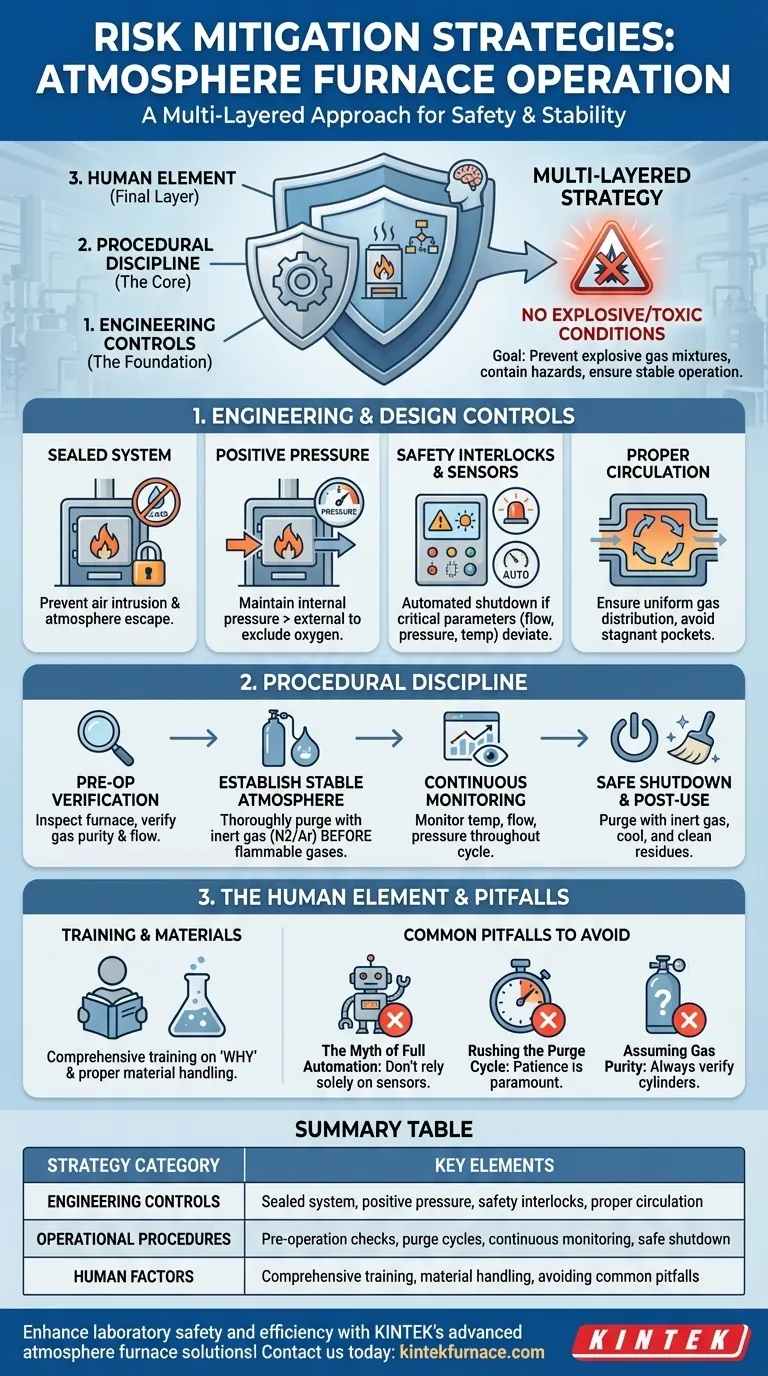
Effective risk mitigation for atmosphere furnaces is achieved through a multi-layered strategy that integrates robust engineering controls, strict operational procedures, and comprehensive personnel training. The primary goals are to prevent the formation of explosive gas mixtures, contain hazardous atmospheres, and ensure stable, predictable operation. This involves maintaining a sealed, positively-pressurized environment, verifying gas purity, and continuously monitoring the system from startup to shutdown.
An atmosphere furnace is fundamentally a controlled chemical reactor. True safety is not achieved through individual precautions, but by systematically managing the three core elements—the furnace's physical integrity, the gas atmosphere's composition, and the human operator's actions—to prevent the formation of explosive or toxic conditions at all times.
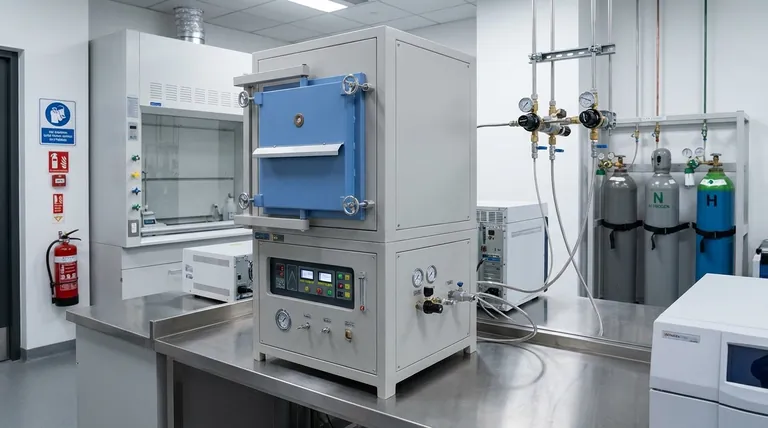

The Foundation: Engineering and Design Controls
The furnace itself is the first line of defense. Its design and integrated safety systems are non-negotiable elements that prevent catastrophic failure before an operator even begins a cycle.
Ensuring a Sealed System
A critical safety requirement is a sealed furnace design. Any leak path is a potential point for the controlled atmosphere to escape or, more dangerously, for external air (containing oxygen) to intrude.
Air intrusion into a hot furnace containing flammable gases like hydrogen or carbon monoxide can create a potent explosive mixture.
Maintaining Positive Pressure
The furnace must be operated at a slight positive pressure relative to the surrounding room. This engineering control ensures that if any microscopic leak does exist, the internal atmosphere gas will flow outward, preventing air from ever flowing inward.
This simple principle is one of the most effective methods for excluding oxygen and preventing an explosion.
Integrating Safety Interlocks and Sensors
Modern furnaces should be equipped with automated safety interlocks. These systems are designed to initiate a safe shutdown or alarm if critical parameters deviate from their setpoints.
Essential sensors include those for temperature, gas flow rates, and pressure. If the atmosphere supply is lost or pressure drops, the system should automatically stop the process to prevent a hazardous state.
Designing for Proper Atmosphere Circulation
Uniform gas circulation is vital. Poor circulation can lead to stagnant pockets where the atmosphere composition is incorrect or localized zones where air has not been fully purged.
Effective design ensures a consistent, homogenous atmosphere throughout the heating chamber, which is crucial for both safety and process quality.
The Core of Operations: Procedural Discipline
Even the best-designed furnace is only as safe as the procedures used to run it. Rigorous, documented protocols are essential for every phase of operation.
Pre-Operation Verification
Before every run, operators must conduct a series of checks. This includes visually inspecting the furnace for cleanliness and integrity and, critically, verifying the purity and flow rates of the supply gases.
Contaminated gas can introduce unwanted reactants, while incorrect flow can fail to maintain positive pressure or properly purge the chamber.
Establishing a Stable Atmosphere
The most dangerous phase of operation can be the initial startup. The furnace chamber must be thoroughly purged with an inert gas, such as nitrogen or argon, to remove all air before any flammable or reactive process gases are introduced.
Operators must monitor gas flow closely during this phase to ensure a complete and successful purge.
Continuous In-Process Monitoring
An atmosphere furnace should never be a "set it and forget it" device. Operators must continuously monitor and record key data points like temperature, gas flow, and pressure throughout the heating cycle.
This vigilance allows for the early detection of deviations that could indicate a developing problem, allowing for correction before it becomes a safety incident.
Safe Shutdown and Post-Use Protocols
The shutdown procedure is just as important as startup. The flammable atmosphere must be purged with an inert gas before the furnace is cooled and opened to the air.
Furthermore, post-use cleaning to remove any residues is vital. Some process byproducts can be pyrophoric (ignite on contact with air) or reactive, posing a risk for the next operation.
Understanding Common Pitfalls
Building a true safety culture requires understanding not just what to do, but also what common mistakes to avoid.
The Myth of Full Automation
While interlocks and sensors are critical, they do not replace a well-trained and vigilant operator. Over-reliance on automation can lead to complacency. The operator must understand the process and be able to recognize signs of trouble that a sensor might miss.
Rushing the Purge Cycle
Patience during the purge cycle is paramount. Introducing flammable gas before all oxygen is removed from the chamber is a direct recipe for an internal explosion. The time or volume required for a full purge is a fixed parameter that must not be compromised for the sake of speed.
Assuming Gas Purity
Never assume a gas cylinder contains what it claims without verification. Using a cylinder of mislabeled or contaminated gas can have unpredictable and dangerous consequences within the hot furnace environment.
The Human Element: Training and Materials
The final layer of safety is the person running the equipment and the materials being put inside it.
Comprehensive Personnel Training
Personnel must be trained not just on the steps to run the furnace (the "how") but on the chemical and physical principles behind those steps (the "why"). Understanding why a purge is necessary fosters a deeper commitment to executing it correctly every time.
Proper Material Selection and Handling
Care must be taken to avoid processing materials that could release toxic vapors or react unexpectedly at high temperatures. Furthermore, materials should be handled to prevent overheating or creating conditions that could damage the furnace or compromise the atmosphere.
Making the Right Choice for Your Operation
Use these principles to build a robust safety protocol tailored to your primary concerns.
- If your primary focus is preventing explosions: Your non-negotiable priorities are maintaining positive furnace pressure and verifying a complete air purge before introducing flammable gases.
- If your primary focus is protecting personnel from toxic exposure: You must ensure absolute furnace integrity, use reliable gas sensors, and have a validated emergency ventilation and response plan.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process consistency and quality: Meticulous pre-operation checks, continuous gas flow monitoring, and post-use cleaning are essential to prevent contamination and ensure repeatable results.
By treating the furnace as an integrated safety system, you transform risk management from a checklist into a fundamental operational principle.
Summary Table:
| Strategy Category | Key Elements |
|---|---|
| Engineering Controls | Sealed system, positive pressure, safety interlocks, proper circulation |
| Operational Procedures | Pre-operation checks, purge cycles, continuous monitoring, safe shutdown |
| Human Factors | Comprehensive training, material handling, avoiding common pitfalls |
Enhance your laboratory's safety and efficiency with KINTEK's advanced atmosphere furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with high-temperature furnaces like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you mitigate risks and achieve reliable results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your operations!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- What are some specific applications of atmosphere furnaces in the ceramics industry? Enhance Purity and Performance
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What is inert gas technology used for in high-temperature atmosphere vacuum furnaces? Protect Materials and Speed Up Cooling



















