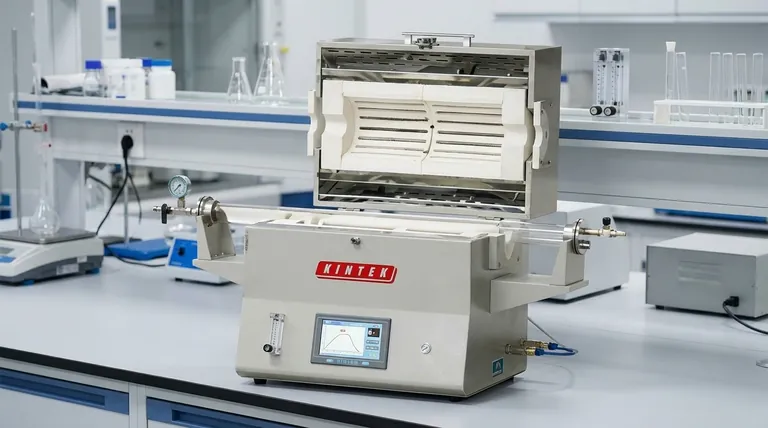
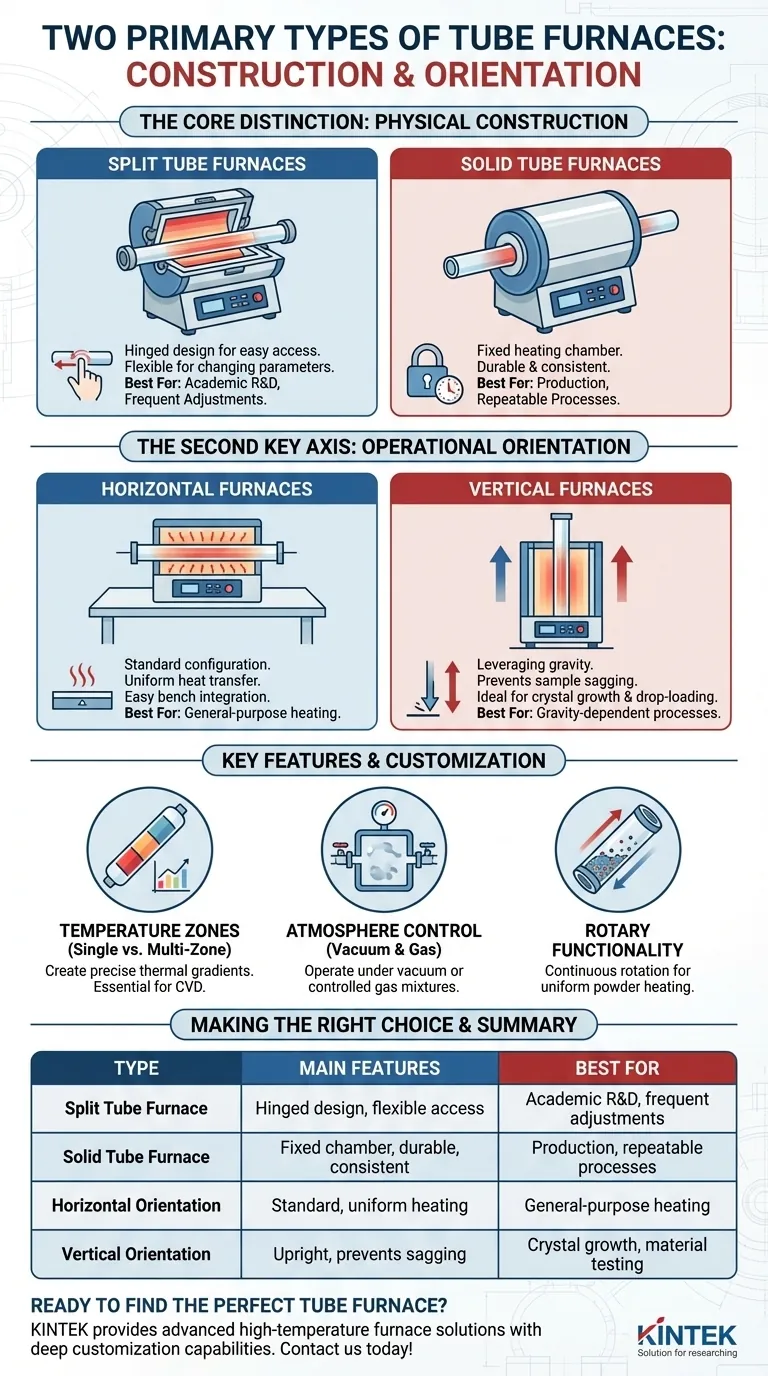
At their core, tube furnaces are classified by their physical construction. The two primary types are split tube furnaces, which have a hinged body that opens for easy access, and solid (or non-split) tube furnaces, which have a fixed heating cylinder that the process tube slides through. This fundamental design difference dictates how you interact with the furnace and what applications it is best suited for.
While the distinction between split and solid construction is the most fundamental, your true choice depends on combining this with a second key axis: operational orientation. Understanding how construction (split vs. solid) and orientation (horizontal vs. vertical) serve your specific scientific or industrial goal is the key to selecting the right instrument.

The Core Distinction: Physical Construction
The most immediate and practical difference between tube furnace types is whether the heating chamber can be opened. This single feature defines its flexibility and ease of use.
Split Tube Furnaces: Accessibility and Flexibility
Split tube furnaces feature a chamber that is hinged to open into two halves. This design offers significant convenience.
You can easily place, adjust, or remove the process tube and the sample within it. This makes them ideal for academic research and development (R&D) environments where experiments, materials, and tube sizes change frequently.
Solid Tube Furnaces: Durability and Consistency
Solid, or non-split, tube furnaces have a single, fixed cylindrical heating chamber. The process tube must be carefully slid through the chamber from one end to the other.
Because of their simpler, more robust construction, these furnaces are excellent for established, repeatable processes where the same sample size and tube diameter are used consistently. They are often favored in production or quality control settings.
The Second Key Axis: Operational Orientation
After construction, the next critical classification is the furnace's orientation. This choice is not about preference but is dictated by the physics of your process.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Standard Configuration
Horizontal furnaces are the most common configuration, with the tube oriented parallel to the workbench. This setup is straightforward and suitable for a vast range of general-purpose heating applications.
They provide efficient, uniform heat transfer along the length of a sample and are typically more compact and easier to set up on a standard lab bench.
Vertical Furnaces: Leveraging Gravity
In a vertical furnace, the tube is oriented upright. This design is critical for specific applications where gravity plays a role.
It is used to prevent samples from bending or deforming at very high temperatures, a common issue in a horizontal setup. It is also ideal for processes like crystal growth, material testing with drop-down sample loading, or when heating fine powders that need to remain settled.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace type involves balancing convenience, performance, and application-specific needs. Each design comes with inherent compromises.
The Cost of Convenience in Split Furnaces
While incredibly convenient, the hinge mechanism of a split tube furnace can be a point of minor heat loss. Over a long operational life, it also represents a mechanical component that could require maintenance, unlike the seamless body of a solid furnace.
The Rigidity of Solid Furnaces
The primary drawback of a solid tube furnace is its lack of access. If a process tube breaks inside the chamber, removal can be significantly more difficult than in a split tube model. You are also locked into using tubes that can fit through the fixed bore.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Practicalities
Vertical furnaces often require more overhead clearance and may need specialized stands or mounting to ensure stability. Horizontal furnaces are generally simpler to integrate into an existing lab space.
Key Features That Define Your Furnace
Beyond these primary classifications, other features function as configurable options that tailor the furnace to a specific task. These are often misunderstood as distinct "types" but are better seen as critical specifications.
Temperature Zones (Single vs. Multi-Zone)
A standard furnace has a single heating zone for uniform temperature. Multi-zone furnaces (with two, three, or more zones) allow you to create a precise temperature gradient or profile along the length of the tube, which is essential for processes like chemical vapor deposition (CVD).
Atmosphere Control (Vacuum and Gas)
Nearly any tube furnace can be configured for atmosphere control. With the right end caps and pump systems, furnaces can operate under a high vacuum (down to 10⁻⁵ torr) or be filled with a precise mixture of inert or reactive gases.
Rotary Functionality
For heating powders, granules, or small parts uniformly, a rotary furnace is a specialized option. It features a mechanism that continuously rotates the process tube, tumbling the contents to ensure every particle is equally exposed to the heat source.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your decision should be driven by your primary application.
- If your primary focus is rapid R&D with changing parameters: A split tube furnace offers the best flexibility for frequent access and adjustments.
- If your primary focus is a standardized, high-volume process: A solid tube furnace provides the durability and consistency needed for production environments.
- If your primary focus is processing materials that may sag or require drop-loading: A vertical furnace is the necessary choice to counteract the effects of gravity at high temperatures.
- If your primary focus is creating a specific thermal gradient: A multi-zone furnace is non-negotiable for controlling temperature along the process tube.
Ultimately, selecting the right tube furnace comes from a clear understanding of your experimental or production requirements.
Summary Table:
| Type | Main Features | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Split Tube Furnace | Hinged design for easy access, flexible for changing experiments | Academic R&D, frequent adjustments |
| Solid Tube Furnace | Fixed heating chamber, durable and consistent | Production, repeatable processes |
| Horizontal Orientation | Standard setup, uniform heating, easy bench integration | General-purpose heating |
| Vertical Orientation | Upright design, prevents sagging, ideal for gravity-dependent processes | Crystal growth, material testing |
Ready to find the perfect tube furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line includes Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, with strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your efficiency and results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a tube heating furnace facilitate the carbon coating process? Boost Layered Oxide Conductivity
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- What is flash vacuum pyrolysis and how is a tube furnace utilized in this process? Unlock High-Temp Chemical Reactions
- What function does a tube furnace serve in the PVT growth of J-aggregate molecular crystals? Mastery of Thermal Control
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing



















