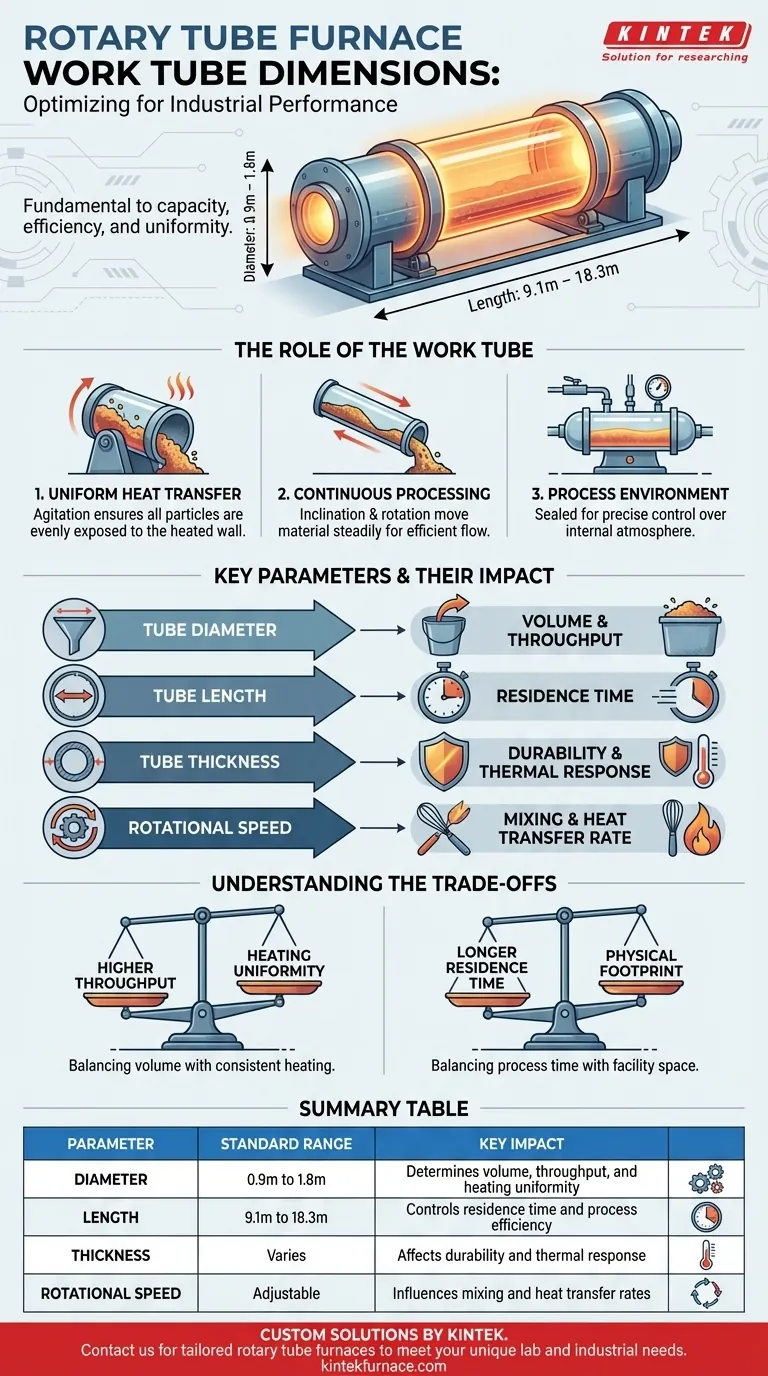
For industrial applications, a rotary tube furnace's work tube typically has a diameter ranging from 0.9 to 1.8 meters and a length from 9.1 to 18.3 meters. These dimensions are not arbitrary; they are fundamental to the furnace's capacity, heat transfer efficiency, and ability to process materials uniformly.
The size of a work tube is more than a measure of capacity. It is a critical design choice that dictates how heat is transferred, how long material is processed, and ultimately, the uniformity and quality of the final product.
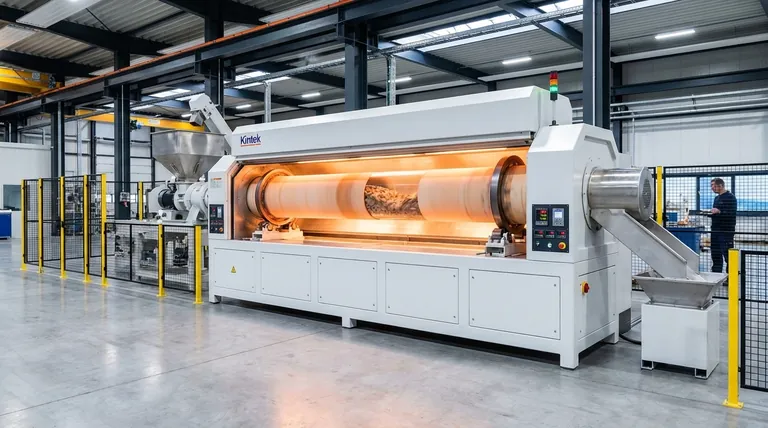

The Role of the Work Tube in Furnace Performance
The work tube is the heart of a rotary furnace. Its dimensions and motion are engineered to solve specific material processing challenges.
Facilitating Uniform Heat Transfer
The cylindrical shape and slow rotation of the tube are its most critical features. As the tube rotates, it constantly tumbles the material inside.
This action, known as agitation, ensures that all particles are cyclically exposed to the heated inner wall of thetube, promoting exceptionally uniform heat distribution throughout the batch.
Enabling Continuous Processing
The tube is typically mounted on a slight incline. This incline, combined with the rotation, causes material fed into the higher end to travel steadily toward the lower end.
This design facilitates continuous batch processing, making it highly efficient for applications like powder processing by minimizing manual material handling.
Containing the Process Environment
The work tube acts as a sealed container for the materials being processed. This allows for precise control over the internal atmosphere, which is essential for many chemical reactions and material synthesis applications.
Key Dimensional Parameters and Their Impact
Choosing a furnace requires understanding how each dimension affects your process. The standard ranges provide a baseline, but the interplay between them is what matters most.
Tube Diameter (0.9m to 1.8m)
The diameter is the primary factor determining the furnace's volume and throughput. A larger diameter can process more material per hour.
However, a wider tube means the heat must penetrate a deeper bed of material, which can make it more challenging to achieve perfect temperature uniformity to the core of the batch.
Tube Length (9.1m to 18.3m)
The length of the tube, combined with its rotational speed and angle of inclination, dictates the residence time—how long the material spends inside the furnace.
Longer tubes are necessary for processes that require gradual heating, extended reaction times, or complex temperature profiles managed by multiple heating zones.
Tube Thickness
While not a primary dimension, tube thickness is a key parameter affecting durability and thermal response. A thicker wall offers greater structural integrity but also has higher thermal mass, meaning it will heat up and cool down more slowly.
Rotational Speed
Rotational speed is an operational parameter, not a fixed dimension, but it works directly with the tube's size. Faster rotation increases mixing but reduces the time material spends in contact with the hot wall, affecting the rate of heat transfer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right work tube dimensions involves balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" size, only the best size for a specific goal.
Throughput vs. Heating Uniformity
A larger diameter significantly increases throughput, but it comes at the risk of less uniform heating. Achieving temperature consistency in a deep bed of material requires careful optimization of rotational speed and heat input.
Residence Time vs. Physical Footprint
A very long tube provides extended residence time, which is ideal for slow reactions. However, this directly translates to a very large and expensive physical footprint within a facility.
Material Compatibility vs. Cost
The material of the work tube itself (e.g., quartz, alumina, metal alloys) must be chosen for chemical compatibility and temperature resistance. High-performance materials that can withstand extreme temperatures or corrosive atmospheres are significantly more expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of work tube dimensions should be driven by the specific requirements of your material and process goals.
- If your primary focus is high-volume industrial production: Prioritize a larger diameter and length to maximize throughput, and ensure the tube's construction material is robust enough for continuous operation.
- If your primary focus is processing heat-sensitive materials: A longer tube equipped with multiple, independent thermal control zones will be necessary to execute a precise temperature profile.
- If your primary focus is achieving perfect process uniformity: You may need to favor a smaller diameter-to-length ratio to ensure the entire material bed is heated evenly, even if it reduces absolute throughput.
Understanding how these dimensions work as a system empowers you to select a furnace that will deliver consistent and efficient results for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Standard Range | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | 0.9m to 1.8m | Determines volume, throughput, and heating uniformity |
| Length | 9.1m to 18.3m | Controls residence time and process efficiency |
| Thickness | Varies | Affects durability and thermal response |
| Rotational Speed | Adjustable | Influences mixing and heat transfer rates |
Need a custom rotary tube furnace tailored to your lab's unique needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your industrial processing goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What are the key features of rotary tube furnaces regarding heat treatment? Achieve Uniform Heating and High Throughput



















