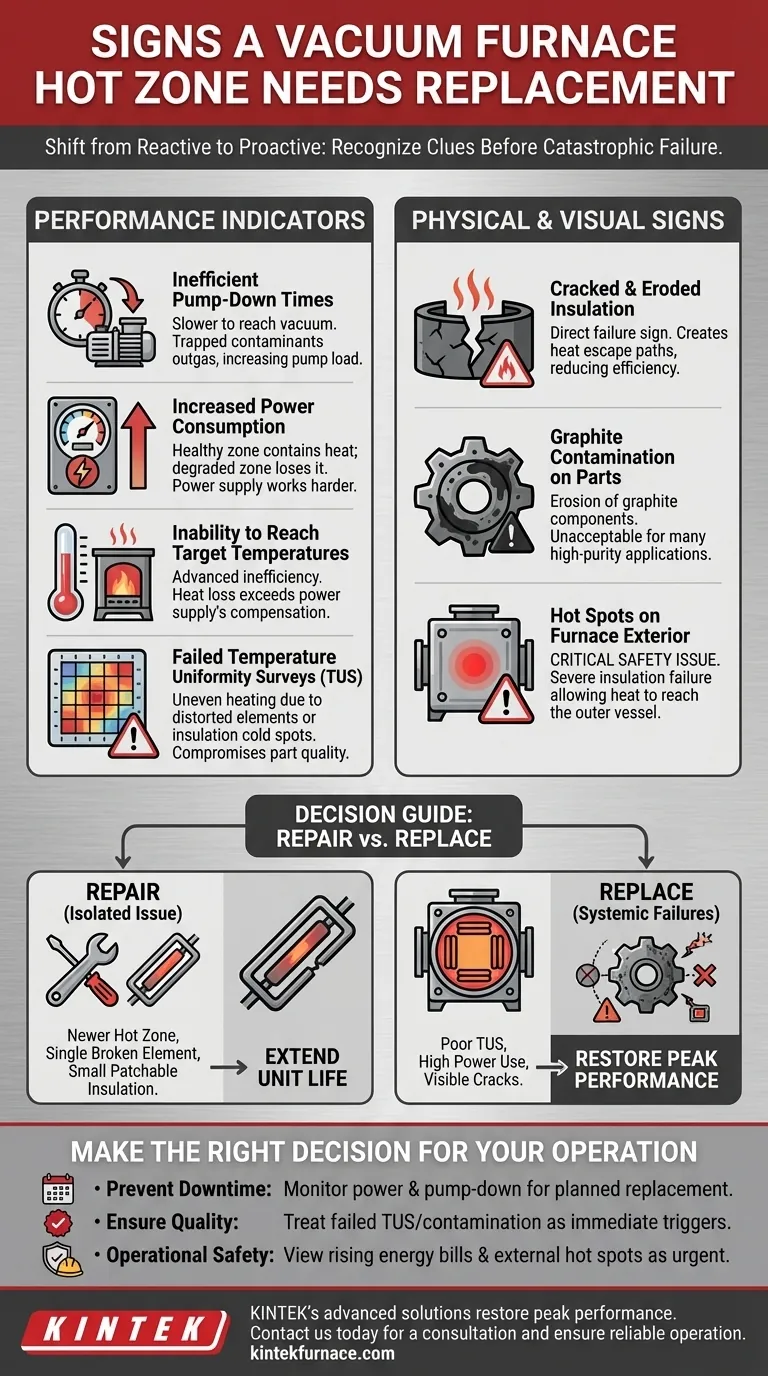
Recognizing the signs of a failing hot zone is critical to preventing costly downtime and ensuring product quality. The most common indicators are a decline in performance—such as longer pump-down times and difficulty reaching temperature—and visible physical degradation, like cracked insulation or contamination on finished parts. These symptoms point to a loss of thermal efficiency and structural integrity within the furnace's core.
A failing hot zone rarely fails suddenly. Instead, it provides a series of performance and physical clues. By understanding these signs, you can shift from reactive repair to a proactive strategy, scheduling replacement on your terms rather than in response to a catastrophic failure.
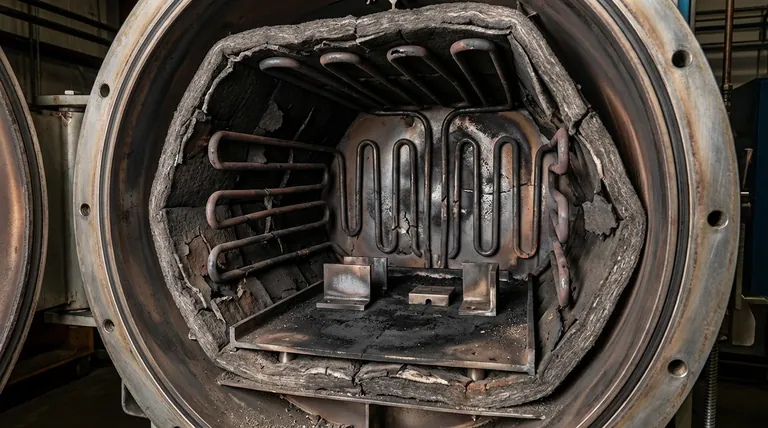

Understanding the Root Causes of Hot Zone Failure
A vacuum furnace hot zone is the insulated, high-temperature core containing the heating elements and the workload. It is designed for extreme conditions, but those same conditions inevitably lead to its degradation over time.
The Core Components and Their Role
The hot zone is typically constructed from materials like graphite or refractory metals such as molybdenum and tungsten. Its primary components are the heating elements that generate heat and the insulation pack that contains it, ensuring temperature uniformity and protecting the outer furnace vessel.
The Inevitable Effects of Heat and Time
Every thermal cycle contributes to wear. Graphite can erode and outgas, insulation boards can become brittle and crack, and metallic elements can warp, sag, or become embrittled. This gradual breakdown is the root cause of all performance-related symptoms.
Key Performance Indicators of a Failing Hot Zone
Tracking furnace performance data is the most effective way to identify a developing problem. A decline in these key metrics is a clear signal that the hot zone is losing its efficiency.
Symptom: Inefficient Pump-Down Times
If your furnace takes progressively longer to reach the required vacuum level, it may be a sign of internal contamination. Cracked or degraded insulation can trap moisture and other contaminants, which then outgas during the pump-down cycle, increasing the load on your vacuum pumps.
Symptom: Increased Power Consumption
A healthy hot zone is highly efficient at containing thermal energy. As insulation degrades, more heat escapes the work area and radiates to the cold wall of the furnace. Your power supply must work harder and draw more power to compensate for this heat loss and maintain the setpoint temperature.
Symptom: Inability to Reach Target Temperatures
This is an advanced stage of inefficiency. If the system's heat loss becomes so great that the power supply cannot compensate, the furnace will struggle or fail to reach its maximum or even its standard operating temperatures.
Symptom: Failed Temperature Uniformity Surveys (TUS)
A failed TUS is an unambiguous indicator of a problem. It means the hot zone can no longer provide even heating. This is often caused by sagging or distorted heating elements, or localized insulation failure creating cold spots within the workload area, directly compromising part quality.
Physical and Visual Signs of Degradation
While performance data offers early warnings, a visual inspection provides definitive proof of wear. These signs are often the final justification for a full replacement.
Symptom: Cracks and Erosion in Insulation
Visible cracks, flaking, or erosion in the graphite felt or board insulation is a direct sign of failure. These breaches create paths for heat to escape, drastically reducing efficiency and uniformity.
Symptom: Graphite Contamination on Parts
If you find a black, sooty film on your parts after a cycle, it is likely due to the erosion of graphite components inside the hot zone. For many applications, particularly in medical and aerospace, this contamination is unacceptable.
Symptom: Hot Spots on the Furnace Exterior
A hot spot on the furnace's outer shell is a critical safety and operational issue. It means the insulation has failed so completely that significant heat is reaching the water-cooled vessel, indicating a severe breach in the hot zone's integrity. This requires immediate attention.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Repair vs. Replace
When a problem is identified, the decision is not always a simple replacement. You must weigh the costs and benefits of a partial repair versus a full rebuild.
The Case for Partial Repair
For a newer hot zone with an isolated issue, a repair can be cost-effective. Replacing a single broken heating element or patching a small section of damaged insulation can extend the life of the unit if the surrounding components are still in good condition.
The Tipping Point for Full Replacement
A repair becomes impractical when you are facing multiple, systemic failures. If you have poor TUS results, high power consumption, and visible insulation cracking, you are likely fighting a losing battle. A full hot zone replacement restores the furnace to its original performance and efficiency specifications, effectively resetting the clock on its operational life.
Making the Right Decision for Your Operation
Use these indicators to align your maintenance strategy with your most critical business goals.
- If your primary focus is preventing unplanned downtime: Proactively monitor power consumption and pump-down times to predict failure and schedule a replacement during planned maintenance.
- If your primary focus is ensuring product quality: Treat a failed TUS or any sign of part contamination as a non-negotiable trigger for immediate hot zone inspection and action.
- If your primary focus is operational safety and efficiency: View rising energy bills and especially any external hot spots as urgent signals that the hot zone's integrity is compromised and requires investigation.
By learning to interpret these signs, you transform hot zone maintenance from a reactive crisis into a controlled, strategic process.
Summary Table:
| Sign Type | Key Indicators | What It Means |
|---|---|---|
| Performance | Longer pump-down times, increased power consumption, failed TUS | Loss of thermal efficiency and temperature uniformity |
| Physical | Cracked insulation, graphite contamination on parts, hot spots on furnace exterior | Structural degradation and safety risk |
| Decision Point | Single issue vs. multiple systemic failures | Guides repair vs. full replacement strategy |
Is your vacuum furnace showing signs of hot zone failure? Don't wait for a catastrophic breakdown to impact your productivity and product quality. KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including our Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, are backed by exceptional R&D and deep customization capabilities. We can provide a robust replacement hot zone tailored to your specific operational requirements, restoring peak performance and efficiency. Contact our experts today for a consultation and ensure your furnace operates reliably.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Disilicide MoSi2 Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of molybdenum disilicide heating elements are available? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What are the primary applications of Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) heating elements in furnaces? Achieve High-Temp Excellence
- What are the key differences between SiC and MoSi2 heating elements in sintering furnaces? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs
- What role do MoSi2 heating elements play in 1500 °C experiments? Key to Stability and Precision
- What are the primary applications of MoSi2 heating elements in research? Achieve Reliable High-Temp Control for Material Synthesis



















