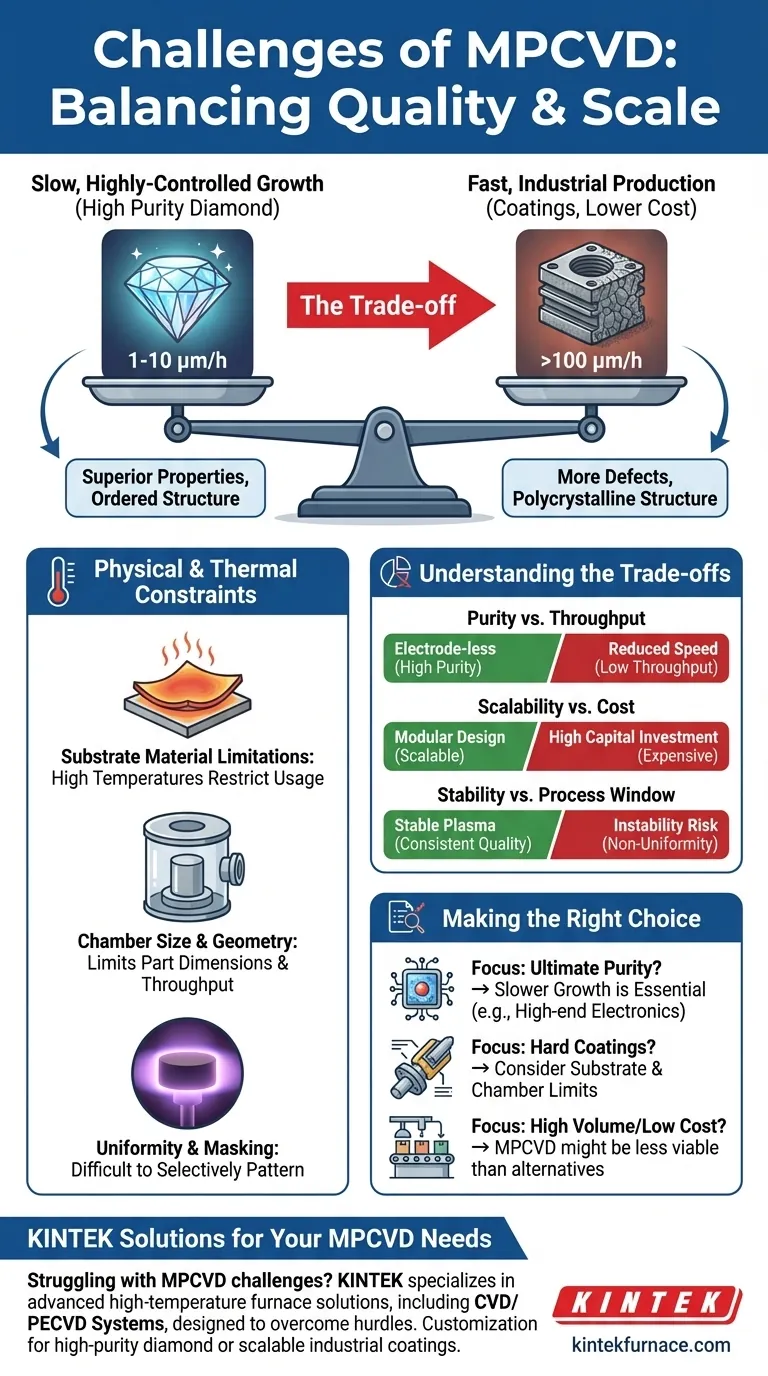
The Growth Rate vs. Quality Dilemma
One of the most debated aspects of MPCVD is its deposition speed. Contradictory reports exist because the growth rate is not a fixed number; it is a variable that is directly tied to the desired outcome.
The Case for Slow Growth
For applications demanding the highest purity and crystalline perfection, such as in high-end electronics or gem-quality diamonds, a slow growth rate is often a necessity. Slower deposition, sometimes as low as 1-10 µm/h, allows for a more ordered atomic structure with fewer defects.
This meticulous, layer-by-layer process ensures the final film has superior thermal, optical, and electronic properties.
The Push for High-Speed Growth
Conversely, for industrial coatings where thickness and cost are more critical than perfect crystalline structure, MPCVD can be pushed to much higher rates, sometimes exceeding 100 µm/h. This is achieved by increasing microwave power and optimizing gas concentrations.
However, this speed comes at a cost. Faster growth often introduces more defects and can lead to a polycrystalline structure, which may not be suitable for all advanced applications.
Inherent Physical and Thermal Constraints
Beyond the speed-versus-quality balance, MPCVD is subject to several physical limitations inherent to the CVD process itself. These constraints directly impact its range of applications.
Substrate Material Limitations
The MPCVD process requires high temperatures to facilitate the chemical reactions that form diamond. This heat can restrict the types of materials that can be used as substrates, as many materials may warp, melt, or degrade under these conditions.
Chamber Size and Geometry
The dimensions of the vacuum chamber inherently limit the maximum size of the part that can be coated. This makes MPCVD challenging for very large components or high-volume, continuous roll-to-roll processes.
Uniformity and Masking
The plasma generated in an MPCVD system tends to coat all exposed surfaces within the reactive zone. It is difficult to selectively mask off areas, making it less suitable for applications requiring precise patterning without post-processing steps like laser ablation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing to use MPCVD requires an objective evaluation of its advantages against these practical challenges. Its key strengths—purity and stability—are often in direct opposition to the industrial need for speed and scale.
Purity vs. Throughput
The electrode-less nature of MPCVD is a major advantage, as it eliminates a key source of contamination found in other CVD methods. However, maintaining this level of purity often requires the slower, more controlled growth parameters mentioned earlier, reducing throughput.
Scalability vs. Cost
While MPCVD systems are modular and can be scaled, scaling up to accommodate larger substrates or higher volumes involves significant capital investment in larger chambers, more powerful microwave generators, and complex gas handling systems.
Stability vs. Process Window
MPCVD is celebrated for its stable and reproducible plasma, which allows for long, continuous deposition runs with consistent quality. This stability, however, is achieved within a specific set of process parameters. Pushing for higher growth rates can risk plasma instability, impacting the final film's uniformity and quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the "challenges" of MPCVD are better understood as design constraints. Your specific goal will determine whether they are prohibitive limitations or acceptable trade-offs.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and crystalline quality (e.g., for quantum sensing, high-power electronics): The slower, controlled growth rate is not a bug but a feature, and the benefits of MPCVD will likely outweigh its throughput limitations.
- If your primary focus is hard, wear-resistant coatings on complex tools: You must carefully consider if the substrate can handle the heat and if the geometry fits within the chamber limitations.
- If your primary focus is high-volume, low-cost deposition: The potentially slow growth rate and batch-processing nature of MPCVD may make other techniques, like hot-filament CVD (HFCVD) or physical vapor deposition (PVD), more economically viable despite their own trade-offs.
Deciding on MPCVD is a strategic choice based on a clear understanding of what attribute—purity, hardness, or cost—is most critical to your success.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| Growth Rate vs. Quality | Slow growth (1-10 µm/h) for high purity; fast growth (>100 µm/h) introduces defects |
| Substrate Material Limitations | High temperatures restrict usable materials, risking warping or degradation |
| Chamber Size and Geometry | Limits part size, challenging for large components or continuous processes |
| Uniformity and Masking | Coats all exposed surfaces, difficult for precise patterning without post-processing |
| Purity vs. Throughput | Electrode-less design ensures purity but reduces throughput with controlled growth |
| Scalability vs. Cost | Scaling requires high investment in equipment, increasing capital expenses |
| Stability vs. Process Window | Stable plasma ensures quality, but pushing limits risks instability and non-uniformity |
Struggling with MPCVD challenges like slow growth or substrate limitations? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, designed to overcome these hurdles. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs—whether for high-purity diamond films or scalable industrial coatings. Contact us today to optimize your process and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- Why is the temperature control system important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Precise Diamond Growth and Process Stability
- How is MPCVD used in the production of polycrystalline diamond optical components? Discover High-Purity Diamond Growth for Optics
- How is CVD classified based on physical characteristics of vapor? Explore AACVD and DLICVD Methods
- What is the role of inert gas doping in the MPCVD method? Accelerate Single-Crystal Diamond Growth
- Why is keeping maintenance records important for MPCVD equipment? Ensure Reliability and Quality in Crystal Growth



















